-
TLC59581/82 48-Channel, 16-Bit ES-PWM LED Driver with Pre-Charge FET, LOD Caterpillar Cancelling and Display Data Memory
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Device Functional Modes
- 9.3.1 Brightness Control (BC) Function
- 9.3.2 Color Brightness Control (CC) Function
- 9.3.3 Select RIREF For a Given BC
- 9.3.4 Choosing BC/CC For a Different Application
- 9.3.5 LED Open Detection (LOD)
- 9.3.6 Internal Circuit for Caterpillar Removal
- 9.3.7 Power Save Mode (PSM)
- 9.3.8 Internal Pre-Charge FET
- 9.3.9 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 9.3.10 IREF Resistor Short Protection (ISP)
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
TLC59581/82 48-Channel, 16-Bit ES-PWM LED Driver with Pre-Charge FET, LOD Caterpillar Cancelling and Display Data Memory
1 Features
- 48 Constant-Current Sink Output Channels
- Sink Current Capability with Max BC/CC data:
- 25 mA at 5 VCC
- 20 mA at 3.3 VCC
- Global Brightness Control (BC): 3-Bit (8-Step)
- Color Brightness Control (CC) for Each Color
Group: 9-Bit (512-Step), Three Groups - LED Power Supply Voltage Up To 10 V
- VCC = 3.0 V to 5.5 V
- Constant Current Accuracy
- Channel-to-Channel = ±1%(Typ), ±3%(Max)
- Device-to-Device = ±1%(Typ), ±2%(Max)
- Data Transfer Rate: 25 MHz
- Gray Scale Clock: 33 MHz
- Pre-Charge FET to Avoid Ghosting Phenomenon
- Enhanced Circuit for Caterpillar Cancelling
- Low-Grayscale Enhancement
- LED Open Detection (LOD)
- Thermal Shut Down (TSD)
- Operating Temperature: –40°C to 85°C
2 Applications
- LED Video Displays with Multiplexing System
- LED Signboards with Multiplexing system
- High Refresh Rate & High Density LED Panel
3 Description
The TLC59581/82are 48-channel constant-current sink drivers. Each channel has an individually-adjustable, 65536-step, pulse width modulation (PWM) grayscale (GS) brightness control.
The TLC59581 can support 32-multiplexing while TLC59582 can support 16-multiplexing.
The output channels are divided into three groups. Each group has a 512-step color brightness control (CC). CC adjusts brightness control between colors. The maximum current value of all 48 channels can be set by 8-step global brightness control (BC). BC adjusts brightness deviation between LED drivers. GS, CC and BC data are accessible through a serial interface port.
See application note Build High Density, High Refresh Rate, Multiplexing LED Panel with TLC59581, SLVA744.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TLC59581 | VQFN (56) | 8.00 mm × 8.00 mm |
| TLC59582 |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
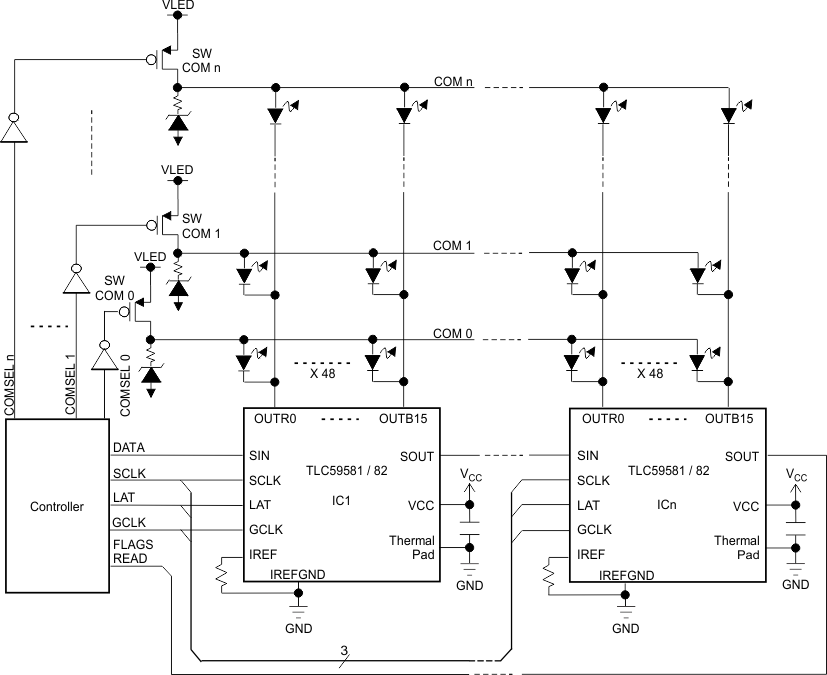
Typical Application Schematic (Multiple Daisy-Chained TLC59581/82)
4 Revision History
Changes from * Revision (October 2015) to A Revision
- Added TLC59582 device to data sheet. Go
5 Description (continued)
The TLC59581/82 device has one error flag: the LED open detection (LOD), which can be read through a serial interface port. To resolve this caterpillar issue caused by an open LED, the TLC59581/82 device has an enhanced circuit for caterpillar canceling, thermal shut down (TSD) and IREF resistor short protection (ISP), which ensures a higher system reliability. The TLC59581/82 device also has a power-save mode that sets the total current consumption to 0.8 mA (typical) when all outputs are off. The TLC59581/82 device is a good solution to improve display performance of a multiplexing panel for low-grayscale patterns.
6 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| GCLK | 29 | I | Grayscale(GS) pulse width modulation (PWM) reference clock control for OUTXn. Each GCLK rising edge increase the GS counter by 1 for PWM control. |
| GND | ThermalPad | – | Power ground. The thermal pad must be soldered to GND on PCB. |
| IREF | 1 | – | Maximum constant-current value setting. The OUTR0 to OUTB15 maximum constant output current are set to the desired values by connecting an external resistor between IREF and IREFGND. See (1) for more detail. The external resistor should be placed close to the device. |
| IREFGND | 56 | – | Analog ground. Dedicated ground pin for the external IREF resistor. This pin should be connected to analog ground trace which is connected to power ground near the common GND point of board. |
| LAT | 27 | I | The LAT falling edge latches the data from the common shift register into the GS data memory or function control (FC) register FC1 or FC2. |
| OUTR0 | 8 | O | Constant current output for RED LED. Multiple outputs can be tied together to increase the constant current capability. Different voltages can be applied to each output. These outputs are turned on-off by GCLK signal and the data in GS data memory. |
| OUTR1 | 11 | ||
| OUTR2 | 14 | ||
| OUTR3 | 17 | ||
| OUTR4 | 20 | ||
| OUTR5 | 23 | ||
| OUTR6 | 30 | ||
| OUTR7 | 33 | ||
| OUTR8 | 36 | ||
| OUTR9 | 39 | ||
| OUTR10 | 44 | ||
| OUTR11 | 47 | ||
| OUTR12 | 50 | ||
| OUTR13 | 53 | ||
| OUTR14 | 2 | ||
| OUTR15 | 5 | ||
| OUTG0 | 9 | O | Constant current output for GREEN LED. Multiple outputs can be tied together to increase the constant current capability. Different voltages can be applied to each output. These outputs are turned on-off by GCLK signal and the data in GS data memory. |
| OUTG1 | 12 | ||
| OUTG2 | 15 | ||
| OUTG3 | 18 | ||
| OUTG4 | 21 | ||
| OUTG5 | 24 | ||
| OUTG6 | 31 | ||
| OUTG7 | 34 | ||
| OUTG8 | 37 | ||
| OUTG9 | 40 | ||
| OUTG10 | 45 | ||
| OUTG11 | 48 | ||
| OUTG12 | 51 | ||
| OUTG13 | 54 | ||
| OUTG14 | 3 | ||
| OUTG15 | 6 | ||
| OUTB0 | 10 | O | Constant current output for BLUE LED. Multiple outputs can be tied together to increase the constant current capability. Different voltages can be applied to each output. These outputs are turned on-off by GCLK signal and the data in GS data memory. |
| OUTB1 | 13 | ||
| OUTB2 | 16 | ||
| OUTB3 | 19 | ||
| OUTB4 | 22 | ||
| OUTB5 | 25 | ||
| OUTB6 | 32 | ||
| OUTB7 | 35 | ||
| OUTB8 | 38 | ||
| OUTB9 | 41 | ||
| OUTB10 | 46 | ||
| OUTB11 | 49 | ||
| OUTB12 | 52 | ||
| OUTB13 | 55 | ||
| OUTB14 | 4 | ||
| OUTB15 | 7 | ||
| SCLK | 28 | I | Serial data shift clock. Data present on SIN are shifted to the 48-bit common shift register LSB with the SCLK rising edge. Data in the shift register are shifted towards the MSB at each SCLK rising edge. The common shift register MSB appears on SOUT. |
| SIN | 26 | I | Serial data input of the 48-bit common shift register. When SIN is high level, the LSB is set to '1' for only one SCLK input rising edge. If two SCLK rising edges are input while SIN is high, then the 48-bit shift register LSB and LSB+1 are set to '1'. When SIN is low, the LSB is set to '0' at the SCLK input rising edge. |
| SOUT | 42 | O | Serial data output of the 48-bit common shift register. SOUT is connected to the MSB of the register. |
| VCC | 43 | – | Power-supply voltage. |