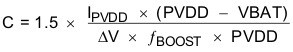JAJSOU4C November 2011 – June 2022 TPA2015D1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 説明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.2.1.2.2 Boost Converter Capacitor Selection
The value of the boost capacitor is determined by the minimum value of working capacitance required for stability and the maximum voltage ripple allowed on PVDD in the application. Working capacitance refers to the available capacitance after derating the capacitor value for DC bias, temperature, and aging.
Do not use any component with a working capacitance less than 4.7 μF. This corresponds to a 4.7 µF / 16 V capacitor, or a 6.8 µF / 10 V capacitor. Do not use above 22 µF capacitance as it will reduce the boost converter response time to large output current transients.
Equation 3 shows the relationship between the boost capacitance, C, to load current, load voltage, ripple voltage, input voltage, and switching frequency (IPVDD, PVDD, ΔV, VBAT, and fBOOST respectively).
Insert the maximum allowed ripple voltage into Equation 3 and solve for C. The 1.5 multiplier accounts for capacitance loss due to applied dc voltage and temperature for X5R and X7R ceramic capacitors.