-
TPS62125 3V~17V、300mA降圧型コンバータ、可変イネーブル・スレッショルドおよびヒステリシス付き
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
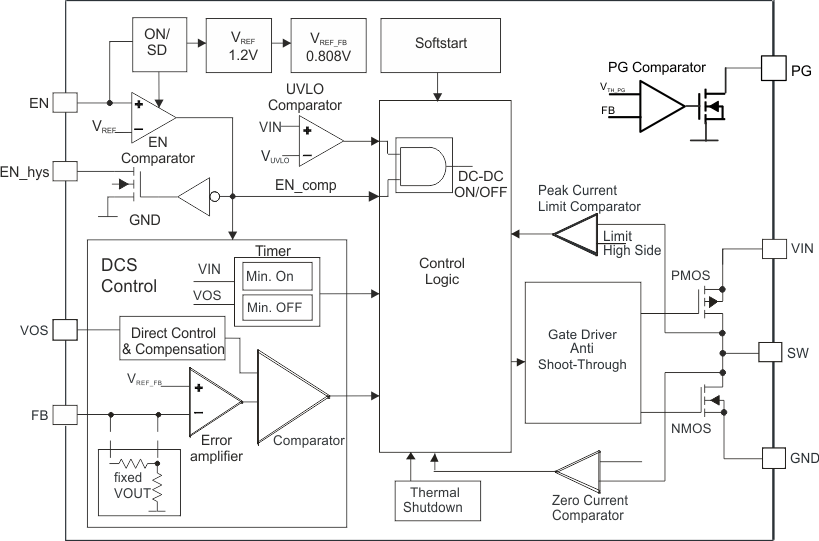
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
- 重要なお知らせ
TPS62125 3V~17V、300mA降圧型コンバータ、可変イネーブル・スレッショルドおよびヒステリシス付き
1 特長
- 3V~17Vの広い入力電圧範囲
- 入力電源電圧スーパーバイザ(SVS)、スレッショルドおよびヒステリシスを設定可能、標準静止電流6µA
- 広い出力電圧範囲: 1.2V~10V
- 静止電流: 13μA (標準値)
- シャットダウン時電流: 350nA (標準値)
- シームレスなパワーセーブ・モード移行
- DCS-Control™方式
- 低い出力リップル電圧
- 最大1MHzのスイッチング周波数
- 広いVINおよびVOUT範囲にわたって最高の効率を維持
- TPS62160/70とピン互換
- 100%デューティ・サイクル・モード
- パワー・グッド用オープン・ドレイン出力
- 出力放電機能
- 小型の2mm×2mm、8ピンWSONパッケージ
2 アプリケーション
- 組み込み処理
- 4セルのアルカリ、または1~4セルのリチウムイオン・バッテリ駆動のアプリケーション
- 9V~15Vのスタンバイ電源
- 環境発電
- インバータ(負のVOUT)
3 概要
TPS62125デバイスは、高効率の同期整流降圧型コンバータで、最大300mAの出力電流を供給する低消費電力、および超低消費電力のアプリケーション用に最適化されています。入力電圧範囲が3V~17Vと広く、4セルのアルカリ、および1~4セルのリチウムイオン・バッテリの直列構成、および9V~15Vの電源で動作するアプリケーションをサポートします。このデバイスには、高精度の低消費電力イネーブル・コンパレータが内蔵されており、入力電源電圧スーパーバイザ(SVS)として使用することで、システム固有の電源オンおよび電源オフの要件に対応できます。イネーブル・コンパレータはわずか6μAの静止電流しか消費せず、正確な1.2V(標準値)のスレッショルドおよび可変ヒステリシスを備えています。これらの機能により、このコンバータはソーラー・パネルや電流ループなどの高インピーダンスのソースから電力を供給されるストレージ・コンデンサからエネルギーを抽出し、電源レールを生成できます。このコンバータは、DCS-Control方式によりパワー・セーブ・モードで動作し、負荷電流範囲の全体にわたって最高の効率を維持します。コンバータは、軽負荷時にはパルス周波数変調(PFM)モードで動作し、負荷電流の大きいときにはシームレスかつ自動的にパルス幅変調(PWM)モードへ移行します。この DCS-Control™方式はPFMモードで出力リップル電圧が低くなるよう最適化されており、出力ノイズを最小に抑え、非常に優れたAC負荷レギュレーションを行えます。出力電圧がレギュレート状態になると、オープン・ドレインのパワー・グッド出力により通知されます。
製品情報(1)
| 型番 | パッケージ | 本体サイズ(公称) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS62125 | WSON (8) | 2.00mm×2.00mm |
- 利用可能なすべてのパッケージについては、このデータシートの末尾にある注文情報を参照してください。
代表的なアプリケーションの回路図

効率と入力電圧との関係

4 改訂履歴
Changes from D Revision (July 2015) to E Revision
- Added SW node AC abs max ratings Go
Changes from C Revision (December 2013) to D Revision
- Added 「ピン構成および機能」セクション、「ESD定格」表、「機能説明」セクション、「デバイスの機能モード」セクション、「アプリケーションと実装」セクション、「電源に関する推奨事項」セクション、「レイアウト」セクション、「デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート」セクション、「メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報」セクションGo
5 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| EN | 3 | IN | Input pin for the enable comparator. Pulling this pin to GND turns the device into shutdown mode. The DC/DC converter is enabled once the rising voltage on this pin trips the enable comparator threshold, VTH EN ON of typ. 1.2 V. The DC/DC converter is turned off once a falling voltage on this pin trips the threshold, VTH EN OFF of typ. 1.15 V. The comparator threshold can be increased by connecting an external resistor to pin EN_hys. See also application section. This pin must be terminated. | |
| EN_hys | 4 | OUT | Enable hysteresis open-drain output. This pin is pulled to GND when the voltage on the EN pin is below the comparator threshold VTH EN ON of typ. 1.2 V and the comparator has not yet tripped. The pin is high impedance once the enable comparator has tripped and the voltage at the pin EN is above the threshold VTH EN ON. The pin is pulled to GND once the falling voltage on the EN pin trips the threshold VTH EN OFF (1.15 V typical). This pin can be used to increase the hysteresis of the enable comparator. If not used, tie this pin to GND, or leave it open. | |
| FB | 5 | IN | This is the feedback pin for the regulator. An external resistor divider network connected to this pin sets the output voltage. In case of fixed output voltage option, the resistor divider is integrated and the pin need to be connected directly to the output voltage. | |
| GND | 1 | PWR | GND supply pin. | |
| PG | 8 | OUT | Open drain power good output. This pin is internally pulled to GND when the device is disabled or the output voltage is below the PG threshold. The pin is floating when the output voltage is in regulation and above the PG threshold. For power good indication, the pin can be connected via a pull up resistor to a voltage rail up to 10 . The pin can sink a current up to 0.4 mA and maintain the specified high/low voltage levels. It can be used to discharge the output capacitor with up to 10 mA. In this case the current into the pin must be limited with an appropriate pull up resistor. More details can be found in the application section. If not used, leave the pin open, or connect to GND. | |
| SW | 7 | OUT | This is the switch pin and is connected to the internal MOSFET switches. Connect the inductor to this pin. Do not tie this pin to VIN, VOUT or GND. | |
| VIN | 2 | PWR | VIN power supply pin. | |
| VOS | 6 | IN | This is the output voltage sense pin for the DCS-Control circuitry. This pin must be connected to the output voltage of the DC/DC converter. | |
| Exposed Thermal PAD | – | – | This pad must be connected to GND. | |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin voltage(2) | VIN | –0.3 | 20 | V | |
| SW (DC) | –0.3 | VIN + 0.3V | V | ||
| SW (AC, less than 10ns)(3) | -3.0 | 23.5 | V | ||
| EN | –0.3 | VIN + 0.3 | V | ||
| FB | –0.3 | 3.6 | V | ||
| VOS, PG | –0.3 | 12 | V | ||
| EN_hys | –0.3 | 7 | V | ||
| Power good sink current | IPG | 10 | mA | ||
| EN_hys sink current | IEN_hys | 3 | mA | ||
| Maximum operating junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Supply voltage | 3 | 17 | V | ||
| Output current capability | 3 V ≤ VIN < 6 V | 200 | mA | |||
| 6 V ≤ VIN ≤ 17 V | 300 | |||||
| TA | Operating ambient temperature (1) (Unless Otherwise Noted) | –40 | 85 | °C | ||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature, | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS62125 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSG (WSON) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 65.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 93.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 30.1 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.5 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 47.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 7.2 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
TA = –40°C to 85°C, typical values are at TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted), VIN = 12 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY | ||||||
| VIN | Input voltage range(1) | 3 | 17 | V | ||
| VOUT | Output voltage range | 1.2 | 10 | V | ||
| IQ | Quiescent current | IOUT = 0 mA, device not switching, EN = VIN, regulator sleeps | 13 | 23 | µA | |
| IOUT = 0 mA, device switching, VIN = 7.2 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, L = 22 µH |
14 | µA | ||||
| VIN = 5 V, EN = 1.1 V, enable comparator active, device DC/DC converter off | 6 | 11 | µA | |||
| IActive | Active mode current consumption | VIN = 5 V = VOUT, TA = 25°C, high-side MOSFET switch fully turned on (100% mode) | 230 | 275 | µA | |
| ISD | Shutdown current(2) | Enable comparator off, EN < 0.4 V,
VOUT = SW = 0 V, VIN = 5 V |
0.35 | 2.4 | µA | |
| VUVLO | Undervoltage lockout threshold | Falling VIN | 2.8 | 2.85 | V | |
| Rising VIN | 2.9 | 2.95 | V | |||
| ENABLE COMPARATOR THRESHOLD AND HYSTERESIS (EN, EN_hys) | ||||||
| VTH EN ON | EN pin threshold rising edge | 3 V ≤ V≤ 17 V | 1.16 | 1.20 | 1.24 | V |
| VTH EN OFF | EN pin threshold falling edge | 1.12 | 1.15 | 1.19 | V | |
| VTH EN Hys | EN pin hysteresis IN | 50 | mV | |||
| IIN EN | Input bias current into EN pin | EN = 1.3 V | 0 | 50 | nA | |
| VEN_hyst | EN_hys pin output low | IEN_hyst = 1 mA, EN = 1.1 V | 0.4 | V | ||
| IIN EN_hyst | Input bias current into EN_hyst pin | EN_hyst = 1.3 V | 0 | 50 | nA | |
| POWER SWITCH | ||||||
| RDS(ON) | High-side MOSFET ON-resistance | VIN = 3 V, I = 100 mA | 2.4 | 4 | Ω | |
| VIN = 12 V, I = 100 mA | 1.5 | 2.6 | ||||
| Low-side MOSFET ON-resistance | VIN = 3 V, I = 100 mA | 0.75 | 1.3 | |||
| VIN = 12 V, I = 100 mA | 0.6 | 1 | ||||
| ILIMF | Switch current limit high-side MOSFET | VIN = 12 V | 600 | 750 | 900 | mA |
| TSD | Thermal shutdown | Increasing junction temperature | 150 | °C | ||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis | Decreasing junction temperature | 20 | °C | |||
| OUTPUT | ||||||
| tONmin | Minimum ON-time | VIN = 5 V, VOUT = 2.5 V | 500 | ns | ||
| tOFFmin | Minimum OFF-time | VIN = 5 V | 60 | ns | ||
| VREF_FB | Internal reference voltage of error amplifier | 0.808 | V | |||
| VFB | Feedback voltage accuracy | Referred to internal reference (VREF_FB) | –2.5% | 0% | 2.5% | |
| Feedback voltage line regulation | IOUT = 100 mA, 5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 17 V, VOUT = 3.3 V(3) | –0.05 | %/V | |||
| Feedback voltage load regulation | VOUT = 3.3 V; IOUT = 1 mA to 300 mA, VIN = 12 V(3) | –0.004 | %/mA | |||
| IIN_FB | Input bias current into FB pin | VFB = 0.8 V | 0 | 50 | nA | |
| tStart | Regulator start-up time | Time from EN high to device starts switching, VIN = 5 V |
50 | µs | ||
| tRamp | Output voltage ramp time | Time to ramp up VOUT = 1.8 V, no load | 200 | |||
| ILK_SW | Leakage current into SW pin(4) | VOS = VIN = VSW = 1.8 V, EN = GND, device in shutdown mode | 1.8 | 2.85 | µA | |
| IIN_VOS | Bias current into VOS pin | 0 | 50 | nA | ||
| POWER GOOD OUTPUT (PG) | ||||||
| VTH_PG | Power good threshold voltage | Rising VFB feedback voltage | 93% | 95% | 97% | |
| Falling VFB feedback voltage | 87% | 90% | 93% | |||
| VOL | PG pin output low voltage | Current into PG pin IPG= 0.4 mA | 0.3 | V | ||
| VOH | PG pin output high voltage | Open drain output, external pullup resistor | 10 | V | ||
| IIN_PG | Bias current into PG pin | V(PG) = 3 V, EN = 1.3 V, FB = 0.85 V | 0 | 50 | nA | |
6.6 Typical Characteristics
 Figure 1. Shutdown Current vs. Input Voltage
Figure 1. Shutdown Current vs. Input Voltage
 Figure 3. Quiescent Current vs. EN Voltage, Rising VEN
Figure 3. Quiescent Current vs. EN Voltage, Rising VEN
 Figure 5. EN Comparator Thresholds vs. Input Voltage
Figure 5. EN Comparator Thresholds vs. Input Voltage
 Figure 2. Quiescent Current vs. Input Voltage
Figure 2. Quiescent Current vs. Input Voltage
 Figure 4. Quiescent Current vs. VEN Voltage, Falling VEN
Figure 4. Quiescent Current vs. VEN Voltage, Falling VEN
 Figure 6. RDSON High-Side Switch
Figure 6. RDSON High-Side Switch
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The TPS62125 high-efficiency synchronous switch mode buck converter includes TI's DCS-Control (Direct Control with Seamless Transition into Power-Save Mode), an advanced regulation topology, which combines the advantages of hysteretic and voltage mode control. Characteristics of DCS-Control are excellent AC load regulation and transient response, low-output ripple voltage and a seamless transition between PFM and PWM mode operation.
DCS-Control includes an AC loop which senses the output voltage (VOS pin) and directly feeds the information to a fast comparator stage. This comparator sets the switching frequency, which is constant for steady state operating conditions, and provides immediate response to dynamic load changes. In order to achieve accurate DC load regulation, a voltage feedback loop is used. The internally compensated regulation network achieves fast and stable operation with small external components and low ESR capacitors. The DCS-Control topology supports pulse width modulation (PWM) mode for medium and high load conditions and a power-save mode at light loads. During PWM mode, it operates in continuous conduction. The switch frequency is up to 1 MHz with a controlled frequency variation depending on the input voltage. If the load current decreases, the converter seamless enters power-save mode to maintain high efficiency down to very light loads. In power-save mode the switching frequency varies linearly with the load current. Because DCS-Control supports both operation modes within one single building block, the transition from PWM to power-save mode is seamless without effects on the output voltage. The TPS62125 offers both excellent DC voltage and superior load transient regulation, combined with very low-output voltage ripple, minimizing interference with RF circuits.
At high load currents the converter operates in quasi fixed frequency PWM mode operation and at light loads in pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode to maintain highest efficiency over the full load current range. In PFM mode, the device generates a single switching pulse to ramp up the inductor current and recharge the output capacitor, followed by a sleep period where most of the internal circuits are shutdown to achieve a quiescent current of typically 13 µA. During this time, the load current is supported by the output capacitor. The duration of the sleep period depends on the load current and the inductor peak current.
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout
In addition to the EN comparator, the device includes an under-voltage lockout circuit which prevents the device from misoperation at low input voltages. Both circuits are fed to an AND gate and prevents the converter from turning on the high-side MOSFET switch or low-side MOSFET under undefined conditions. The UVLO threshold is set to 2.9 V typical for rising VIN and 2.8 V typical for falling VIN. The hysteresis between rising and falling UVLO threshold ensures proper start-up. Fully functional operation is permitted for an input voltage down to the falling UVLO threshold level. The converter starts operation again once the input voltage trips the rising UVLO threshold level and the voltage at the EN pin trips VTH_EN_ON.
7.3.2 Enable Comparator (EN / EN_hys)
The EN pin is connected to an on/shutdown detector (ON/SD) and an input of the enable comparator. With a voltage level of 0.4 V or less at the EN pin, the ON/SD detector turns the device into Shutdown mode and the quiescent current is reduced to typically 350 nA. In this mode the EN comparator as well the entire internal-control circuitry are switched off. A voltage level of typical 900 mV (rising) at the EN pin triggers the on/shutdown detector and activates the internal reference VREF (typical 1.2 V), the EN comparator and the UVLO comparator. In applications with slow rising voltage levels at the EN pin, the quiescent current profile before this trip point needs to be considered, see Figure 3. Once the ON/SD detector has tripped, the quiescent current consumption of the device is typical 6 µA. The TPS62125 starts regulation once the voltage at the EN pin trips the threshold VEN_TH ON (typical 1.2 V) and the input voltage is above the UVLO threshold. It enters softstart and ramps up the output voltage. For proper operation, the EN pin must be terminated and must not be left floating. The quiescent current consumption of the TPS62125 is typical 13 µA under no load condition (not switching). See Figure 1. The DC/DC regulator stops operation once the voltage on the EN pin falls below the threshold VEN_TH OFF (typical 1.15 V) or the input voltage falls below UVLO threshold. The enable comparator features a built in hysteresis of typical 50 mV. This hysteresis can be increased with an external resistor connected to pin EN_hys.
7.3.3 Power Good Output and Output Discharge (PG)
The power good output (PG pin) is an open drain output. The circuit is active once the device is enabled. It is driven by an internal comparator connected to the FB pin voltage and an internal reference. The PG output provides a high level (open drain high impedance) once the feedback voltage exceeds typical 95% of its nominal value. The PG output is driven to low level once the FB pin voltage falls below typical 90% of its nominal value VREF_FB. The PG output goes high (high impedance) with a delay of typically 2 µs. A pull up resistor is needed to generate a high level. The PG pin can be connected via a pull up resistors to a voltage up to 10 V. This pin can also be used to discharge the output capacitor. See section Application Information for more details.
The PG output is pulled low if the voltage on the EN pin falls below the threshold VEN_TH OFF or the input voltage is below the undervoltage lockout threshold UVLO.
7.3.4 Thermal Shutdown
As soon as the junction temperature, TJ, exceeds 150°C (typical) the device goes into thermal shutdown. In this mode, the high-side and low-side MOSFETs are turned-off. The device continues its operation when the junction temperature falls below the thermal shutdown hysteresis.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Operation
The TPS62125 operates with pulse width modulation in continuous conduction mode (CCM) with a nominal switching frequency of about 1 MHz. The frequency variation in PWM mode is controlled and depends on VIN, VOUT and the inductance. The device operates in PWM mode as long the output current is higher than half the inductor's ripple current. To maintain high efficiency at light loads, the device enters power-save mode at the boundary to discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). This happens if the output current becomes smaller than half the inductor's ripple current.
7.4.2 Power-Save Mode
With decreasing load current, the TPS62125 transitions seamlessly from PWM mode to power-save mode once the inductor current becomes discontinuous. This ensures a high efficiency at light loads. In power-save mode the converter operates in pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode and the switching frequency decreases linearly with the load current. DCS-Control features a small and predictable output voltage ripple in power-save mode. The transition between PWM mode and power-save mode occurs seamlessly in both directions.
The minimum ON-time TONmin for a single pulse can be estimated by:
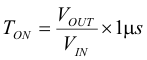
Therefore the peak inductor current in PFM mode is approximately:
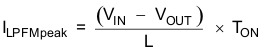
where
- TON: High-side MOSFET switch on time [µs]
- VIN: Input voltage [V]
- VOUT: Output voltage [V]
- L : Inductance [µH]
- ILPFMpeak : PFM inductor peak current [mA]
The transition from PFM mode to PWM mode operation and back occurs at a load current of approximately 0.5 x ILPFMpeak.
The maximum switching frequency can be estimated by:
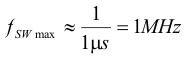
7.4.3 100% Duty Cycle Low Dropout Operation
The device increases the ON-time of the high-side MOSFET switch as the input voltage comes close to the output voltage in order to keep the output voltage in regulation. This reduces the switching frequency.
With further decreasing input voltage VIN, the high-side MOSFET switch is turned on completely. In this case, the converter provides a low input-to-output voltage difference. This is particularly useful in applications with a widely variable supply voltage to achieve longest operation time by taking full advantage of the whole supply voltage span.
The minimum input voltage to maintain output voltage regulation depends on the load current and output voltage, and can be calculated as:
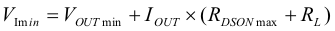
where
- IOUT: Output current
- RDS(ON)max: Maximum high-side switch RDS(ON)
- RL: DC resistance of the inductor
- VOUTmin: Minimum output voltage the load can accept
7.4.4 Soft-Start
The TPS62125 has an internal soft-start circuit which controls the ramp up of the output voltage and limits the inrush current during start-up. This limits input voltage drop.
The soft-start system generates a monotonic ramp up of the output voltage and reaches an output voltage of 1.8 V typical within 240 µs after the EN pin was pulled high. For higher output voltages, the ramp up time of the output voltage can be estimated with a ramp up slew rate of about 12 mV/us. TPS62125 is able to start into a prebiased output capacitor. The converter starts with the applied bias voltage and ramps the output voltage to its nominal value. In case the output voltage is higher than the nominal value, the device starts switching once the output has been discharged by an external load or leakage current to its nominal output voltage value.
During start-up the device can provide an output current of half of the high-side MOSFET switch current limit ILIMF. Large output capacitors and high load currents may exceed the current capability of the device during start-up. In this case the start-up ramp of the output voltage will be slower.
7.4.5 Short-Circuit Protection
The TPS62125 integrates a high-side MOSFET switch current limit, ILIMF, to protect the device against a short circuit. The current in the high-side MOSFET switch is monitored by a current limit comparator and once the current reaches the limit of ILIMF , the high-side MOSFET switch is turned off and the low-side MOSFET switch is turned on to ramp down the inductor current. The high-side MOSFET switch is turned on again once the zero current comparator trips and the inductor current has become zero. In this case, the output current is limited to half of the high-side MOSFET switch current limit, 0.5 x ILIMF, typ. 300mA.
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The TPS62125 is a high-efficiency synchronous step-down converter providing a wide output voltage range from 1.2 V to 10 V.
8.2 Typical Application
 Figure 8. TPS62125 3.3-V Output Voltage Configuration
Figure 8. TPS62125 3.3-V Output Voltage Configuration
8.2.1 Design Requirements
The device operates over an input voltage range from 3 V to 17 V. The output voltage is adjustable using an external feedback divider.
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
8.2.2.1 Output Voltage Setting
The output voltage can be calculated by:

The internal reference voltage for the error amplifier, VREF_FB, is nominal 0.808 V. However for the feedback resistor divider selection, it is recommended to use the value 0.800 V as the reference. Using this value, the output voltage sets 1% higher and provides more headroom for load transients as well for line and load regulation. The current through the feedback resistors R1 and R2 should be higher than 1 µA. In applications operating over full temperature range or in noisy environments, this current may be increased for robust operation. However, higher currents through the feedback resistors impact the light load efficiency of the converter.
Table 1 shows a selection of suggested values for the feedback divider network for most common output voltages.
Table 1. Suggested Values for Feedback Divider Network
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE | 1.2 V | 1.8 V | 3.3 V | 5 V | 6.7 V | 8 V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 [kΩ] | 180 | 300 | 1800 | 1100 | 1475 | 1800 |
| R2 [kΩ] | 360 | 240 | 576 | 210 | 200 | 200 |
8.2.2.2 Enable Threshold and Hysteresis Setting
 Figure 9. Using the Enable Comparator Threshold and Hysteresis for an Input SVS (Supply Voltage Supervisor)
Figure 9. Using the Enable Comparator Threshold and Hysteresis for an Input SVS (Supply Voltage Supervisor)
The enable comparator can be used as an adjustable input supply voltage supervisor (SVS) to start and stop the DC/DC converter depending on the input voltage level. The input voltage level, VIN_startup, at which the device starts up is set by the resistors REN1 and REN2 and can be calculated by :

The resistor values REN1 and REN2 can be calculated by:


The input voltage level VIN_stop at which the device will stop operation is set by REN1, REN2 and REN HYS and can be calculated by:

The resistor value REN_hys can be calculated according to:

The current through the resistors REN1, REN2, and REN HYS should be higher than 1 µA. In applications operating over the full temperature range and in noisy environments, the resistor values can be reduced to smaller values.
 Figure 10. Using the EN Comparator as Input SVS for Proper VOUT Ramp Up
Figure 10. Using the EN Comparator as Input SVS for Proper VOUT Ramp Up
8.2.2.3 Power Good (PG) Pullup and Output Discharge Resistor
The power good open collector output needs an external pull up resistor to indicate a high level. The pull up resistor can be connected to a voltage level up to 10 V. The output can sink current up to 0.4 mA with specified output low level of less than 0.3 V. The lowest value for the pull up resistor can be calculated by:

 Figure 11. PG Open Collector Output
Figure 11. PG Open Collector Output
The PG pin can be used to discharge the output capacitor. The PG output has an internal resistance RIPG of typical 600 Ω and minimum 400 Ω. The maximum sink current into the PG pin is 10 mA. In order to limit the discharge current to the maximum allowable sink current into the PG pin, the external pull up resistor RPull up can be calculated to:

In case a negative value is calculated, the external pull up resistor can be removed and the PG pin can be directly connected to the output.
8.2.2.4 Output Filter Design (Inductor and Output Capacitor)
The external components have to fulfill the needs of the application, but also the stability criteria of the devices control loop. The TPS62125 is optimized to work within a range of L and C combinations. The LC output filter inductance and capacitance have to be considered together, creating a double pole, responsible for the corner frequency of the converter. Table 2 can be used to simplify the output filter component selection.
Table 2. Recommended LC Output Filter Combinations
| INDUCTOR VALUE [µH](2) | OUTPUT CAPACITOR VALUE [µF](1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 µF | 2 x 10 µF | 22 µF | 47 µF | |
| VOUT 1.2 V - 1.8 V | ||||
| 15 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 22 | √(3) | √ | √ | √ |
| VOUT 1.8 V - 3.3 V | ||||
| 15 | √(3) | √ | √ | √ |
| 22 | √(3) | √ | √ | √ |
| VOUT 3.3 V - 5 V | ||||
| 10 | √ | √ | √ | |
| 15 | √(3) | √(3) | √ | |
| 22 | ||||
| VOUT 5 V - 10 V | ||||
| 10 | √(3) | √(3) | √ | |
| 15 | √ | √ | √ | |
| 22 | √ | √ | √ | |
More detailed information on further LC combinations can be found in application note SLVA515.
8.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
The inductor value affects its peak-to-peak ripple current, the PWM-to-PFM transition point, the output voltage ripple and the efficiency. The selected inductor has to be rated for its DC resistance and saturation current. The inductor ripple current (ΔIL) decreases with higher inductance and increases with higher VIN or VOUT and can be estimated according to Equation 13.
Equation 14 calculates the maximum inductor current under static load conditions. The saturation current of the inductor should be rated higher than the maximum inductor current as calculated with Equation 14. This is recommended because during heavy load transient the inductor current will rise above the calculated value. A more conservative way is to select the inductor saturation current according to the high-side MOSFET switch current limit ILIMF.


where
- TON: See Equation 1
- L: Inductance
- ΔIL: Peak to Peak inductor ripple current
- ILmax: Maximum Inductor current
In DC/DC converter applications, the efficiency is essentially affected by the inductor AC resistance (i.e. quality factor) and by the inductor DCR value. To achieve high-efficiency operation, take care in selecting inductors featuring a quality factor above 25 at the switching frequency. Increasing the inductor value produces lower RMS currents, but degrades transient response. For a given physical inductor size, increased inductance usually results in an inductor with lower saturation current.
The total losses of the coil consist of both the losses in the DC resistance (RDC) and the following frequency-dependent components:
- The losses in the core material (magnetic hysteresis loss, especially at high switching frequencies)
- Additional losses in the conductor from the skin effect (current displacement at high frequencies)
- Magnetic field losses of the neighboring windings (proximity effect)
- Radiation losses
The following inductor series from different suppliers have been used with the TPS62125.
Table 3. List of Inductors
| INDUCTANCE [µH] | DCR [Ω] | DIMENSIONS [mm3] | INDUCTOR TYPE | SUPPLIER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 / 15 | 0.33 max / 0.44 max. | 3.3 x 3.3 x 1.4 | LPS3314 | Coilcraft |
| 22 | 0.36 max. | 3.9 x 3.9 x 1.8 | LPS4018 | Coilcraft |
| 15 | 0.33 max. | 3.0 x 2.5 x 1.5 | VLF302515 | TDK |
| 10/15 | 0.44 max / 0.7 max. | 3.0 x 3.0 x 1.5 | LPS3015 | Coilcraft |
| 10 | 0.38 typ. | 3.2 × 2.5 × 1.7 | LQH32PN | Murata |
8.2.2.6 Output Capacitor Selection
Ceramic capacitors with low ESR values provide the lowest output voltage ripple and are recommended. The output capacitor requires either an X7R or X5R dielectric. Y5V and Z5U dielectric capacitors, aside from their wide variation in capacitance over temperature, become resistive at high frequencies.
At light load currents the converter operates in power-save mode and the output voltage ripple is dependent on the output capacitor value and the PFM peak inductor current. Higher output capacitor values minimize the voltage ripple in PFM Mode and tighten DC output accuracy in PFM mode. In order to achieve specified regulation performance and low-output voltage ripple, the DC-bias characteristic of ceramic capacitors must be considered. The effective capacitance of ceramic capacitors drops with increasing DC-bias voltage. Due to this effect, it is recommended for output voltages above 3.3 V to use at least 1 x 22-µF or 2 x 10-µF ceramic capacitors on the output.
8.2.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
Because of the nature of the buck converter having a pulsating input current, a low ESR input capacitor is required for best input voltage filtering and minimizing the interference with other circuits caused by high input voltage spikes. For most applications, a 10-µF ceramic capacitor is recommended. The voltage rating and DC bias characteristic of ceramic capacitors need to be considered. The input capacitor can be increased without any limit for better input voltage filtering.
For applications powered from high impedance sources, a tantalum polymer capacitor should be used to buffer the input voltage for the TPS62125. Tantalum polymer capacitors provide a constant capacitance vs. DC bias characteristic compared to ceramic capacitors. In this case, a 10-µF ceramic capacitor should be used in parallel to the tantalum polymer capacitor to provide low ESR.
Take care when using only small ceramic input capacitors. When a ceramic capacitor is used at the input and the power is being supplied through long wires, such as from a wall adapter, a load step at the output or VIN step on the input can induce large ringing at the VIN pin. This ringing can couple to the output and be mistaken as loop instability or could even damage the part by exceeding the maximum ratings. In case the power is supplied via a connector e.g. from a wall adapter, a hot-plug event can cause voltage overshoots on the VIN pin exceeding the absolute maximum ratings and can damage the device, too. In this case a tantalum polymer capacitor or overvoltage protection circuit reduces the voltage overshoot, see Figure 45.
Table 4 shows a list of input/output capacitors.
Table 4. List of Capacitors
| CAPACITANCE [µF] | SIZE | CAPACITOR TYPE | USAGE | SUPPLIER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0805 | GRM21B 25V X5R | CIN /COUT | Murata |
| 10 | 0805 | GRM21B 16V X5R | COUT | Murata |
| 22 | 1206 | GRM31CR61 16V X5R | COUT | Murata |
| 22 | B2 (3.5x2.8x1.9) | 20TQC22MYFB | CIN / input protection | Sanyo |
.
8.2.3 Application Curves
 Figure 12. Efficiency vs. Output Current VOUT = 1.8 V
Figure 12. Efficiency vs. Output Current VOUT = 1.8 V
 Figure 14. Efficiency vs. Output current, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 14. Efficiency vs. Output current, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 16. Efficiency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 16. Efficiency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 18. Efficiency vs. Output current, VOUT = 6.8 V
Figure 18. Efficiency vs. Output current, VOUT = 6.8 V
 Figure 20. Efficiency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 8 V
Figure 20. Efficiency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 8 V
 Figure 22. Efficiency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 10 V
Figure 22. Efficiency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 10 V
 Figure 24. Output Voltage vs. Output Current, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 24. Output Voltage vs. Output Current, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 26. Output Voltage vs. Output current, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 26. Output Voltage vs. Output current, VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 28. Output Voltage vs. Output Current, VOUT = 6.7 V
Figure 28. Output Voltage vs. Output Current, VOUT = 6.7 V
 Figure 30. Output Voltage vs. Output Current, VOUT = 8 V
Figure 30. Output Voltage vs. Output Current, VOUT = 8 V
 Figure 32. Output Ripple Voltage vs. Output Current,
Figure 32. Output Ripple Voltage vs. Output Current, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 34. Switch Frequency vs. Output Current, VOUT 5 V
Figure 34. Switch Frequency vs. Output Current, VOUT 5 V
 Figure 36. Power-Save Mode VOUT= 3.3 V, IOUT = 1 mA
Figure 36. Power-Save Mode VOUT= 3.3 V, IOUT = 1 mA
 Figure 38. Load Transient 5 mA to 200 mA, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 38. Load Transient 5 mA to 200 mA, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 40. Load Transient 1 mA to 50 mA, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 40. Load Transient 1 mA to 50 mA, VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 42. AC Load Regulation VOUT = 5 V
Figure 42. AC Load Regulation VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 44. VIN Hotplug Overshoot
Figure 44. VIN Hotplug Overshoot
 Figure 46. Short Circuit and Overcurrent Protection
Figure 46. Short Circuit and Overcurrent Protection
 Figure 48. Operation With EN = VIN, VIN Tracks VOUT
Figure 48. Operation With EN = VIN, VIN Tracks VOUT
 Figure 50. Start-Up 1.8 V VOUT
Figure 50. Start-Up 1.8 V VOUT
 Figure 52. Start-Up 5 V VOUT
Figure 52. Start-Up 5 V VOUT
 Figure 54. VOUT Ramp Up/Down With EN On/Off
Figure 54. VOUT Ramp Up/Down With EN On/Off
 Figure 56. VOUT Ramp Down With Falling VIN, See Schematic Figure 59
Figure 56. VOUT Ramp Down With Falling VIN, See Schematic Figure 59
 Figure 13. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 1.8 V
Figure 13. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 1.8 V
 Figure 15. Efficiency vs. Input voltage, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 15. Efficiency vs. Input voltage, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 17. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 17. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 19. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 6.8 V
Figure 19. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 6.8 V
 Figure 21. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 8 V
Figure 21. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 8 V
 Figure 23. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 10 V
Figure 23. Efficiency vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 10 V
 Figure 25. Output Voltage vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 25. Output Voltage vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 27. Output Voltage vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 27. Output Voltage vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 29. Output voltage vs. Input voltage, VOUT = 6.7 V
Figure 29. Output voltage vs. Input voltage, VOUT = 6.7 V
 Figure 31. Output Voltage vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 8 V
Figure 31. Output Voltage vs. Input Voltage, VOUT = 8 V
 Figure 33. Switch Frequency vs. Output Current,
Figure 33. Switch Frequency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 35. Switch Frequency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 8 V
Figure 35. Switch Frequency vs. Output Current, VOUT = 8 V
 Figure 37. PWM Mode VOUT= 3.3 V, IOUT = 100 mA
Figure 37. PWM Mode VOUT= 3.3 V, IOUT = 100 mA
 Figure 39. AC Load Regulation, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 39. AC Load Regulation, VOUT = 3.3 V
 Figure 41. Load Transient 10 mA to 200 mA, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 41. Load Transient 10 mA to 200 mA, VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 43. Line Transient Response VIN = 9 V to 12 V
Figure 43. Line Transient Response VIN = 9 V to 12 V
 Figure 45. VIN Hotplug Overshoot Reduction With Poscap
Figure 45. VIN Hotplug Overshoot Reduction With Poscap
 Figure 47. Input Supply Voltage Supervisor (SVS),
Figure 47. Input Supply Voltage Supervisor (SVS), VOUT = 5 V
 Figure 49. 0.5 mA Current Source, 20 mA Pulse Load
Figure 49. 0.5 mA Current Source, 20 mA Pulse Load
 Figure 51. Start-Up 3.3 V VOUT
Figure 51. Start-Up 3.3 V VOUT
 Figure 53. Start-Up 8 V VOUT
Figure 53. Start-Up 8 V VOUT
 Figure 55. Output Discharge Using PG Pin, Triggered by EN Comparator
Figure 55. Output Discharge Using PG Pin, Triggered by EN Comparator
8.3 System Examples
8.3.1 TPS62125 5-V Output Voltage Configuration
 Figure 57. TPS62125 5-V Output Voltage Configuration
Figure 57. TPS62125 5-V Output Voltage Configuration
8.3.2 TPS62125 5-V VOUT
 Figure 58. TPS62125 5-V VOUT, Start-up Voltage VIN_Start = 10 V, Stop Voltage VIN_Stop = 6 V, See Figure 47
Figure 58. TPS62125 5-V VOUT, Start-up Voltage VIN_Start = 10 V, Stop Voltage VIN_Stop = 6 V, See Figure 47
8.3.3 TPS62125 Operation From a Storage Capacitor Charged From a 0.5 mA Current Source
 Figure 59. TPS62125 Operation From a Storage Capacitor Charged From a 0.5 mA Current Source,
Figure 59. TPS62125 Operation From a Storage Capacitor Charged From a 0.5 mA Current Source, VOUT = 3.3 V, See Figure 49
8.3.4 5 V to –5 V Inverter Configuration
 Figure 60. 5 V to –5 V Inverter Configuration, See SLVA514
Figure 60. 5 V to –5 V Inverter Configuration, See SLVA514