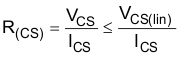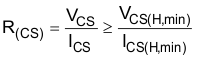JAJSES3D December 2015 – December 2019 TPS2H160-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|16
発注情報
8.3.2 Accurate Current Sense
High-accuracy current sense is implemented in the version-B device. It allows a better real-time monitoring effect and more-accurate diagnostics without further calibration.
One integrated current mirror can source 1 / K(CS) of the load current, and the mirrored current flows into the external current sense resistor to become a voltage signal. The current mirror is shared by the four channels. K(CS) is the ratio of the output current and the sense current. It is a constant value across the temperature and supply voltage. Each device is calibrated accurately during production, so post-calibration is not required. See Figure 23 for more details.
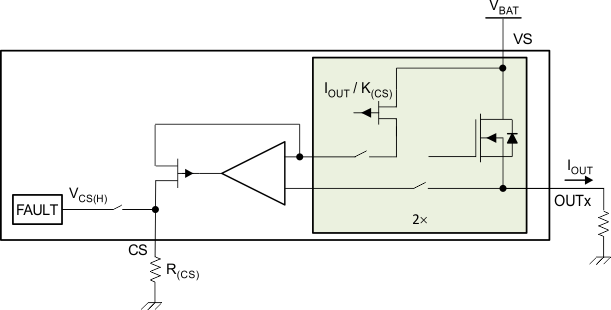 Figure 23. Current-Sense Block Diagram
Figure 23. Current-Sense Block Diagram When a fault occurs, the CS pin also works as a fault report with a pullup voltage, VCS(H). See Figure 24 for more details.
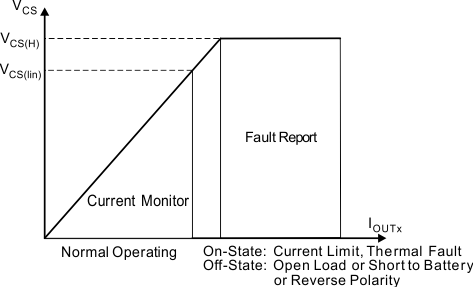 Figure 24. Current-Sense Output-Voltage Curve
Figure 24. Current-Sense Output-Voltage Curve Use Equation 1 to calculate R(CS).
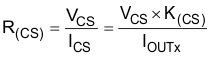
Take the following points into consideration when calculating R(CS).
- Ensure VCS is within the current-sense linear region (VCS, IOUTx(lin)) across the full range of the load current. Check R(CS) with Equation 2.
- In fault mode, ensure ICS is within the source capacity of the CS pin (ICS(H)). Check R(CS) with Equation 3.