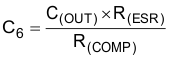JAJSFQ6E March 2014 – July 2018 TPS92601-Q1 , TPS92602-Q1
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope-Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Boost-Current Limit
- 7.3.4 Oscillator and PLL
- 7.3.5 Control Loop Compensation
- 7.3.6 LED Open-Circuit Detection
- 7.3.7 Output Short-Circuit and Overcurrent Detection
- 7.3.8 Measuring LED Current During a Non-Failure Condition
- 7.3.9 LED Dimming Options
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Boost Regulator With Separate or Paralleled Channels
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.2 Maximum Output-Current Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Overvoltage-Protection Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.4 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.1.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.1.2.7 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.1.2.10 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.1.2.11 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2
Boost-to-Battery Regulator
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2.2 Maximum Output-Current Set Point
- 8.2.2.2.3 Output Overvoltage-Protection Set Point
- 8.2.2.2.4 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.6 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.2.2.7 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.9 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.2.2.10 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.2.2.11 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.2.3 TPS92602y-Q1 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Boost Regulator With Separate or Paralleled Channels
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
8.2.2.2.11 Loop Compensation
The COMP pin on the TPS92602y-Q1 device is for external compensation, allowing optimization of the loop response for each application. The COMP pin is the output of the internal transconductance amplifier. The external resistor R7, along with ceramic capacitors C5 and C6 (see Figure 22 ), connect to the COMP pin to provide poles and zero. The poles and zero, along with the inherent pole and zero in a peak-current-mode control boost converter, determine the closed-loop frequency response. This is important to converter stability and transient response. The first step is to calculate the pole and the right half-plane zero of the peak-current-mode boost converter by Equation 73 and Equation 74. To make the loop stable, the loop must have sufficient phase margin at the crossover frequency where the loop gain is 1. To avoid the effect of the right half-plane zero on the loop stability, choose the crossover frequency less than 1/5 of f(ZRHP).
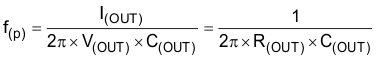
where
- C(OUT) is the bulk output capacitance previously calculated
- R(OUT) is the effective output impedance
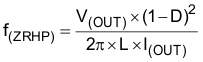
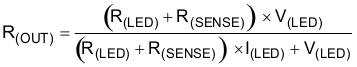
where
The loop compensation consists of a series resistor and capacitor (R(COMP) and C(COMP)) from COMP to SGND. R(COMP) sets the crossover frequency and C(COMP) sets the zero frequency of the integrator. For optimum performance, use the following equations:
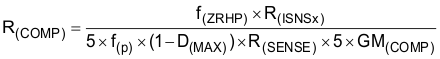
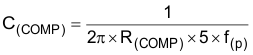
where
An output capacitor that is an electrolytic capacitor which has large ESR requires a capacitor to cancel the zero of the output capacitor. Equation 79 calculates the value of this capacitor.