JAJSEO7I October 2008 – December 2017 TPS23754 , TPS23754-1 , TPS23756
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1
PoE Overview
- 8.4.1.1 Threshold Voltages
- 8.4.1.2 PoE Start-Up Sequence
- 8.4.1.3 Detection
- 8.4.1.4 Hardware Classification
- 8.4.1.5 Inrush and Start-Up
- 8.4.1.6 Maintain Power Signature
- 8.4.1.7 Start-Up and Converter Operation
- 8.4.1.8 PD Hotswap Operation
- 8.4.1.9 Converter Controller Features
- 8.4.1.10 Bootstrap Topology
- 8.4.1.11 Current Slope Compensation and Current Limit
- 8.4.1.12 Blanking – RBLNK
- 8.4.1.13 Dead Time
- 8.4.1.14 FRS and Synchronization
- 8.4.1.15 T2P, Start-Up, and Power Management
- 8.4.1.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4.1.17 Adapter ORing
- 8.4.1.18 PPD ORing Features
- 8.4.1.19 Using DEN to Disable PoE
- 8.4.1.20 ORing Challenges
- 8.4.1
PoE Overview
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Input Bridges and Schottky Diodes
- 9.2.2.2 Protection, D1
- 9.2.2.3 Capacitor, C1
- 9.2.2.4 Detection Resistor, RDEN
- 9.2.2.5 Classification Resistor, RCLS
- 9.2.2.6 Dead Time Resistor, RDT
- 9.2.2.7 Switching Transformer Considerations and RVC
- 9.2.2.8 Special Switching MOSFET Considerations
- 9.2.2.9 Thermal Considerations and OTSD
- 9.2.2.10 APD Pin Divider Network, RAPD1, RAPD2
- 9.2.2.11 PPD Pin Divider Network, RPPD1, RPPD2
- 9.2.2.12 Setting Frequency (RFRS) and Synchronization
- 9.2.2.13 Current Slope Compensation
- 9.2.2.14 Blanking Period, RBLNK
- 9.2.2.15 Estimating Bias Supply Requirements and CVC
- 9.2.2.16 T2P Pin Interface
- 9.2.2.17 Advanced ORing Techniques
- 9.2.2.18 Soft Start
- 9.2.2.19 Frequency Dithering for Conducted Emissions Control
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|20
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|20
発注情報
9.2.2.11 PPD Pin Divider Network, RPPD1, RPPD2
The PPD pin can be used to override the internal hotswap MOSFET UVLO (VUVLO_R and VUVLO_H) when using low voltage adapters connected between VDD and VSS. The PPD pin has an internal 5-μA pulldown current source. As an example, consider the choice of RPPD1 and RPPD2, for a 24-V adapter.
- Select the start-up voltage, VADPTR-ON approximately 75% of nominal for a 24-V adapter. Assuming that the adapter output is 24 V ± 10%, this provides 15% margin below the minimum adapter operating voltage.
- Choose VADPTR-ON = 24 V × 0.75 = 18 V.
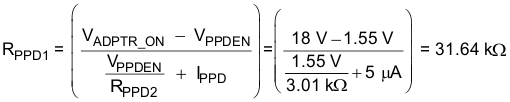
- Choose RPPD2 = 3.01 kΩ.
- Calculate RPPD1.
- Check PPD turnon and PPD turnoff voltages.
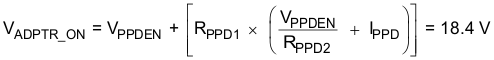
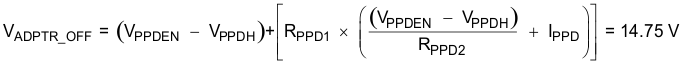
- Voltages look acceptable.
- Check PPD resistor power consumption.
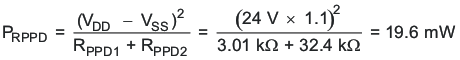
- Power is acceptable, but resistor values could be increased to reduce the power loss.
The PPD pin can also be used to modify the internal MOSFET UVLO for use with a lower output voltage PSE (within certain limits). Connect the RPPD1 and RPPD2 dividers directly between VDD and VSS with the midpoint connected to PPD. For this case and to allow classification, target the minimum PSE OFF voltage (VADPTR_OFF) > VCU_OFF = 23 V. Then follow the procedure outlined above to select RPPD1, RPPD2, and determine the PSE ON (VADPTR_ON) and PSE OFF (VADPTR_OFF) voltages ensuring that PSE OFF > 23 V. Lastly, because the RPPD1 and RPPD2 divider is in parallel with RDEN during detection, RDEN must be increased such that the equivalent detection resistance is 25 kΩ nominal.