JAJSKL9B September 2020 – November 2022 SN65MLVD203B
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Multipoint Communications
- 9.2.2 Design Requirements
- 9.2.3
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3.1 Supply Voltage
- 9.2.3.2 Supply Bypass Capacitance
- 9.2.3.3 Driver Input Voltage
- 9.2.3.4 Driver Output Voltage
- 9.2.3.5 Termination Resistors
- 9.2.3.6 Receiver Input Signal
- 9.2.3.7 Receiver Input Threshold (Failsafe)
- 9.2.3.8 Receiver Output Signal
- 9.2.3.9 Interconnecting Media
- 9.2.3.10 PCB Transmission Lines
- 9.2.4 Application Curves
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RUM|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RUM|16
発注情報
9.4.1.4 Separation Between Traces
The separation between traces depends on several factors; however, the amount of coupling that can be tolerated usually dictates the actual separation. Low noise coupling requires close coupling between the differential pair of an M-LVDS link to benefit from the electromagnetic field cancellation. The traces should be 100-Ω differential and thus coupled in the manner that best fits this requirement. In addition, differential pairs should have the same electrical length to ensure that they are balanced, thus minimizing problems with skew and signal reflection.
In the case of two adjacent single-ended traces, one should use the 3-W rule, which stipulates that the distance between two traces must be greater than two times the width of a single trace, or three times its width measured from trace center to trace center. This increased separation effectively reduces the potential for crosstalk. The same rule should be applied to the separation between adjacent M-LVDS differential pairs, whether the traces are edge-coupled or broad-side-coupled.
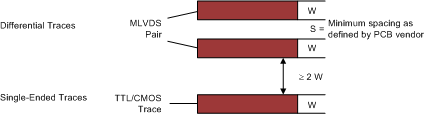 Figure 9-11 3-W Rule
for Single-Ended and Differential Traces (Top View)
Figure 9-11 3-W Rule
for Single-Ended and Differential Traces (Top View)You should exercise caution when using autorouters, because they do not always account for all factors affecting crosstalk and signal reflection. For instance, it is best to avoid sharp 90° turns to prevent discontinuities in the signal path. Using successive 45° turns tends to minimize reflections.