SLVSCG3F January 2014 – July 2017 TPS22968
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DPU|14
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DPU|14
発注情報
10.2.2.3 Thermal Considerations
The maximum IC junction temperature must be restricted to 125°C under normal operating conditions. To calculate the maximum allowable dissipation, PD(max) for a given output current and ambient temperature, use Equation 6.

where
- PD(max) is the maximum allowable power dissipation
- TJ(max) is the maximum allowable junction temperature (125°C for the TPS22968)
- TA is the ambient temperature of the device
- RθJA is the junction to air thermal impedance. See theThermal Information table. This parameter is highly dependent upon board layout.
Equation 7 to Equation 10 and Equation 11 to Equation 13 show two examples to determine how to use this information correctly:
For VBIAS = 5 V, VIN = 5 V, the maximum ambient temperature with a 4-A load through each channel can be determined by using Equation 7 to Equation 10:
White Space
White Space

White Space
White Space
White Space
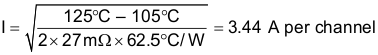
For VBIAS = 5 V, VIN = 5 V, the maximum continuous current for an ambient temperature of 85°C with the same current flowing through each channel can be determined by using Equation 11 to Equation 13:
Space

Space

Space