JAJSJP5C September 2022 – September 2023 TLV1811 , TLV1812 , TLV1814 , TLV1821 , TLV1822 , TLV1824
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTE|16
発注情報
9.1.2.2 Non-Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis
A non-inverting comparator with hysteresis requires a two-resistor network and a voltage reference (VREF) at the inverting input, as shown in Figure 9-5,
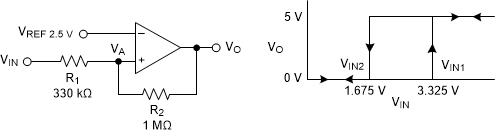 Figure 9-5 TLV181x in a Non-Inverting Configuration With Hysteresis
Figure 9-5 TLV181x in a Non-Inverting Configuration With HysteresisThe equivalent resistor networks when the output is high and low are shown in Figure 9-6.
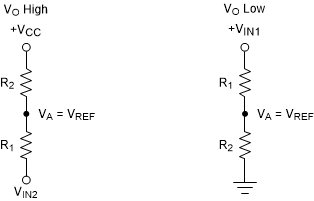 Figure 9-6 Non-Inverting Configuration Resistor Networks
Figure 9-6 Non-Inverting Configuration Resistor NetworksWhen VIN is less than VREF,, the output is low. For the output to switch from low to high, VIN must rise above the VIN1 threshold. Use Equation 4 to calculate VIN1.
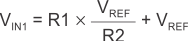
When VIN is greater than VREF, the output is high. For the comparator to switch back to a low state, VIN must drop below VIN2. Use Equation 5 to calculate VIN2.
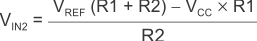
The hysteresis of this circuit is the difference between VIN1 and VIN2, as shown in Equation 6.
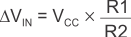
For more information, please see Application Notes SNOA997 "Inverting comparator with hysteresis circuit" and SBOA313 "Non-Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis Circuit".