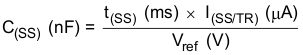JAJSIZ2B october 2016 – june 2021 TPS54388C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.4.2 Enable Functionality and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.4.3 Slow-Start or Tracking Pin
- 7.4.4 Sequencing
- 7.4.5 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.4.6 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4.7 Frequency Shift
- 7.4.8 Reverse Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4.9 Synchronize Using the RT/CLK Pin
- 7.4.10 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.4.11 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.4.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4.13 Small-Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.4.14 Simple Small-Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 7.4.15 Small-Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Slow-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Output-Voltage and Feedback-Resistor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Compensation
- 8.2.2.9 Power-Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTE|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTE|16
発注情報
8.2.2.5 Slow-Start Capacitor
The slow-start capacitor determines the minimum amount of time it takes for the output voltage to reach its nominal programmed value during power up. Slow start is useful if a load requires a controlled rate of voltage slew. Another use for slow start is if the output capacitance is large and would require large amounts of current to charge the capacitor quickly to the output-voltage level. The large current necessary to charge the capacitor may make the TPS54388C-Q1 device reach the current limit, or excessive current draw from the input power supply may cause the input voltage rail to sag. Limiting the output-voltage slew rate solves both of these problems.
Calculate the slow-start capacitor value using Equation 32. For the example circuit, the slow-start time is not too critical because the output-capacitor value is 44 μF, which does not require much current to charge to 1.8 V. The example circuit has the slow-start time set to an arbitrary value of 4 ms, which requires a 10-nF capacitor. In the TPS54388C-Q1 device, I(SS/TR) is 2.2 μA and Vref is 0.8 V.