SLVS274A March 2000 – April 2016 TPS60200 , TPS60201 , TPS60202 , TPS60203
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Tables
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Careful board layout is necessary due to the high transient currents and switching frequency of the converter. All capacitors should be placed in close proximity to the device. A PCB layout proposal for a one-layer board is given in Figure 21.
An evaluation module for the TPS60200 is available and can be ordered under product code TPS60200EVM–145. The EVM uses the layout shown in Figure 21. All components including the pins are shown. The EVM is built so that it can be connected to a 14-pin dual inline socket; therefore, the space needed for the IC, the external parts, and 8 pins is 17.9 mm × 10.2 mm = 182.6 mm2.
11.2 Layout Example
space
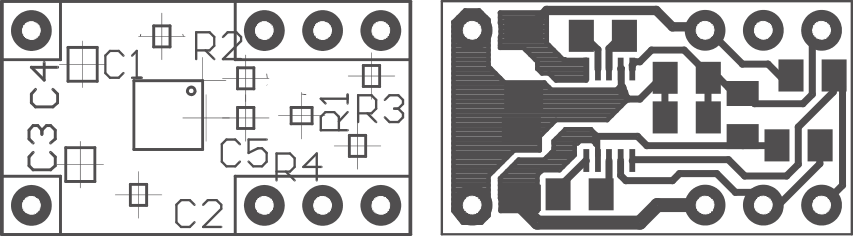 Figure 21. TPS6020x EVM Board Layout
Figure 21. TPS6020x EVM Board Layout
space
Table 6. Component Identification
| IC1 | TPS60200 |
|---|---|
| C1, C2 | Flying capacitors |
| C3 | Input capacitors |
| C4 | Output capacitors |
| C5(1) | Stabilization capacitor for LBI |
| R1, R2 | Resistive divider for LBI |
| R3 | Pullup resistor for LBO |
| R4 | Pullup resistor for EN |
11.3 Power Dissipation
The power dissipated in the TPS6020x devices depends mainly on input voltage and output current and is approximated with Equation 5.
spacer
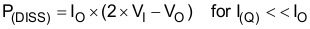
By observing Equation 5, it can be seen that the power dissipation is worst for highest input voltage VI and highest output current IO. For an input voltage of 3.6 V and an output current of 100 mA the calculated power dissipation P(DISS) is 390 mW. This is also the point where the charge pump operates with its lowest efficiency.
With the recommended maximum junction temperature of 125°C and an assumed maximum ambient operating temperature of 85°C, the maximum allowed thermal resistance junction to ambient of the system is calculated with Equation 6.
spacer
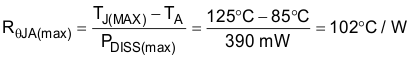
spacer
PDISS must be less than that allowed by the package rating. The thermal resistance junction to ambient of the used 10-pin MSOP is 294°C/W for an unsoldered package. The thermal resistance junction to ambient with the IC soldered to a printed circuit using a board layout as described in Application Information, the RθJA is typically 200°C/W, which is higher than the maximum value calculated above. However in a battery-powered application, both VI and TA will typically be lower than the worst-case ratings used in Equation 6, and power dissipation should not be a problem in most applications.