JAJS239G June 2007 – April 2018 TPS62290 , TPS62291 , TPS62293
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.2.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
The inductor value has a direct effect on the ripple current. The selected inductor has to be rated for its DC resistance and saturation current. The inductor ripple current (ΔIL) decreases with higher inductance and increases with higher VIN or VOUT.
The inductor selection has also impact on the output voltage ripple in PFM mode. Higher inductor values will lead to lower output voltage ripple and higher PFM frequency, lower inductor values will lead to a higher output voltage ripple but lower PFM frequency.
Equation 2 calculates the maximum inductor current under static load conditions. The saturation current of the inductor should be rated higher than the maximum inductor current as calculated with Equation 3. This is recommended because during heavy load transient the inductor current will rise above the calculated value.
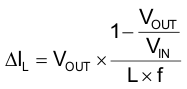
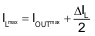
where
- f = Switching frequency (2.25 MHz typical)
- L = Inductor value
- ΔIL = Peak-to-peak inductor ripple current
- ILmax = Maximum inductor current
A more conservative approach is to select the inductor current rating just for the maximum switch current of the corresponding converter.
Accepting larger values of ripple current allows the use of low inductance values, but results in higher output voltage ripple, greater core losses, and lower output current capability.
The total losses of the coil have a strong impact on the efficiency of the DC/DC conversion and consist of both the losses in the DC resistance R(DC)) and the following frequency-dependent components:
- The losses in the core material (magnetic hysteresis loss, especially at high switching frequencies)
- Additional losses in the conductor from the skin effect (current displacement at high frequencies)
- Magnetic field losses of the neighboring windings (proximity effect)
- Radiation losses
Table 2. List of Inductors
| DIMENSIONS [mm3] | INDUCTOR TYPE | SUPPLIER(1) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 × 3 × 1.5 | LPS3015 | Coilcraft |
| 3 x 3 x 1.5 | LQH3NPN2R2NM0 | MURATA |
| 3.2 x 2.6 x 1.2 | MIPSA3226D2R2 | FDK |