JAJSE23C August 2017 – June 2019 TPS1H000-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DGN|8
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DGN|8
発注情報
7.3.6.5 Reverse-Current Protection
Reverse current occurs in two conditions: short to supply and reverse polarity.
- When a short to the supply occurs, there is only reverse current through the body diode. IR(1) specifies the limit of the reverse current.
- In a reverse-polarity condition, there are reverse currents through the body diode and the device GND pin. IR(2) specifies the limit of the reverse current.
To protect the device, TI recommends two types of external circuitry.
- Adding a blocking diode (method 1). Both the device and load are protected when in reverse polarity.
- Adding a GND network (method 2). The reverse current through the device GND is blocked. The reverse current through the FET is limited by the load itself. TI recommends a resistor in parallel with the diode as a GND network. The recommended configuration is a 1-kΩ resistor in parallel with a >100-mA diode. The reverse current protection diode in the GND network forward voltage should be less than 0.6 V in any circumstances. In addition a minimum resistance of 4.7 K is recommended on the I/O pins.
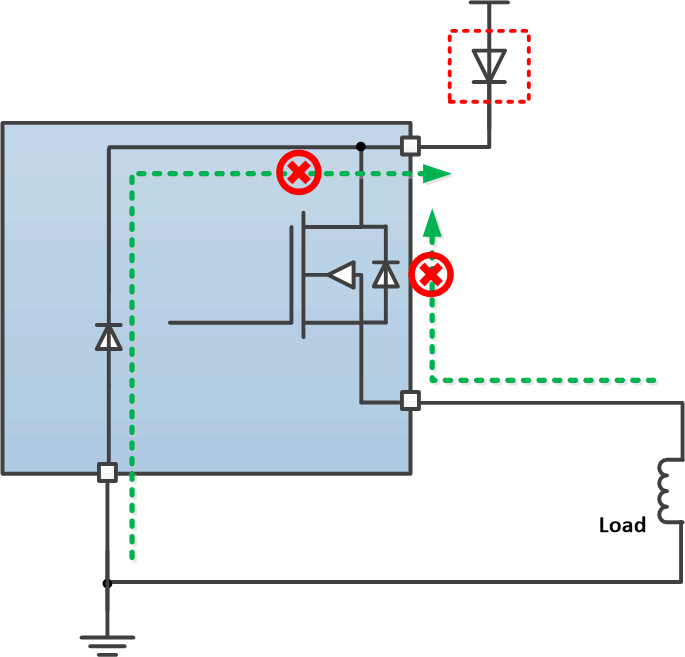 Figure 29. Reverse-Current External Protection, Method 1
Figure 29. Reverse-Current External Protection, Method 1 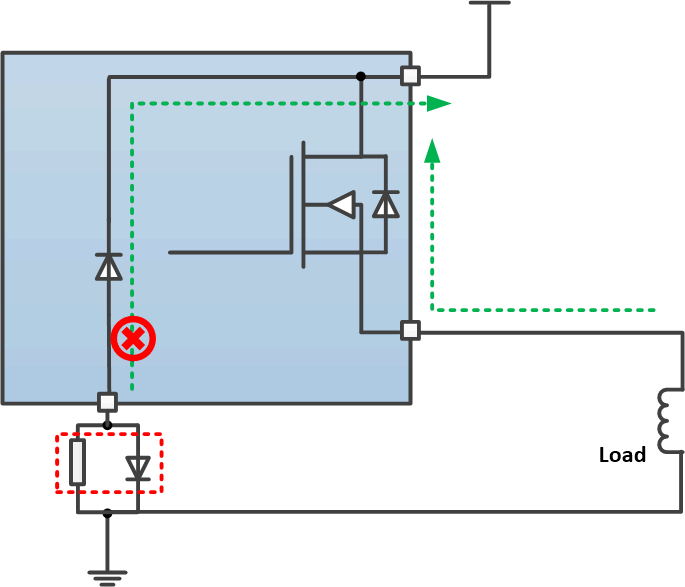 Figure 30. Reverse-Current External Protection, Method 2
Figure 30. Reverse-Current External Protection, Method 2