JAJSDH5B December 2008 – July 2017 TPA6132A2
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The TPA6132A2 is a DirectPath™ stereo headphone amplifier that requires no output DC blocking capacitors and is capable of delivering 25m-W/Ch into16-Ω speakers. The device has built-in pop suppression circuitry to completely eliminate pop noise during turn- on and turn-off. The amplifier outputs have short- circuit and thermal-overload protection.
The TPA6132A2 features fully differential inputs to reduce system noise pickup between the audio source and the headphone amplifier. The high power supply noise rejection performance and differential architecture provides increased RF noise immunity.
Differential stereo inputs and built-in resistors set the device gain, reducing external component count. The TPA6132A2 has four gain settings which are controlled with pins G0 and G1. The combination of these pins set the device to –6-dB, 0-dB, 3-dB or 6-dB gain.
The TPA6132A2 operates from a single 2.3-V to 5.5-V supply with 2.1 mA of typical supply current, as it uses a built-in charge pump to generate a negative voltage supply for the headphone amplifiers. Shutdown mode reduces supply current to less than 1 μA
7.2 Functional Block Diagram

7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Headphone Amplifiers
Single-supply headphone amplifiers typically require dc-blocking capacitors to remove dc bias from their output voltage. The top drawing in Figure 23 illustrates this connection. If dc bias is not removed, large dc current will flow through the headphones which wastes power, clip the output signal, and potentially damage the headphones.
These dc-blocking capacitors are often large in value and size. Headphone speakers have a typical resistance between 16 Ω and 32 Ω. This combination creates a high-pass filter with a cutoff frequency as shown in Equation 1, where RL is the load impedance, CO is the dc-block capacitor, and fC is the cutoff frequency.
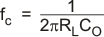
For a given high-pass cutoff frequency and load impedance, the required dc-blocking capacitor is found as:

Reducing fC improves low frequency fidelity and requires a larger dc-blocking capacitor. To achieve a 20 Hz cutoff with 16 Ω headphones, CO must be at least 500 μF. Large capacitor values require large packages, consuming PCB area, increasing height, and increasing cost of assembly. During start-up or shutdown the dc-blocking capacitor has to be charged or discharged. This causes an audible pop on start-up and power-down. Large dc-blocking capacitors also reduce audio output signal fidelity.
Two different headphone amplifier architectures are available to eliminate the need for dc-blocking capacitors. The Capless amplifier architecture is similar provides a reference voltage to the headphone connector shield pin as shown in the middle drawing of Figure 23. The audio output signals are centered around this reference voltage, which is typically half of the supply voltage to allow symmetrical output voltage swing.
When using a Capless amplifier do not connect the headphone jack shield to any ground reference or large currents will result. This makes Capless amplifiers ineffective for plugging non-headphone accessories into the headphone connector. Capless amplifiers are useful only with floating GND headphones.
 Figure 23. Amplifier Applications
Figure 23. Amplifier Applications
The DirectPath™ amplifier architecture operates from a single supply voltage and uses an internal charge pump to generate a negative supply rail for the headphone amplifier. The output voltages are centered around 0 V and are capable of positive and negative voltage swings as shown in the bottom drawing of Figure 23. DirectPath amplifiers require no output dc-blocking capacitors. The headphone connector shield pin connects to ground and will interface will headphones and non-headphone accessories. The TPA6132A2 is a DirectPath amplifier.
7.3.2 Eliminating Turn-on Pop and Power Supply Sequencing
The TPA6132A2 has excellent noise and turn-on / turn-off pop performance. It uses an integrated click-and-pop suppression circuit to allow fast start-up and shutdown without generating any voltage transients at the output pins. Typical start-up time from shutdown is 5 ms.
DirectPath technology keeps the output dc voltage at 0 V even when the amplifier is powered up. The DirectPath technology together with the active pop-and-click suppression circuit eliminates audible transients during start up and shutdown.
Use input coupling capacitors to ensure inaudible turn-on pop. Activate the TPA6132A2 after all audio sources have been activated and their output voltages have settled. On power-down, deactivate the TPA6132A2 before deactivating the audio input source. The EN pin controls device shutdown: Set to 0.6 V or lower to deactivate the TPA6132A2; set to 1.3 V or higher to activate.
7.3.3 RF and Power Supply Noise Immunity
The TPA6132A2 employs a new differential amplifier architecture to achieve high power supply noise rejection and RF noise rejection. RF and power supply noise are common in modern electronics. Although RF frequencies are much higher than the 20 kHz audio band, signal modulation often falls in-band. This, in turn, modulates the supply voltage, allowing a coupling path into the audio amplifier. A common example is the 217 Hz GSM frame-rate buzz often heard from an active speaker when a cell phone is placed nearby during a phone call.
The TPA6132A2 has excellent rejection of power supply and RF noise, preventing audio signal degradation.
7.3.4 Constant Maximum Output Power and Acoustic Shock Prevention
Typically the output power increases with increasing supply voltage on an unregulated headphone amplifier. The TPA6132A2 maintains a constant output power independent of the supply voltage. Thus the design for prevention of acoustic shock (hearing damage due to exposure to a loud sound) is simplified since the output power will remain constant, independent of the supply voltage. This feature allows maximizing the audio signal at the lowest supply voltage.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Gain Control
The TPA6132A2 has four gain settings which are controlled with pins G0 and G1. Table 1 gives an overview of the gain function.
| G0 VOLTAGE | G1 VOLTAGE | AMPLIFIER GAIN |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 0.5 V | ≤ 0.5 V | –6 dB |
| ≥ 1.3 V | ≤ 0.5 V | 0 dB |
| ≤ 0.5 V | ≥ 1.3 V | 3 dB |
| ≥ 1.3 V | ≥ 1.3 V | 6 dB |
Table 1. Windows Vista™ Premium Mobile Mode Specifications
| Device Type | Requirement | Windows Premium Mobile Vista Specifications | TPA6132A2 Typical Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Speaker Line Jack (RL = 10 kΩ, FS = 0.707 Vrms) | THD+N | ≤ –65 dB FS [20 Hz, 20 kHz] | –75 dB FS[20 Hz, 20 kHz] |
| Dynamic Range with Signal Present | ≤ –80 dB FS A-Weight | –100 dB FS A-Weight | |
| Line Output Crosstalk | ≤ –60 dB [20 Hz, 20 kHz] | –90 dB [20 Hz, 20 kHz] | |
| Analog Headphone Out Jack (RL = 32Ω, FS = 0.300 Vrms) | THD+N | ≤ –45 dB FS [20 Hz, 20 kHz] | –65 dB FS [20 Hz, 20 kHz] |
| Dynamic Range with Signal Present | ≤ –80 dB FS A-Weight | –94 dB FS A-Weight | |
| Headphone Output Crosstalk | ≤ –60 dB [20 Hz, 20 kHz] | –90 dB [20 Hz, 20 kHz] |