JAJS360D January 2008 – October 2016 TPS62560 , TPS62561 , TPS62562
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DRV|6
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DRV|6
発注情報
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The TPS6256x devices are high-efficiency synchronous step-down DC–DC converter featuring power-save mode or 2.25-MHz fixed frequency operation.
9.2 Typical Application
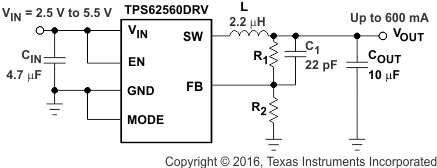 Figure 6. TPS62560DRV Adjustable
Figure 6. TPS62560DRV Adjustable
9.2.1 Design Requirements
The TPS6256x is a highly integrated DC/DC converter. The output voltage is set with an external voltage divider for the adjustable output voltage version. The output voltage is fixed to 1.8V for the TPS62562. For proper operation a input- and output capacitor and an inductor is required. Table 2 shows the components used for the application characteristic curves.
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
9.2.2.1 Output Voltage Setting
For adjustable output voltage versions, the output voltage can be calculated by Equation 2 with the internal reference voltage VREF = 0.6 V typically.

To minimize the current through the feedback divider network, R2 should be 180 kΩ or 360 kΩ. The sum of R1 and R2 should not exceed ~1 MΩ, to keep the network robust against noise. An external feed-forward capacitor C1 is required for optimum load transient response. The value of C1 should be in the range between 22 pF and 33 pF.
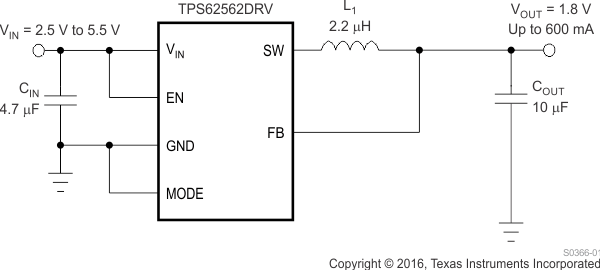
In case of using the fixed output voltage version (TPS62562), Vout has to be connected to the feedback pin FB.
Route the FB line away from noise sources, such as the inductor or the SW line.
9.2.2.2 Output Filter Design (inductor and Output Capacitor)
The TPS62560 is designed to operate with inductors in the range of 1.5 μH to 4.7 μH and with output capacitors in the range of 4.7 μF to 22 μF. The part is optimized for operation with a 2.2-μH inductor and 10-μF output capacitor.
Larger or smaller inductor values can be used to optimize the performance of the device for specific operation conditions. For stable operation, the L and C values of the output filter may not fall below 1 μH effective inductance and 3.5 μF effective capacitance.
9.2.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
The inductor value has a direct effect on the ripple current. The selected inductor must be rated for its dc resistance and saturation current. The inductor ripple current (ΔIL) decreases with higher inductance and increases with higher VIN or VOUT.
The inductor selection also impacts the output voltage ripple in PFM mode. Higher inductor values lead to lower output voltage ripple and higher PFM frequency; lower inductor values lead to a higher output voltage ripple but lower PFM frequency.
Equation 3 calculates the maximum inductor current in PWM mode under static load conditions. The saturation current of the inductor should be rated higher than the maximum inductor current as calculated with Equation 4. This is recommended because during heavy load transients the inductor current rises above the calculated value.


where
- f = Switching frequency (2.25 MHz, typical)
- L = Inductor value
- ΔIL = Peak-to-peak inductor ripple current
- ILmax = Maximum inductor current
A more conservative approach is to select the inductor current rating just for the switch current limit ILIMF of the converter.
Accepting larger values of ripple current allows the use of lower inductance values, but results in higher output voltage ripple, greater core losses, and lower output current capability.
The total losses of the coil have a strong impact on the efficiency of the dc/dc conversion and consist of both the losses in the dc resistance (R(DC)) and the following frequency-dependent components:
- The losses in the core material (magnetic hysteresis loss, especially at high switching frequencies)
- Additional losses in the conductor from the skin effect (current displacement at high frequencies)
- Magnetic field losses of the neighboring windings (proximity effect)
- Radiation losses
Table 1. List of Inductors
| DIMENSIONS, mm | INDUCTANCE, μH | INDUCTOR TYPE | SUPPLIER(1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2,5 × 2 × 1 max | 2 | MIPS2520D2R2 | FDK |
| 2,5 × 2 × 1,2 max | 2 | MIPSA2520D2R2 | FDK |
| 2,5 × 2 × 1 max | 2.2 | KSLI-252010AG2R2 | Hitachi Metals |
| 2,5 × 2 × 1,2 max | 2.2 | LQM2HPN2R2MJ0L | Murata |
| 3 × 3 × 1,5 max | 2.2 | LPS3015 2R2 | Coilcraft |
9.2.2.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
The advanced fast-response voltage-mode control scheme of the TPS62560 allows the use of tiny ceramic capacitors. Ceramic capacitors with low ESR values have the lowest output voltage ripple and are recommended. The output capacitor requires either an X7R or X5R dielectric. Y5V and Z5U dielectric capacitors, aside from their wide variation in capacitance over temperature, become resistive at high frequencies.
At nominal load current, the device operates in PWM mode, and the RMS ripple current is calculated by Equation 5:

At nominal load current, the device operates in PWM mode, and the overall output voltage ripple is the sum of the voltage spike caused by the output capacitor ESR plus the voltage ripple caused by charging and discharging the output capacitor shown in Equation 6:
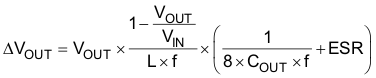
At light load currents, the converter operates in power-save mode, and the output voltage ripple is dependent on the output capacitor and inductor values. Larger output capacitor and inductor values minimize the voltage ripple in PFM mode and tighten dc output accuracy in PFM mode.
9.2.2.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
An input capacitor is required for best input voltage filtering and minimizing the interference with other circuits caused by high input voltage spikes. For most applications, a 4.7-μF to 10-μF ceramic capacitor is recommended. Because a ceramic capacitor loses up to 80% of its initial capacitance at 5 V, it is recommended that 10-μF input capacitors be used for input voltages > 4.5 V. The input capacitor can be increased without any limit for better input voltage filtering. Take care when using only small ceramic input capacitors. When a ceramic capacitor is used at the input and the power is being supplied through long wires, such as from a wall adapter, a load step at the output or VIN step on the input can induce ringing at the VIN terminal. This ringing can couple to the output and be mistaken as loop instability or could even damage the part by exceeding the maximum ratings.
Table 2. List of Capacitors(1)
| CAPACITANCE | TYPE | SIZE | SUPPLIER |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.7 μF | GRM188R60J475K | 0603—1,6 × 0,8 × 0,8 mm | Murata |
| 10 μF | GRM188R60J106M69D | 0603—1,6 × 0,8 × 0,8 mm | Murata |
9.2.3 Application Curves
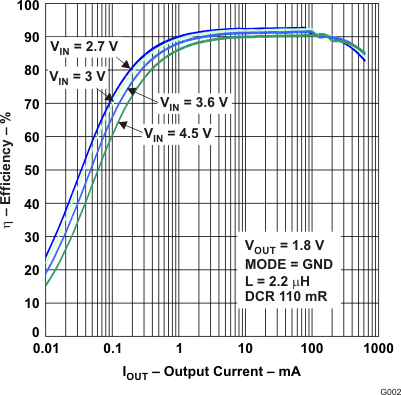 Figure 7. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 7. Efficiency vs Output Current
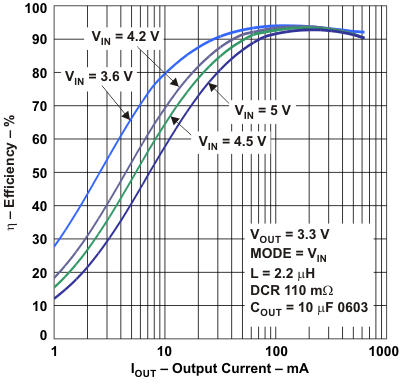 Figure 9. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 9. Efficiency vs Output Current
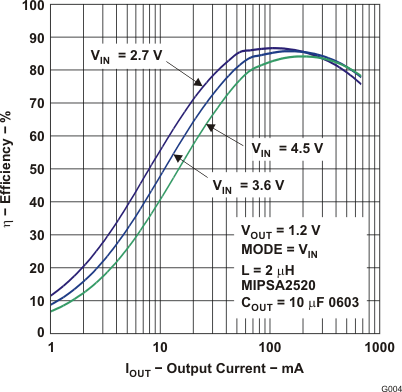 Figure 11. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 11. Efficiency vs Output Current
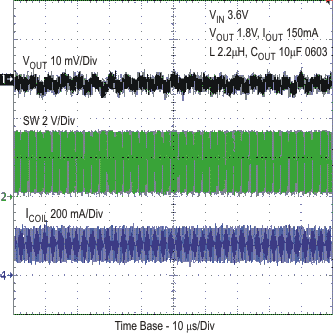 Figure 13. Typical Operation - PWM Mode
Figure 13. Typical Operation - PWM Mode
 Figure 15. Mode Pin Transition from PWM to PFM MODE at Light Load
Figure 15. Mode Pin Transition from PWM to PFM MODE at Light Load
 Figure 17. Forced PWM Load Transient
Figure 17. Forced PWM Load Transient
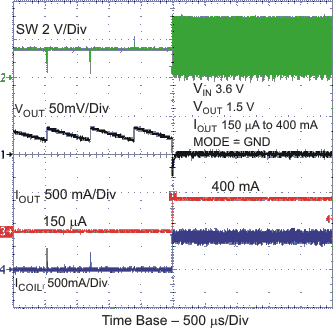 Figure 19. PFM Load Transient
Figure 19. PFM Load Transient
 Figure 21. PFM Load Transient
Figure 21. PFM Load Transient
 Figure 23. PFM Load Transient
Figure 23. PFM Load Transient
 Figure 25. PFM Load Transient
Figure 25. PFM Load Transient
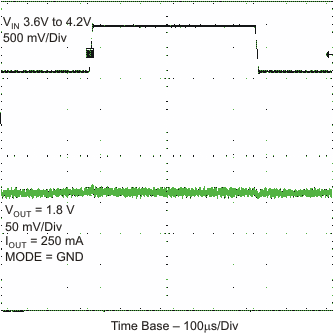 Figure 27. PWM Line Transient
Figure 27. PWM Line Transient
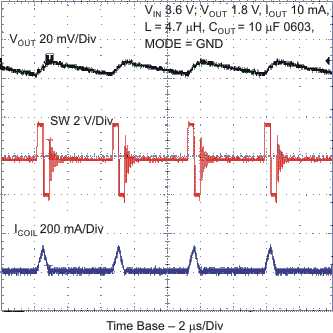 Figure 29. Typical Operation - PFM Mode
Figure 29. Typical Operation - PFM Mode
 Figure 8. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 8. Efficiency vs Output Current
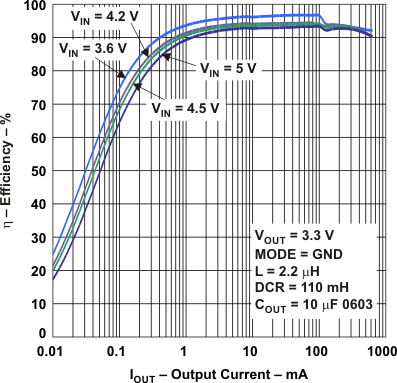 Figure 10. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 10. Efficiency vs Output Current
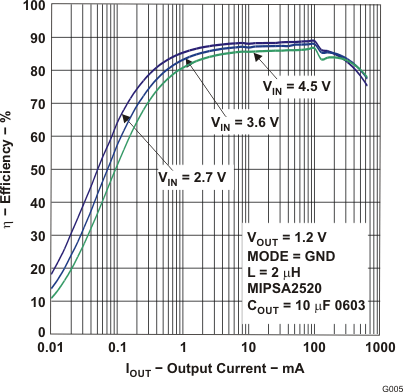 Figure 12. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 12. Efficiency vs Output Current
 Figure 14. Mode Pin Transition from PFM to FORCED PWM Mode at Light Load
Figure 14. Mode Pin Transition from PFM to FORCED PWM Mode at Light Load
 Figure 16. Start-UP Timing
Figure 16. Start-UP Timing
 Figure 18. Forced PWM Load Transient
Figure 18. Forced PWM Load Transient
 Figure 20. PFM Load Transient
Figure 20. PFM Load Transient
 Figure 22. PFM Load Transient
Figure 22. PFM Load Transient
 Figure 24. PFM Load Transient
Figure 24. PFM Load Transient
 Figure 26. PFM Line Transient
Figure 26. PFM Line Transient
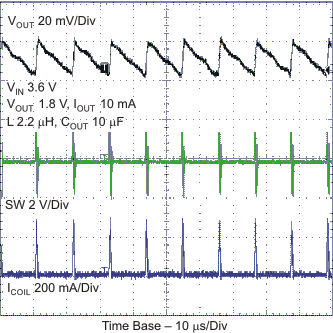 Figure 28. Typical Operation - PFM Mode
Figure 28. Typical Operation - PFM Mode