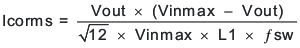JAJSBF8B June 2011 – April 2018 TPS54478
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation and Output Current
- 7.3.3 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT) and Low Dropout Operation
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Slow Start / Tracking Pin
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.10 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.11 START-UP into Prebiased Output
- 7.3.12 Synchronize Using the RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.13 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.14 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.17 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.18 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTE|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTE|16
発注情報
8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
There are three primary considerations for selecting the value of the output capacitor. The output capacitor determines the modulator pole, the output voltage ripple, and how the regulator responds to a large change in load current. The output capacitance needs to be selected based on the more stringent of these three criteria.
The desired response to a large change in the load current is the first criteria. The output capacitor needs to supply the load with current when the regulator can not. This situation would occur if there are desired hold-up times for the regulator where the output capacitor must hold the output voltage above a certain level for a specified amount of time after the input power is removed. The regulator is temporarily not able to supply sufficient output current if there is a large, fast increase in the current needs of the load such as transitioning from no load to a full load. The regulator usually needs two or more clock cycles for the control loop to see the change in load current and output voltage and adjust the duty cycle to react to the change. The output capacitor must be sized to supply the extra current to the load until the control loop responds to the load change. The output capacitance must be large enough to supply the difference in current for 2 clock cycles while only allowing a tolerable amount of droop in the output voltage. Equation 23 shows the minimum output capacitance necessary to accomplish this.
For this example, the transient load response is specified as a 3% change in Vout for a load step from 1 A (25% load) to 3 A (75% load). For this example, ΔIout = 3 – 1 = 2.0 A and ΔVout = 0.03 × 1.8 = 0.054 V. Using these numbers gives a minimum capacitance of 74.1 μF. This value does not take the ESR of the output capacitor into account in the output voltage change. For ceramic capacitors, the ESR is usually small enough to ignore in this calculation.
Equation 24 calculates the minimum output capacitance needed to meet the output voltage ripple specification. Where fsw is the switching frequency, Vripple is the maximum allowable output voltage ripple, and Iripple is the inductor ripple current. In this case, the maximum output voltage ripple is 30 mV. Under this requirement, Equation 24 yields 4.4 uF.
vertical spacer
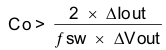
where
- ΔIout is the change in output current, fsw is the regulators switching frequency and ΔVout is the allowable change in the output voltage.
vertical spacer
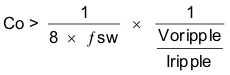
vertical spacer
Equation 25 calculates the maximum ESR an output capacitor can have to meet the output voltage ripple specification. Equation 25 indicates the ESR should be less than 28.6 mΩ. In this case, the ESR of the ceramic capacitor is much less than 28.6 mΩ.
Additional capacitance de-ratings for aging, temperature and DC bias should be factored in which increases this minimum value. For this example, two 47 μF 10 V X5R ceramic capacitors with 3 mΩ of ESR are used. The estimated capacitance after derating is 2 x 45 µF = 90 µF.
Capacitors generally have limits to the amount of ripple current they can handle without failing or producing excess heat. An output capacitor that can support the inductor ripple current must be specified. Some capacitor data sheets specify the RMS (Root Mean Square) value of the maximum ripple current. Equation 26 can be used to calculate the RMS ripple current the output capacitor needs to support. For this application, Equation 26 yields 303 mA.
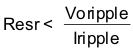
vertical spacer