JAJSFH8G June 2011 – March 2020 TPS7A63-Q1 , TPS7A6401-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|14
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|14
発注情報
7.3.10.7 Watchdog Fault Conditions
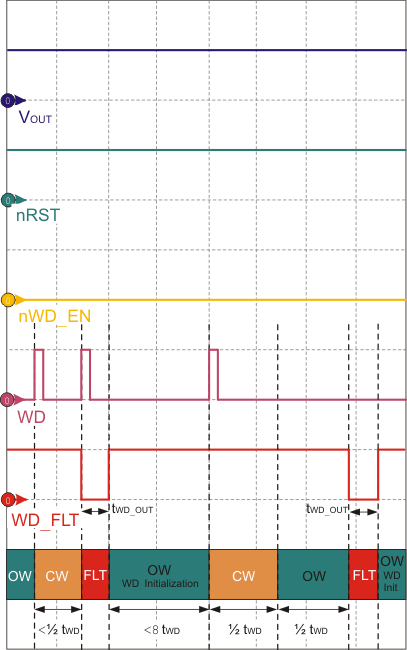 Figure 25. Watchdog Service Fault Conditions for TPS7A63-Q1
Figure 25. Watchdog Service Fault Conditions for TPS7A63-Q1 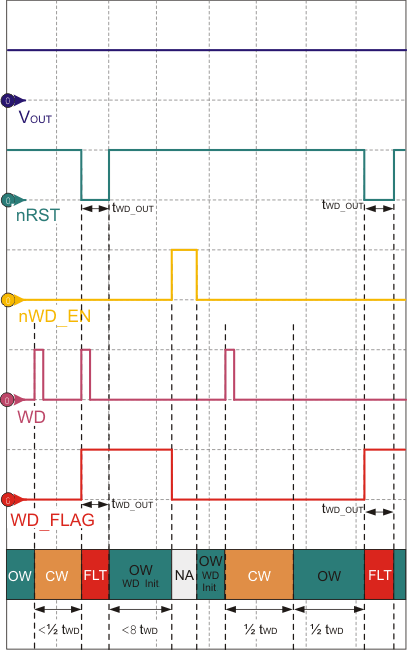 Figure 26. Watchdog Service Fault Conditions for TPS7A6401-Q1
Figure 26. Watchdog Service Fault Conditions for TPS7A6401-Q1 For both device options, a watchdog fault condition occurs in following (non-exhaustive) cases:
- When the watchdog receives service during a closed window.
- When watchdog does not receive service during an open window (this open window could be the one after watchdog initialization, or the one following a closed window).
As shown in Figure 25, for TPS7A63-Q1 the first watchdog fault registers when the watchdog receives service during a closed window. This causes the watchdog fault pin (WD_FLT) to go low temporarily for a duration of tWD_OUT. Following the fault, the watchdog reinitializes. Likewise, the second fault registers when the watchdog does not receive service during an open window (following a closed window). Again, the fault pin (WD_FLT) is asserts low for a duration of tWD_OUT.
As shown in Figure 26, for TPS7A6401-Q1 the first watchdog fault registers when watchdog receives service during a closes window. This causes the watchdog flag pin (WD_FLAG) to become high and stay latched. At the same time, nRST pin goes low temporarily for the duration of tWD_OUT. WD_FLAG remains high until toggling the nWD_EN pin disables and re-enables the watchdog or the watchdog receives service properly (while nWD_EN is low and nRST is high). The second fault registers when the watchdog does not receive service during an open window (following a closed window). While WD_FLAG is high (that is, during a fault condition), if the watchdog stays enabled, and reset is high; a watchdog service signal can also bring WD_FLAG low (about 5 µs after the watchdog receives service).
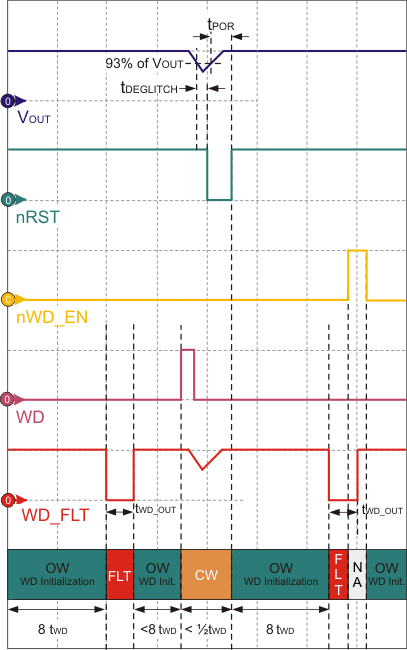 Figure 27. Watchdog Fault During Initialization, and Reinitialization During Reset for TPS7A63-Q1
Figure 27. Watchdog Fault During Initialization, and Reinitialization During Reset for TPS7A63-Q1 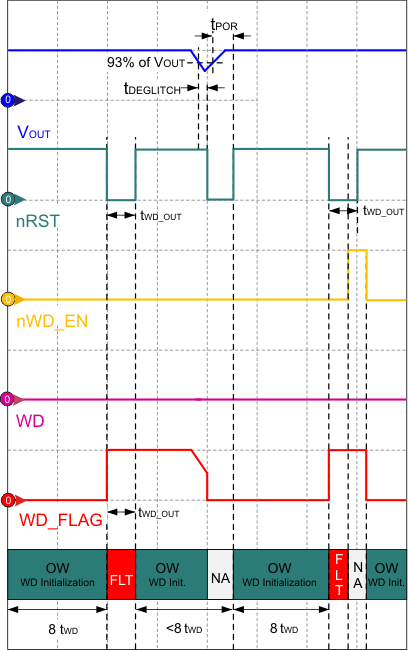 Figure 28. Watchdog Fault During Initialization, and Reinitialization During Reset for TPS7A6401-Q1
Figure 28. Watchdog Fault During Initialization, and Reinitialization During Reset for TPS7A6401-Q1 As shown in Figure 27 for the TPS7A6401-Q1, the watchdog fault condition also occurs if the watchdog does not receive service during the open window after watchdog initialization. That is, if the watchdog does not receive service during the first 8× tWD_OUT period after initialization, a fault condition occurs. This causes the watchdog fault pin (WD_FLT) to go low temporarily for a duration of tWD_OUT. In case of a load transient, if the regulated output voltage drops down causing reset (nRST) to go low, the rising edge on nRST causes the watchdog to reinitialize (that is, when reset becomes high with the watchdog still enabled). During a fault condition (that is, WD_FLT is low) with the watchdog disabled, the fault output continues to stay low until tWD_OUT is elapsed. A falling edge on nWD_EN pin causes the watchdog to reinitialize while nRST is still high.
As shown in Figure 28 for the TPS7A6401-Q1, the watchdog fault condition also occurs if the watchdog does not receive service during the open window after watchdog initialization. That is, if the watchdog does not receive service in first 8× tWD_OUT period after initialization, a fault condition occurs. This causes the watchdog flag pin (WD_FLAG) to become high and stay latched. At the same time, the nRST pin goes low temporarily for a duration of tWD_OUT. In the case of a load transient, if the regulated output voltage drops down causing the reset output to go low, the WD_FLAG asserts low, and the rising edge on nRST causes the watchdog to reinitialize (while the watchdog remains enabled). During a fault condition (that is, WD_FLAG is high), and with a disabled watchdog, the flag output continues to stay high as long as the watchdog remains enabled or receives proper service. However, nRST stays low until tWD_OUT elapses. Re-enabling the watchdog causes watchdog to reinitialize (while nRST is still high).