SLUSCZ1 May 2017 TPS92518-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 General Operation
- 8.3.2 Important System Considerations: Off-Timer and Maximum Peak Threshold Values
- 8.3.3 Shunt FET or Matrix dimming: Maximum Off-timer Calculation
- 8.3.4 VIN and the VCC Internal Regulators
- 8.3.5 Output Enable Control Logic
- 8.3.6 BOOT Capacitor and BOOT UVLO
- 8.3.7 Drop-out Operation
- 8.3.8 Analog and PWM Dimming
- 8.3.9 VIN and CSPx Pin Configuration
- 8.3.10 Enable and Undervoltage Lock-out Configuration
- 8.3.11 Voltage Sampling and DAC Operation
- 8.3.12 Device Functional Modes
- 8.4 Serial Interface
- 8.5
Registers
- 8.5.1 CONTROL Register (Address = 00h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.2 STATUS (FAULT) Register (Address = 01h) [reset = 10h]
- 8.5.3 THERM_WARN_LMT Register (Address = 02h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.4 LED1_PKTH_DAC Register (Address = 03h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.5 LED2_PKTH_DAC Register (Address = 04h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.6 LED1_TOFF_DAC Register (Address = 05h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.7 LED2_TOFF_DAC Register (Address = 06h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.8 LED1_MAXOFF_DAC Register (Address = 07h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.9 LED2_MAXOFF_DAC Register (Address = 08h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.10 VTHERM Register (Address = 09h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.11 LED1_MOST_RECENT Register (Address = 0Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.12 LED1_LAST_ON Register (Address = 0Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.13 LED1_LAST_OFF Register (Address = 0Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.14 LED2_MOST_RECENT Register (Address = 0Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.15 LED2_LAST_ON Register (Address = 0Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.16 LED2_LAST_OFF Register (Address = 0Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.17 Reset Register (Address = 10h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6 Programming
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|24
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|24
発注情報
8.3.6 BOOT Capacitor and BOOT UVLO
The BOOT capacitor provides the power for the high-side gate drive circuitry. The capacitor is charged each cycle from VCC during the off-time phase of the switching cycle. During the off-time, the free-wheeling diode conducts, pulling the switchnode (SW) low and providing a conduction path to charge the capacitor. During the on-time, the current required to charge the high-side FET gate and power the driver are supplied by the capacitor.
A minimum boot capacitor can be calculated by considering: the MOSFET Qg, the driver quiescent current, and the desired nominal maximum on-time. Other factors include: the BOOT diode Vf, the minimum BOOT operation voltage, and the level of the switchnode (SWx) during the off-time. A rough estimate can be calculated using Equation 17: or just use 0.1µF.
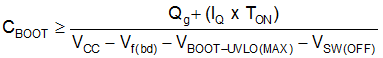
The variables are defined by:
Table 1. CBOOT Variables
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Qg | High-side FET total gate charge (Qg) as shown in the FET datasheet. |
| VCC | 7.5 V |
| VSW(off) | The switchnode voltage when the high-side FET is off. Use 0 V. |
| VBOOT-UVLO(MAX) | 5.2 V |
| IBOOT-Q | 200 µA |
| tON | Estimate your worst case on-time or use 500 µs |
| Vf(bd) | Forward drop of the boot diode |
A typical solution calculates a minimum CBOOT of approximately 60 nF, justifying the 100 nF selection.
If conditions are created which cause the boot capacitor to become depleted (see Drop-out Operation) and reach VBOOT-UVLO, switching is disabled until VBOOT increases by VBOOT-UVLO-HYST.