JAJSBW2H November 2011 – June 2024 UCC27523 , UCC27525 , UCC27526
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 概要 (続き)
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
7.3.1 VDD and Undervoltage Lockout
The UCC2752x devices have internal undervoltage-lockout (UVLO) protection feature on the VDD pin supply circuit blocks. When VDD is rising and the level is still below UVLO threshold, this circuit holds the output LOW, regardless of the status of the inputs. The UVLO is typically 4.2 V with 300-mV typical hysteresis. This hysteresis prevents chatter when low VDD supply voltages have noise from the power supply and also when there are droops in the VDD bias voltage when the system commences switching and there is a sudden increase in IDD. The capability to operate at low voltage levels such as below 5 V, along with best-in-class switching characteristics, is especially suited for driving emerging GaN power semiconductor devices.
For example, at power up, the UCC2752x driver-device output remains LOW until the VDD voltage reaches the UVLO threshold if Enable pin is active or floating. The magnitude of the OUT signal rises with VDD until steady-state VDD is reached. The non-inverting operation in 製品情報 shows that the output remains LOW until the UVLO threshold is reached, and then the output is in-phase with the input. The inverting operation in Figure 7-5 shows that the output remains LOW until the UVLO threshold is reached, and then the output is out-phase with the input. With UCC27526 the output turns to high-state only if INX+ is high and INX– is low after the UVLO threshold is reached.
Because the device draws current from the VDD pin to bias all internal circuits, for the best high-speed circuit performance, TI recommends two VDD bypass capacitors to prevent noise problems. TI highly recommends using surface-mount components. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor must be located as close as possible to the VDD to GND pins of the gate-driver device. In addition, a larger capacitor (such as 1-μF) with relatively low ESR must be connected in parallel and close proximity, in order to help deliver the high-current peaks required by the load. The parallel combination of capacitors presents a low impedance characteristic for the expected current levels and switching frequencies in the application.
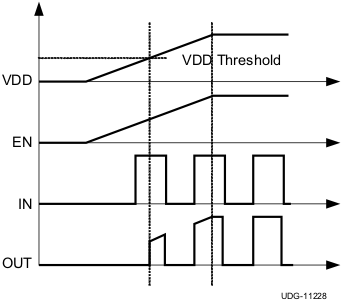 Figure 7-4 Power
up Non-Inverting Driver
Figure 7-4 Power
up Non-Inverting Driver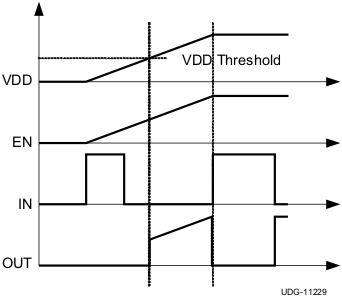 Figure 7-5 Power
up Inverting Driver
Figure 7-5 Power
up Inverting Driver