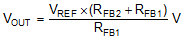JAJSE93B March 2016 – November 2017 LM5161
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Control Circuit
- 7.3.2 VCC Regulator
- 7.3.3 Regulation Comparator
- 7.3.4 Soft-Start
- 7.3.5 Error Transconductance (GM) Amplifier
- 7.3.6 On-Time Generator
- 7.3.7 Current Limit
- 7.3.8 N-Channel Buck Switch and Driver
- 7.3.9 Synchronous Rectifier
- 7.3.10 Enable / Undervoltage Lockout (EN/UVLO)
- 7.3.11 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
LM5161 Synchronous Buck (15-V to 95-V Input, 12-V Output, 1-A Load)
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Resistor Divider Selection
- 8.2.1.2.3 Frequency Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Series Ripple Resistor - RESR (FPWM = 1)
- 8.2.1.2.7 VCC and Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.10 EN/UVLO Resistor Selection
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 LM5161 Isolated Fly-Buck (36-V to 72-V Input, 12-V, 12-W Isolated Output)
- 8.2.3 Ripple Configuration
- 8.2.1
LM5161 Synchronous Buck (15-V to 95-V Input, 12-V Output, 1-A Load)
- 8.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7.3.1 Control Circuit
The LM5161 step-down switching regulator employs a control principle based on a comparator and a one-shot ON-timer, with the output voltage feedback (FB) compared to the voltage at the Soft-Start (SS) pin (VSS). If the FB voltage is below VSS, the internal buck switch is turned on for a time period determined by the input voltage and one-shot programming resistor (RON). Following the ON-time, the buck switch must remain off for the minimum OFF-time forced by the minimum OFF-time one-shot. The buck switch remains off until the FB voltage falls below VSS again, when it turns on for another ON-time one-shot period.
During a rapid start-up or when the load current increases suddenly, the regulator operates with minimum off-time per cycle. When regulating the output in steady state operation, the off-time automatically adjusts to produce the SW pin duty cycle required for output voltage regulation.
When in regulation, the LM5161 operates in continuous conduction mode at heavy load currents. If the FPWM pin is connected to ground or left floating, the regulator operates in discontinuous conduction mode at light load with the synchronous rectifier FET emulating a diode. With sufficient load, the LM5161 operates in continuous conduction mode with the inductor current never reaching zero during the OFF-time of the high-side FET. In this mode the operating frequency remains relatively constant with load and line variations. The minimum load current for continuous conduction mode is one-half the inductor’s ripple current amplitude. The operating frequency (in Hz) is programmed by the RON pin resistor and can be calculated from Equation 1 with RON expressed in ohms.

In discontinuous conduction mode, current through the inductor ramps up from zero to a peak value during the ON-time, then ramps back to zero before the end of the OFF-time. The next ON-time period starts when the voltage at FB falls below VSS. When the inductor current is zero during the high side FET off-time, the load current is supplied by the output capacitor. In this mode, the operating switching frequency is lower than the continuous conduction mode switching frequency and the frequency varies with load. The discontinuous conduction mode maintains higher conversion efficiency at light loads because the switching losses decrease with the decrease in load and frequency.
The output voltage is set by two external resistors ( RFB1, RFB2). The regulated output voltage is calculated from Equation 2, where VREF = 2 V (typ) is the feedback reference voltage.