JAJSG66E September 2018 – November 2024 UCC21540 , UCC21540A , UCC21541 , UCC21542
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 デバイス比較表
- 5 ピン構成および機能
- 6 仕様
- 7 パラメータ測定情報
- 8 詳細説明
-
9 アプリケーションと実装
- 9.1 アプリケーション情報
- 9.2 代表的なアプリケーション
- 10電源に関する推奨事項
- 11レイアウト
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13改訂履歴
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DW|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DW|16
発注情報
7.5 プログラム可能なデッド タイム
UCC21542/A は内部的にデッド タイム回路を VCCI に接続しており、ピン 6 は内部的に接続されていません。このデバイスでは、両方の出力が常にオーバーラップできます。
UCC21540/A と UCC21541 の場合、DT を VCCI に接続すると DT 機能は無効になり、出力がオーバーラップできます。DT と GND の間に抵抗 (RDT) を配置することで、次の式に従ってデッド タイムを調整できます。DT (ns) = 10 × RDT (kΩ)。ノイズ耐性を向上させるため、DT ピンに近接して配置した 1nF 以下のセラミック コンデンサでこのピンをバイパスすることを推奨します。デッド タイムの詳細については、セクション 8.4.2 を参照してください。
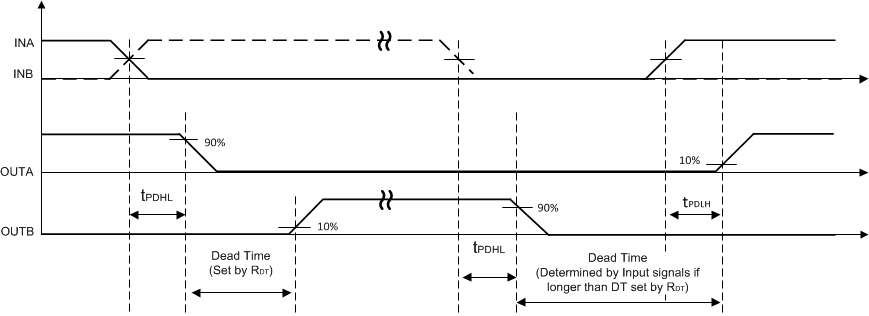 図 7-6 UCC21540/A、UCC21541 のデッド タイムのスイッチング パラメータ
図 7-6 UCC21540/A、UCC21541 のデッド タイムのスイッチング パラメータ