JAJSKM1C october 2019 – september 2021 UCC5870-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Power Supplies
- 7.3.2 Driver Stage
- 7.3.3 Integrated ADC for Front-End Analog (FEA) Signal Processing
- 7.3.4 Fault and Warning Classification
- 7.3.5
Diagnostic Features
- 7.3.5.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) and Overvoltage Lockout (OVLO)
- 7.3.5.2 CLAMP, OUTH, and OUTL Clamping Circuits
- 7.3.5.3 Active Miller Clamp
- 7.3.5.4 DESAT based Short Circuit Protection (DESAT)
- 7.3.5.5 Shunt Resistor based Overcurrent Protection (OCP) and Short Circuit Protection (SCP)
- 7.3.5.6 Temperature Monitoring and Protection for the Power Transistors
- 7.3.5.7 Active High Voltage Clamping (VCECLP)
- 7.3.5.8 Two-Level Turn-Off
- 7.3.5.9 Soft Turn-Off (STO)
- 7.3.5.10 Thermal Shutdown (TSD) and Temperature Warning (TWN) of Driver IC
- 7.3.5.11 Active Short Circuit Support (ASC)
- 7.3.5.12 Shoot-Through Protection (STP)
- 7.3.5.13 Gate Voltage Monitoring and Status Feedback
- 7.3.5.14 VGTH Monitor
- 7.3.5.15 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 7.3.5.16 Configuration Data CRC
- 7.3.5.17 SPI Transfer Write/Read CRC
- 7.3.5.18 TRIM CRC Check
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.5.12 Shoot-Through Protection (STP)
The shoot through protection function (STP) provides an additional layer of protection from shoot through conditions due to incorrect PWM commands from MCU. The output of the driver uses IN+ and the complementary PWM signal provided to the IN- input to set the output state of the driver. Both the IN+ and IN- inputs are deglitched by tGLITCH, which is programmable using CFG1[IO_DEGLITCH] bits (CFG1). There are two available version of STP, IN+/IN- safety interlock and automatic dead-time. The safety interlock function is enabled by setting the CFG1[TDEAD] bits (CFG1) to 0b000000 (tDEAD = 0). When using the safety interlock STP, if IN+ and IN- are both high at the same time, a shoot-through condition (STP fault) is detected. During an STP fault, the STATUS2[STP_FAULT] bit (STATUS2) is set, and, if unmasked, the nFLT1 output pulls low. The output of the driver is forced to the state defined by CFG3[FS_STATE_STP_FAULT] (CFG3). When the tDEAD is non-zero (CFG1[TDEAD] ≠ 0b000000, dead time is added to the falling edge of IN- by the device. In these cases, when IN+ goes high, the device waits until the deglitched falling edge of IN-, then OUTH pulls high tDEAD after the deglitched IN- is low. The implementation diagram and timing schemes are presented in Figure 7-29 and Figure 7-30 respectively.
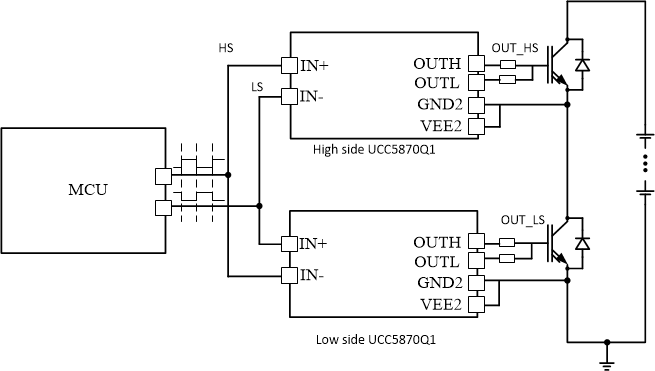 Figure 7-29 Block diagram of implementation of STP
function.
Figure 7-29 Block diagram of implementation of STP
function.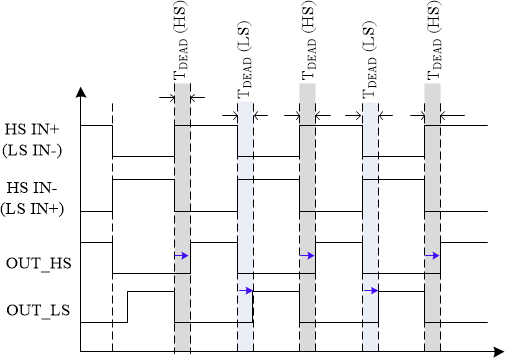 Figure 7-30 Timing scheme of implementation of STP
function.
Figure 7-30 Timing scheme of implementation of STP
function.