SLOSEA8 December 2024 TAS5815
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- Device Comparison Table
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming and Control
- 8 Register Maps
- 9 Application Information Disclaimer
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Revision History
- 14Mechanical and Packaging Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|28
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|28
発注情報
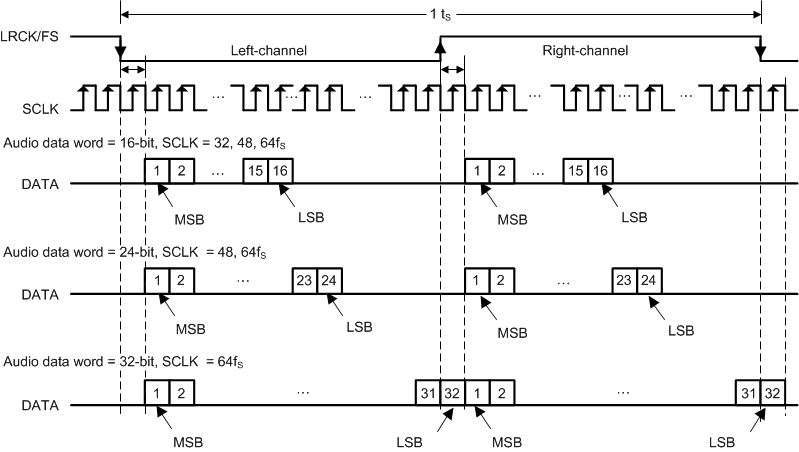
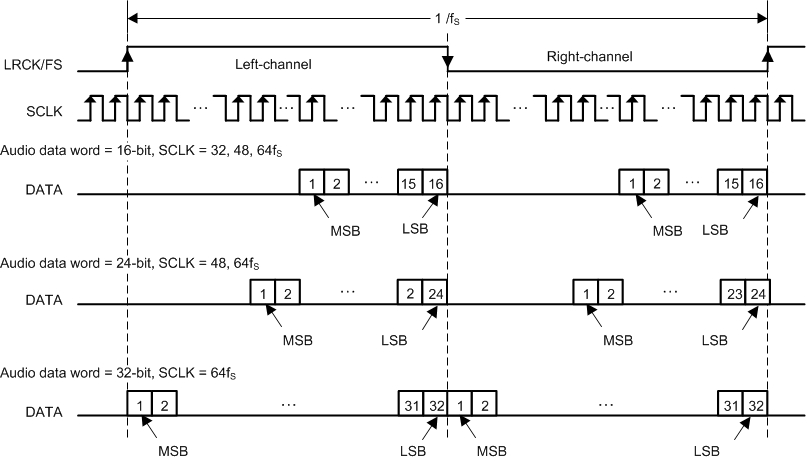
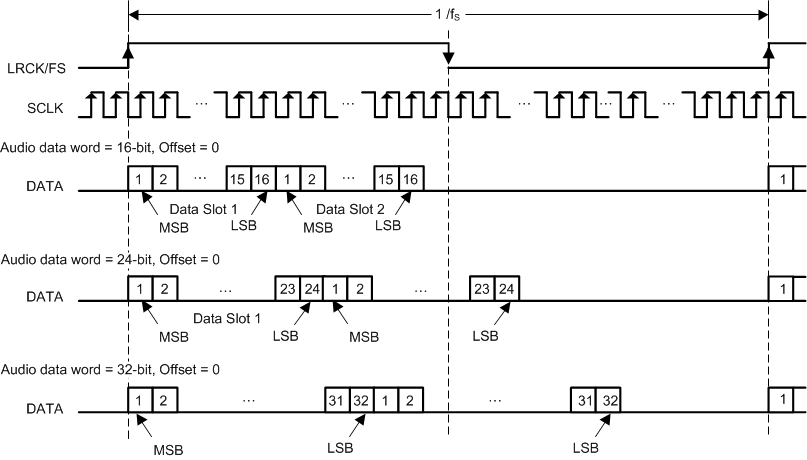
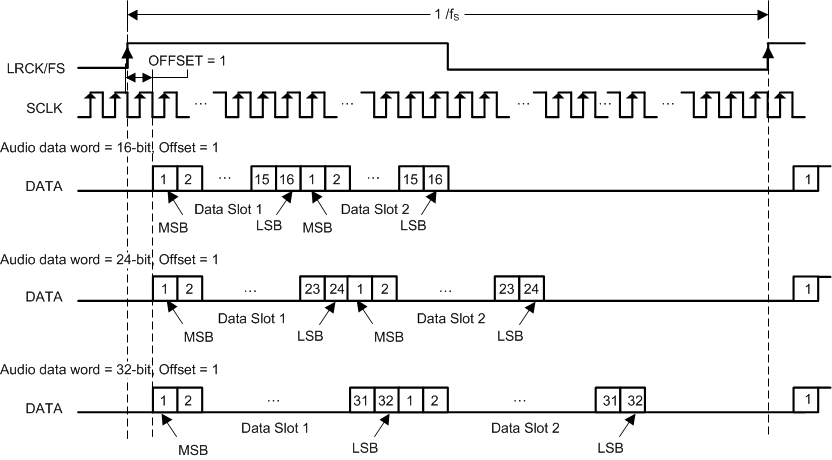
7.3.4 Serial Audio Port - Data Formats and Bit Depths
The serial audio interface port is a 3-wire serial port with the signals LRCK/FS, SCK, and SDIN. SCK is the serial audio bit clock, used to clock the serial data present on SDIN into the serial shift register of the audio interface. Serial data is clocked into the device on the rising edge of SCK. The LRCK/FS pin is the serial audio left/right word clock or frame sync when the device is operated in TDM Mode.
TAS5815 supports industry-standard audio data formats, including standard I2S, left-justified, right-justified and TDM/DSP data. Data formats are selected via Register (Page0-Register 0x33 [5:4]). If the high width of LRCK/FS in TDM/DSP mode is less than 8 cycles of SCK, the register (Page0-Register 0x33 [3:2]) should set to 01. All formats require binary two's complement, MSB-first audio data; up to 32-bit audio data is accepted. All the data formats, word length and clock rate supported by this device are shown in Table 7-1. The data formats are detailed in Figure 6-1 through Figure 6-110. The word length are selected via Register (Page0-Register 0x33 [1:0]). The offsets of data are selected via Register (Page0-Register 0x33 [7]) and Register (Page0-Register 0x34 [7:0]). Default setting is I2S and 24 bit word length.
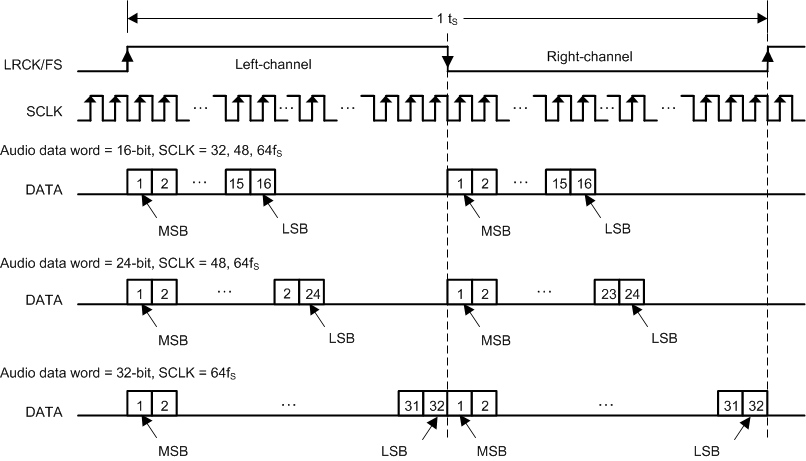 Figure 7-2 Left Justified Audio Data Format
Figure 7-2 Left Justified Audio Data Format