JAJSHC5B May 2019 – October 2022 TPS65987DDJ
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Supply Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.6 Power Consumption Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.8 Cable Detection Characteristics
- 6.9 USB-PD Baseband Signal Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.10 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.11 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.12 Oscillator Characteristics
- 6.13 I/O Characteristics
- 6.14 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.15 SPI Controller Timing Requirements
- 6.16 HPD Timing Requirements
- 6.17 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Port Power Switches
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Dead Battery Operation
- 8.3.6 Battery Charger Detection and Advertisement
- 8.3.7 ADC
- 8.3.8 DisplayPort HPD
- 8.3.9 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.10 Digital Core
- 8.3.11 I2C Interfaces
- 8.3.12 SPI Controller Interface
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.14 Oscillators
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Type-C VBUS Design Considerations
- 9.2.2 Notebook Design Supporting PD Charging
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.3 USB and DisplayPort Dock with Bus-Powered and Self-Powered Support
A flexible dock application that can work either on Bus-Power or Self-Power takes advantage of the two integrated power paths. PPHV1 will sink power into the system when operating off Bus-Power and PPHV2 will source power on VBUS when powered. When the dock can operate in both modes it allows the end-user to use the dock in and out of an office.
The regulators that generate the required system voltages are powered from PPHV1 or the external dock supply. These rails powered from a main 3.3-V rail to ensure that the all the voltages required are valid in Bus-Powered and Self-Powered operation. This will also help for systems that support USB PD3.0 Fast Role Swap. There is a variable regulator to provide 5 V, 9 V, 15 V, and 20 V per the Power Delivery Rules.
The Super Speed signals from the Type-C connector are muxed to USB and MST Hubs through the TUSB1064. The DisplayPort and USB signals from the Super Speed Mux will go to a MST and USB HUB to enable additional video and USB connectors. The TPS65987DDJ can control the TUSB1064 Super Speed mux through I2C or GPIO. The TPD6S300 provides additional protection such as short to VBUS on the CC and SBU pins and ESD for the USB2 DN/P. See Figure 9-9 for the system block diagram.
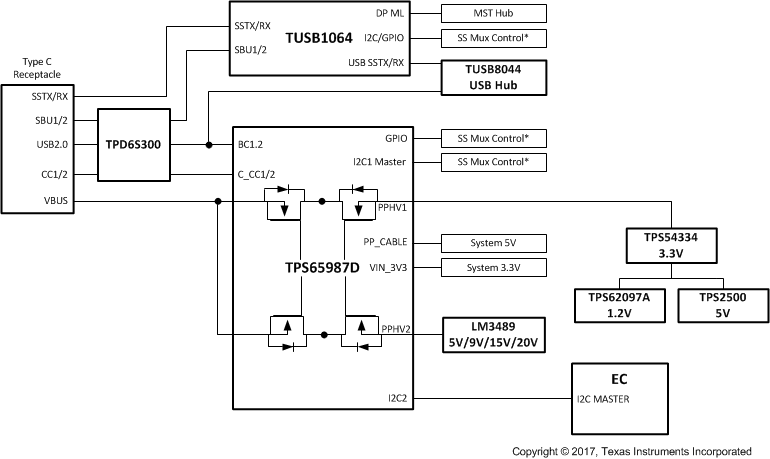 Figure 9-9 USB and DisplayPort Dock Block Diagram
Figure 9-9 USB and DisplayPort Dock Block Diagram