JAJSCF6G July 2016 – December 2019 TPS2660
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 10.3.2 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 10.3.3 Reverse Input Supply Protection
- 10.3.4 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
- 10.3.5 Overload and Short Circuit Protection
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
-
11Application and Implementation
- 11.1 Application Information
- 11.2
Typical Application
- 11.2.1 Design Requirements
- 11.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 11.2.3 Application Curves
- 11.3 System Examples
- 11.4 Do's and Don'ts
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 15メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
10.3.3 Reverse Input Supply Protection
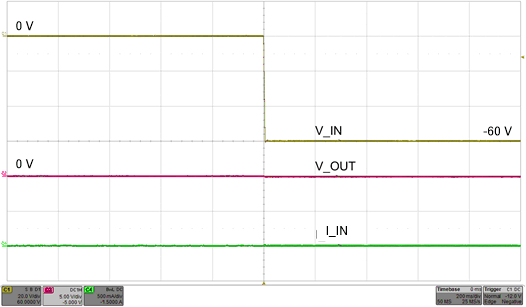
To protect the electronic systems from reverse input supply due to miswiring, often a power component like a schottky diode is added in series with the supply line as shown in Figure 35. These additional discretes result in a lossy and bulky protection solution. The TPS2660x devices feature fully integrated reverse input supply protection and does not need an additional diode. These devices can withstand –60 V reverse voltage without damage. Figure 36 illustrates the reverse input polarity protection functionality.
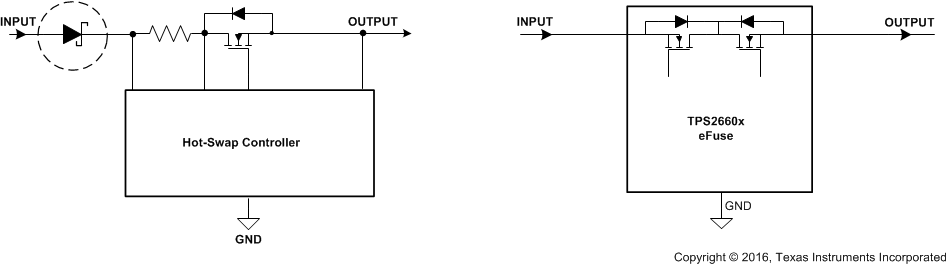 Figure 35. Reverse Input Supply Protection Circuits - Discrete vs TPS2660x
Figure 35. Reverse Input Supply Protection Circuits - Discrete vs TPS2660x