SNOSDJ3 May 2024 TLV1812-EP
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- Pin Configuration and Functions
- 4Specifications
- 5Detailed Description
-
6Application and Implementation
- 6.1 Application Information
- 6.2 Typical Applications
- 6.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 6.4 Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Revision History
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.1.2 Hysteresis
The basic comparator configuration may oscillate or produce a noisy "chatter" output if the applied differential input voltage is near the comparator's offset voltage. This usually occurs when the input signal is moving very slowly across the switching threshold of the comparator.
This problem can be prevented by the addition of hysteresis or positive feedback.
The hysteresis transfer curve is shown in Figure 6-2. This curve is a function of three components: VTH, VOS, and VHYST:
- VTH is the actual set voltage or threshold trip voltage.
- VOS is the internal offset voltage between VIN+ and VIN–. This voltage is added to VTH to form the actual trip point at which the comparator must respond to change output states.
- VHYST is the hysteresis (or trip window) that is designed to reduce comparator sensitivity to noise.
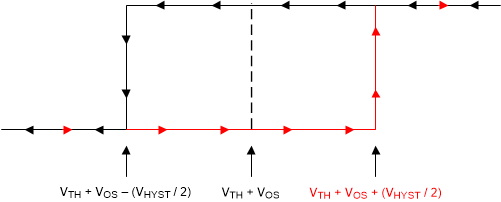 Figure 6-2 Hysteresis Transfer Curve
Figure 6-2 Hysteresis Transfer CurveFor more information, see the Comparator with and without hysteresis circuit application note.