JAJSFH8G June 2011 – March 2020 TPS7A63-Q1 , TPS7A6401-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|14
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|14
発注情報
7.3.10.1 Programmable-Window Watchdog
Program the duration of the watchdog window by connecting an external resistor (ROSC) to ground at the ROSC pin. The current through the resistor sets the clock frequency of the internal oscillator. The user can adjust the duration of the watchdog window (that is, the watchdog timer period) by changing the resistor value. The duration of the watchdog window and the duration of the fault output are multiples of the internal oscillator frequency and are given by the following equations:
where
- tWD = width of watchdog window
- ROSC = resistor connected at ROSC pin
- tWD_OUT = duration of fault output
- fOSC = frequency of internal oscillator
- tCW = duration of closed window
- tOW = duration of open window
As shown in Figure 22, each watchdog window consists of an open window and a closed window, each having a width approximately 50% of the watchdog window. However, there is an exception to this; the first open window after watchdog initialization is eight times the duration of the watchdog window. All open windows except the one after watchdog initialization are one-half the width of the watchdog window. On initialization, the watchdog must receive service (by software, external microcontroller, and so forth) only during an open window. A watchdog serviced during a closed window, or not serviced during a open window, creates a watchdog fault condition.
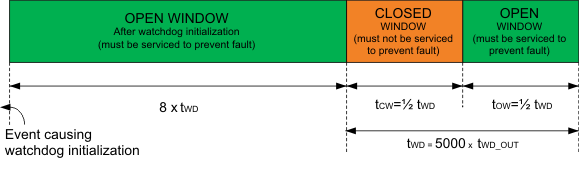 Figure 22. Watchdog Window Duration
Figure 22. Watchdog Window Duration