JAJSF58O MARCH 2001 – April 2018 SN65HVD230 , SN65HVD231 , SN65HVD232
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics: Driver
- 8.6 Electrical Characteristics: Receiver
- 8.7 Switching Characteristics: Driver
- 8.8 Switching Characteristics: Receiver
- 8.9 Switching Characteristics: Device
- 8.10 Device Control-Pin Characteristics
- 8.11 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 15メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
11.2 Typical Application
Figure 36 illustrates a typical application of the SN65HVD23x family. The output of the host µP's CAN controller (TXD) is connected to the transceivers driver input, pin D, and the transceivers receiver output, pin R, is connected to the input of the CAN controller (RXD). The transceiver is attached to the differential bus lines at pins CANH and CANL. Typically, the bus is a twisted pair of wires with a characteristic impedance of 120 Ω, in the standard half-duplex multipoint topology of Figure 37. Each end of the bus is terminated with 120 Ω resistors in compliance with the standard to minimize signal reflections on the bus.
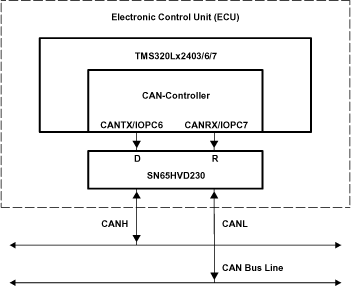 Figure 36. Details of a Typical CAN Node
Figure 36. Details of a Typical CAN Node
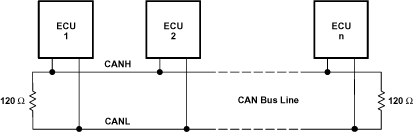 Figure 37. Typical CAN Network
Figure 37. Typical CAN Network