JAJSE93B March 2016 – November 2017 LM5161
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Control Circuit
- 7.3.2 VCC Regulator
- 7.3.3 Regulation Comparator
- 7.3.4 Soft-Start
- 7.3.5 Error Transconductance (GM) Amplifier
- 7.3.6 On-Time Generator
- 7.3.7 Current Limit
- 7.3.8 N-Channel Buck Switch and Driver
- 7.3.9 Synchronous Rectifier
- 7.3.10 Enable / Undervoltage Lockout (EN/UVLO)
- 7.3.11 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
LM5161 Synchronous Buck (15-V to 95-V Input, 12-V Output, 1-A Load)
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Resistor Divider Selection
- 8.2.1.2.3 Frequency Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Series Ripple Resistor - RESR (FPWM = 1)
- 8.2.1.2.7 VCC and Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.10 EN/UVLO Resistor Selection
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 LM5161 Isolated Fly-Buck (36-V to 72-V Input, 12-V, 12-W Isolated Output)
- 8.2.3 Ripple Configuration
- 8.2.1
LM5161 Synchronous Buck (15-V to 95-V Input, 12-V Output, 1-A Load)
- 8.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
8.2.1.2.3 Frequency Selection
The duty cycle required to maintain output regulation at the minimum input voltage restricts the maximum switching frequency of LM5161. The maximum value of the minimum forced OFF-time TOFF,min (max), limits the duty cycle and therefore the switching frequency. The maximum frequency that avoids output dropout at minimum input voltage can be calculated from Equation 7.

For this design example, the maximum frequency based on the minimum OFF-time limitation for TOFF,min(typ) = 170 ns is calculated to be FSW,max(@VIN,min) = 1.2 MHz. This value is above 1 MHz, the maximum possible operating frequency of the LM5161. Therefore, the minimum OFF-time parameter restricts the maximum achievable switching frequency calculation in this application.
At the maximum input voltage, the maximum switching frequency of LM5161 is restricted by the minimum ON-time, TON,min which limits the minimum duty cycle of the converter. The maximum frequency at maximum input voltage can be calculated using Equation 8.
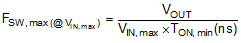
Using Equation 8 and TON,min (typ) = 150 ns, the maximum achievable switching frequency is FSW,max(@VIN,min)= 1000 kHz. Taking this value as the maximum possible operational switching frequency over the input voltage range in this application, a nominal switching frequency of FSW = 300 kHz is chosen for this design.
The value of the resistor, RON sets the nominal switching frequency based on Equation 9.

For this particular application with FSW = 300 kHz, RON calculates to be 396 kΩ . Selecting a standard value for R1 (RON) = 402 kΩ (±1%) results in a nominal frequency of 296 kHz. The resistor value may need to adjusted further in order to achieve the required switching frequency as the switching frequency in Constant ON-Time converters varies slightly(±10%) with input voltage and/or output current. Operation at a lower nominal switching frequency will result in higher efficiency but increase in the inductor and capacitor values leading to a larger total solution size.