JAJSE40A October 2017 – February 2018 UCC28780
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Detailed Pin Description
- 7.3.1 BUR Pin (Programmable Burst Mode)
- 7.3.2 FB Pin (Feedback Pin)
- 7.3.3 VDD Pin (Device Bias Supply)
- 7.3.4 REF Pin (Internal 5-V Bias)
- 7.3.5 HVG and SWS Pins
- 7.3.6 RTZ Pin (Sets Delay for Transition Time to Zero)
- 7.3.7 RDM Pin (Sets Synthesized Demagnetization Time for ZVS Tuning)
- 7.3.8 RUN Pin (Driver Enable Pin)
- 7.3.9 SET Pin
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Adaptive ZVS Control with Auto-Tuning
- 7.4.2 Dead-Time Optimization
- 7.4.3 Control Law across Entire Load Range
- 7.4.4 Adaptive Amplitude Modulation (AAM)
- 7.4.5 Adaptive Burst Mode (ABM)
- 7.4.6 Low Power Mode (LPM)
- 7.4.7 Standby Power Mode (SBP)
- 7.4.8 Startup Sequence
- 7.4.9 Survival Mode of VDD
- 7.4.10 System Fault Protections
- 7.4.11 Pin Open/Short Protections
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application Circuit
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
8.2.2.2.3 Primary Turns (NP)
The turn number on the primary side of the transformer (NP) is determined by two design considerations:
- The maximum flux density (BMAX) must be kept below the saturation limit (BSAT) of the magnetic core under the highest peak magnetizing current (IM+(MAX)) condition, a given cross-section area (AE) of the core geometry, and highest core temperature. When IFB = 0 A, such as VO soft-start or step-up load transient, the peak magnetizing current reaches IM+(MAX), since VCST = VCST(MAX) in those conditions. IM+(MAX) can be calculated based on the output power triggering an OPP fault (PO(OPP)) with VCST = VCST(OPP1) at VBULK(MIN). After NP is chosen, NS can be calculated through NPS.
- The AC flux density (ΔB) affects the core loss of a transformer. For a transition-mode active clamp flyback, the core loss at high line is usually highest, since the switching frequency is highest and duty cycle is smallest for a given load condition. The following equation is the ΔB calculation including the contribution of negative magnetizing current (IM-), used to put into the Steinmetz equation for more accurate core loss estimation. For VBULK ≥ NPS(VO+VF), IM- is calculated with VBULK divided by the characteristic impedance of LM and the lumped time-related switch-node capacitance (CSW). The expression of fSW is derived based on the triangular approximation of the magnetizing current, which also considers IM- effect over wide AC line condition.
Equation 24. 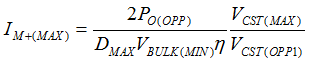
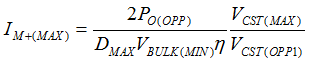
Equation 25. 

Equation 26. 

Equation 27. 

Equation 28. 

Equation 29. 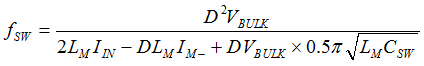
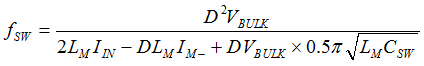
Equation 30. 

Equation 31. 
