JAJS531A December 2010 – November 2016 TPS53321
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGT|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGT|16
発注情報
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The TPS53321 is a high-efficiency switching regulator with two integrated N-channel MOSFETs and is capable of delivering up to 5 A of load current. The TPS53321 provides output voltage between 0.6 V and 0.84 × VIN from 2.9 V to 6 V wide input voltage range.
This device employs five operation modes to fit various application requirements. The master or slave mode enables a two-phase interleaved operation to reduce input ripple. The skip mode operation provides reduced power loss and increases the efficiency at light load. The unique, patented PWM modulator enables smooth light load to heavy load transition while maintaining fast load transient.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
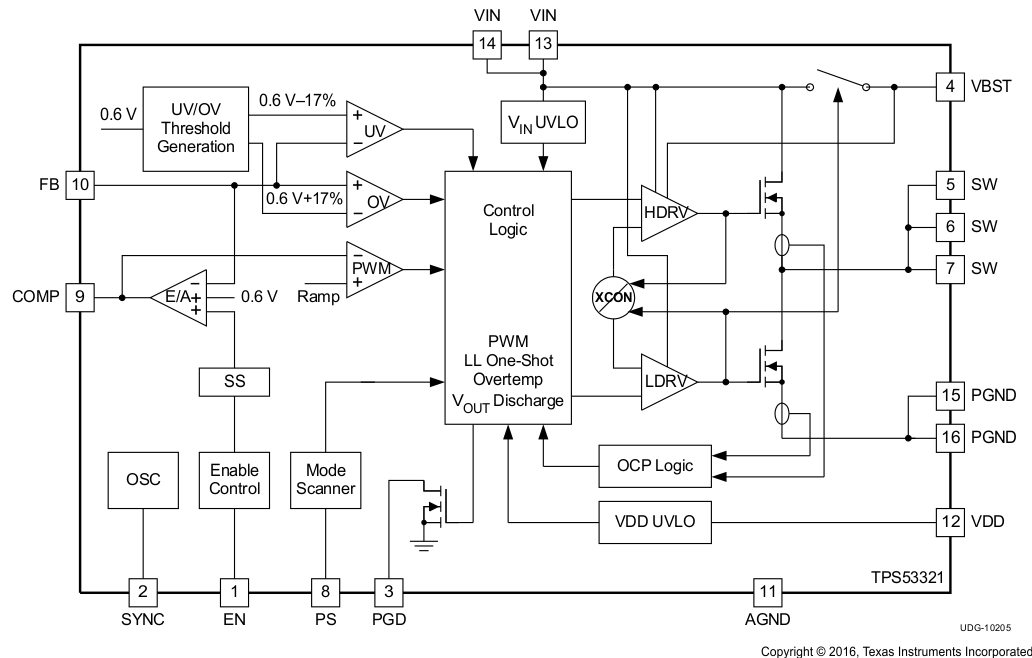
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Soft Start
The soft-start function reduces the inrush current during the start up sequence. A slow-rising reference voltage is generated by the soft-start circuitry and sent to the input of the error amplifier. When the soft-start ramp voltage is less than 600 mV, the error amplifier uses this ramp voltage as the reference. When the ramp voltage reaches 600 mV, the error amplifier switches to a fixed 600-mV reference. The typical soft-start time is 400 µs.
7.3.2 Power Good
The TPS53321 monitors the voltage on the FB pin. If the FB voltage is between 83% and 117% of the reference voltage, the power good signal remains high. If the FB voltage falls outside of these limits, the internal open-drain output pulls the power good pin (PGD) low.
During start-up, VIN must be higher than 1 V to have valid power good logic, and the power good signal is delayed for 1.2 ms after the FB voltage falls to within the power good limits. There is also 10-µs delay during the shutdown sequence.
7.3.3 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Protection
The TPS53321 provides undervoltage lockout (UVLO) protection for both power input (VIN) and bias input (VDD) voltage. If either of them is lower than the UVLO threshold voltage minus the hysteresis, the device shuts off. When the voltage rises above the threshold voltage, the device restarts. The typical UVLO rising threshold is
2.8 V for both VIN and VVDD. A hysteresis voltage of 130 mV for VIN and 75 mV for VVDD is also provided to prevent glitch.
7.3.4 Overcurrent Protection
The TPS53321 continuously monitors the current flowing through the high-side and the low-side MOSFETs. If the current through the high-side FET exceeds 6.5 A, the high-side FET turns off and the low-side FET turns on until the next PWM cycle. An overcurrent (OC) counter starts to increment each occurrence of an overcurrent event. The converter shuts down immediately when the OC counter reaches four. The OC counter resets if the detected current is less 6.5 A after an OC event.
Another set of overcurrent circuitry monitors the current flowing through low-side FET. If the current through the low-side FET exceeds 6.8 A, the overcurrent protection is enabled and immediately turns off both the high-side and the low-side FETs and shuts down the converter. The device is fully protected against overcurrent during both on-time and off-time. The device attempts to restart after a hiccup delay of 14.5 ms (typical). If the overcurrent condition clears before restart, the device starts up normally.
7.3.5 Overvoltage Protection
The TPS53321 monitors the voltage divided feedback voltage to detect overvoltage and undervoltage conditions. When the feedback voltage is greater than 117% of the reference, the high-side MOSFET turns off and the low-side MOSFET turns on. The output voltage then drops until it reaches the undervoltage threshold. At that point the low-side MOSFET turns off and the device enters a high-impedance state.
7.3.6 Undervoltage Protection
When the feedback voltage is lower than 83% of the reference voltage, the undervoltage protection timer starts. If the feedback voltage remains lower than the undervoltage threshold voltage after 10 µs, the device turns off both the high-side and the low-side MOSFETs and goes into a high-impedance state. The device attempts to restart after a hiccup delay of 14.5 ms (typical).
7.3.7 Overtemperature Protection
The TPS53321 continuously monitors the die temperature. If the die temperature exceeds the threshold value (140˚C typical), the device shuts off. When the device temperature falls to 40˚C below the overtemperature threshold, it restarts and returns to normal operation.
7.3.8 Output Discharge
When the enable pin is low, the TPS53321 discharges the output capacitors through an internal MOSFET switch between SW and PGND while high-side and low-side MOSFETs remain off. The typical discharge switch ON-resistance is 60 Ω. This function is disabled when VIN is less than 1 V.
7.3.9 Master and Slave Operation and Synchronization
Two TPS53321 can operate interleaved when configured as master and slave. The SYNC pins of the two devices are connected together for synchronization. In CCM, the master device sends the 180° out-of-phase pulse to the slave device through the SYNC pin, which determines the leading edge of the PWM pulse. If the slave device does not receive the SYNC pulse from the master device or if the SYNC connection is broken during operation, the slave device continues to operate using its own internal clock.
In DE mode, the master and slave switching node does not synchronize to each other if either one of them is operating in DCM. When both master and slave enter CCM, the switching nodes of the master and the slave synchronize to each other.
The SYNC pin of the slave device can also connect to external clock source within ±20% of the 1.1-MHz switching frequency. The falling edge of the SYNC triggers the rising edge of the PWM signal.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Operation Modes
The TPS53321 offers five operation modes determined by the PS pin connections listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Operation Mode Selection
| PS PIN CONNECTION | OPERATION MODE | AUTO-SKIP AT LIGHT LOAD | MASTER/SLAVE SUPPORT |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | FCCM Slave | — | Slave |
| 24.3 kΩ to GND | DE Slave | Yes | Slave |
| 57.6 kΩ to GND | HEF Mode | Yes | — |
| 174 kΩ to GND | DE Master | Yes | Master |
| Floating or pulled to VDD | FCCM Master | — | Master |
In forced continuous conduction mode (FCCM), the high-side FET is ON during the on-time and the low-side FET is ON during the off-time. The switching is synchronized to the internal clock thus the switching frequency is fixed.
In diode emulation (DE) mode, the high-side FET is ON during the on-time and low-side FET is ON during the off-time until the inductor current reaches zero. An internal zero-crossing comparator detects the zero crossing of inductor current from positive to negative. When the inductor current reaches zero, the comparator sends a signal to the logic control and turns off the low-side FET.
When the load is increased, the inductor current is always positive and the zero-crossing comparator does not send a zero-crossing signal. The converter enters into continuous conduction mode (CCM) when no zero-crossing is detected for two consecutive PWM pulses. The switching synchronizes to the internal clock and the switching frequency is fixed.
In high-efficiency (HEF) mode, the operation is the same as DE mode at light load. However, the converter does not synchronize to the internal clock during CCM. Instead, the PWM modulator determines the switching frequency.
7.4.2 Eco-Mode™ Light-Load Operation
In skip modes (DE and HEF) when the load current is less than one-half of the inductor peak current, the inductor current becomes negative by the end of off-time. During light load operation, the low-side MOSFET is turned off when the inductor current reaches zero. The energy delivered to the load per switching cycle is increased compared to the normal PWM mode operation and the switching frequency is reduced. The switching loss is reduced, thereby improving efficiency.
In both DE and HEF mode, the switching frequency is reduced in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). When the load current is 0 A, the minimum switching frequency is reached. The difference between VVBST and VSW must be maintained at a value higher than 2.4 V.
7.4.3 Forced Continuous Conduction Mode (FCCM)
When the PS pin is grounded or greater than 2.2 V, the TPS53321 is operating in forced continuous conduction mode in both light-load and heavy-load conditions. In this mode, the switching frequency remains constant over the entire load range, making it suitable for applications that require tight control of switching frequency at a cost of lower efficiency at light load.