SLVSB99C March 2012 – July 2015 TPS2378
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 PoE Overview
- 7.4.2 Threshold Voltages
- 7.4.3 PoE Start-up Sequence
- 7.4.4 Detection
- 7.4.5 Hardware Classification
- 7.4.6 Inrush and Start-up
- 7.4.7 Maintain Power Signature
- 7.4.8 Start-up and Converter Operation
- 7.4.9 PD Hotswap Operation
- 7.4.10 Start-up and Power Management, CDB and T2P
- 7.4.11 Adapter ORing
- 7.4.12 Using DEN to Disable PoE
- 7.4.13 ORing Challenges
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DDA|8
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DDA|8
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over recommended TJ range; voltages with respect to VVSS (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage | VDD, DEN | –0.3 | 100 | V |
| RTN(2) | –0.6 | 100 | ||
| CLS(3) | –0.3 | 6.5 | ||
| APD to RTN | –0.3 | 19 | ||
| [CDB, T2P] to RTN | –0.3 | 100 | ||
| Sinking current | RTN(4) | Internally limited | mA | |
| CDB, T2P | 5 | |||
| DEN | 1 | |||
| Sourcing current | CLS | 65 | mA | |
| TJMAX | Maximum junction temperature | Internally limited | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) With I(RTN) = 0
(3) Do not apply voltages to these pins
(4) SOA limited to RTN = 80 V at 1.2 A.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | 2000 | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | 500 | ||||
| IEC 61000-4-2 contact discharge(3) | 8000 | ||||
| IEC 61000-4-2 air-gap discharge(3) | 15000 | ||||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(3) Discharges applied to circuit of Figure 24 between RJ-45, adapter, and output voltage rails
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range and voltages with respect to VSS (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage range | RTN, VDD | 0 | 57 | V | |
| APD to RTN | 0 | 18 | |||
| CDB, T2P to RTN | 0 | 57 | |||
| Sinking current | RTN | 0.85 | A | ||
| CDB, T2P | 2 | mA | |||
| Resistance | CLS(1) | 60 | Ω | ||
| Junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
(1) Voltage should not be externally applied to this pin.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS2378 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SO-8 PowerPad™ | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 45.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 51.9 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 28.8 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 8.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 28.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 6.7 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
40 V ≤ VVDD ≤ 57 V, RDEN = 24.9 kΩ, VCDB, VCLS, and VT2P open; VAPD = VRTN; –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C. Positive currents are into pins. Typical values are at 25°C. All voltages are with respect to VVSS unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DETECTION (DEN) | ||||||
| Bias current | DEN open, VVDD = 10.1 V, Measure ISUPPLY(VDD, RTN, DEN), Not in mark | 3 | 4.8 | 12 | µA | |
| Detection current | Measure ISUPPLY(VDD, RTN, DEN), VDD = 1.4 V | 53.8 | 56.5 | 58.3 | µA | |
| Measure ISUPPLY(VDD, RTN, DEN), VDD = 10.1 V, Not in mark | 395 | 410 | 417 | |||
| VPD_DIS | Disable threshold | DEN falling | 3 | 3.7 | 5 | V |
| Hysteresis | 50 | 113 | 200 | mV | ||
| AUXILIARY POWER DETECTION (APD) | ||||||
| VAPDEN | Voltage threshold | VAPD rising, measure to VRTN | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | V |
| VAPDH | Hysteresis, measure to VRTN | 0.27 | 0.3 | 0.33 | ||
| Sinking current | V(APD–RTN) = 5 V, measure IAPD | 1 | 1.73 | 3 | µA | |
| CLASSIFICATION (CLS) | ||||||
| ICLS | Classification current | 13 V ≤ VVDD ≤ 21 V, Measure IVDD + IDEN + IRTN | ||||
| RCLS = 1270 Ω | 1.8 | 2.17 | 2.6 | mA | ||
| RCLS = 243 Ω | 9.9 | 10.6 | 11.2 | |||
| RCLS = 137 Ω | 17.6 | 18.6 | 19.4 | |||
| RCLS = 90.9 Ω | 26.5 | 27.9 | 29.3 | |||
| RCLS = 63.4 Ω | 38 | 39.9 | 42 | |||
| VCL_ON | Class lower threshold | VVDD rising, ICLS ↑ | 11.9 | 12.5 | 13 | V |
| VCL_H | Hysteresis | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.7 | ||
| VCU_ON | Class upper threshold | VVDD rising, ICLS↓ | 21 | 22 | 23 | V |
| VCU_H | Hysteresis | 0.5 | 0.78 | 0.9 | ||
| VMSR | Mark reset threshold | VVDD falling | 3 | 3.9 | 5 | V |
| Mark state resistance | 2-point measurement at 5 V and 10.1 V | 6 | 10 | 12 | kΩ | |
| Leakage current | VVDD = 57 V, VCLS = 0 V, measure ICLS | 1 | µA | |||
| PASS DEVICE (RTN) | ||||||
| rDS(on) | On resistance | 0.2 | 0.42 | 0.75 | Ω | |
| Input bias current | VVDD = VRTN = 30 V, measure IRTN | 30 | µA | |||
| Current limit | VRTN =1.5 V | 0.85 | 1 | 1.2 | A | |
| Inrush current limit | VRTN = 2 V, VVDD: 20 V → 48 V | 100 | 140 | 180 | mA | |
| Inrush termination | Percentage of inrush current | 80% | 90% | 99% | ||
| Foldback threshold | VRTN rising | 11 | 12.3 | 13.6 | V | |
| Foldback deglitch time | VRTN rising to when current limit changes to inrush current limit | 500 | 800 | 1500 | µs | |
| CONVERTER DISABLE (CDB) | ||||||
| Output low voltage | Measure VCDB – VRTN, ICDB = 2 mA, VRTN = 2 V, VDD: 20 V → 48 V |
0.27 | 0.5 | V | ||
| Leakage current | VCDB = 57 V, VRTN = 0 V | 10 | μA | |||
| TYPE 2 PSE INDICATION (T2P) | ||||||
| VT2P | Output low voltage | IT2P = 2 mA, after 2-event classification and inrush is complete, VRTN = 0 V | 0.26 | 0.6 | V | |
| Leakage current | VT2P = 57 V, VRTN = 0 V | 10 | µA | |||
| UVLO | ||||||
| VUVLO_R | UVLO rising threshold | VVDD rising | 36.3 | 38.1 | 40 | V |
| UVLO falling threshold | VVDD falling | 30.5 | 32 | 33.6 | ||
| VUVLO_H | UVLO hysteresis | 6.1 | V | |||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | ||||||
| Shutdown | TJ↑ | 135 | 145 | °C | ||
| Hysteresis (1) | 20 | |||||
| BIAS CURRENT | ||||||
| Operating current | 40 V ≤ VVDD ≤ 57 V | 285 | 500 | µA | ||
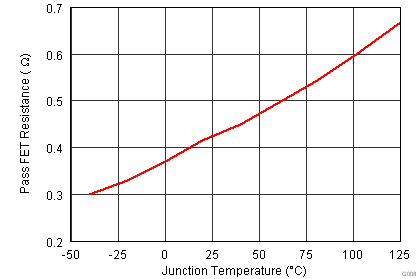
6.6 Typical Characteristics