JAJS462E May 2008 – May 2019 TPS61087
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
6.6 Typical Characteristics
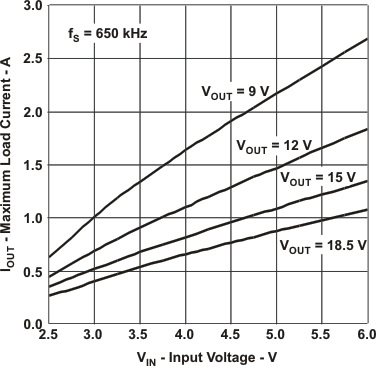
The typical characteristics are measured with the inductors 7447789003 3.3 µH (high frequency) or 74454068 6.8 µH (low frequency) from Wurth and the rectifier diode SL22.Table 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IOUT(max) | Maximum load current | vs. Input voltage at High frequency (1.2 MHz) | Figure 1 |
| IOUT(max) | Maximum load current | vs. Input voltage at Low frequency (650 kHz) | Figure 2 |
| η | Efficiency | vs. Load current, VS = 15 V, VIN = 5 V | Figure 3 |
| η | Efficiency | vs. Load current, VS = 9 V, VIN = 3.3 V | Figure 4 |
| Supply current | vs. Supply voltage | Figure 5 | |
| Oscillator frequency | vs. Load current | Figure 6 | |
| Oscillator frequency | vs. Supply voltage | Figure 7 | |