SCDA049 April 2024 TMUX4827
2.2 Positive Beyond the Supply
Positive Beyond the Supply can be defined as the capability of a device to pass a positive voltage signal greater than the power supply voltage. An application using this feature is commonly seen in interface, where an engineer is connecting an offboard interface operating at 5V to an onboard interface operating at 3V. The interfacing device needs to be capable of being powered by a lower voltage supply, than the voltage it is passing. In this case, the Positive Beyond the Supply can be used.
Table 2-2 highlights the beyond the supply capability of the TMUX1574. Signal path I/O is capable to pass a signal up to 2 x the supply
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Supply voltage | 1.5 | 5.5 | V |
| VS or VD | Signal path input or output voltage (source or drain pin). VDD ≥ 1.5V | 0 | VDD x 2 | V |
Figure 2-2 shows an example of an application for the TMUX1574 where it is used to switch between two interface boards with different voltage levels.
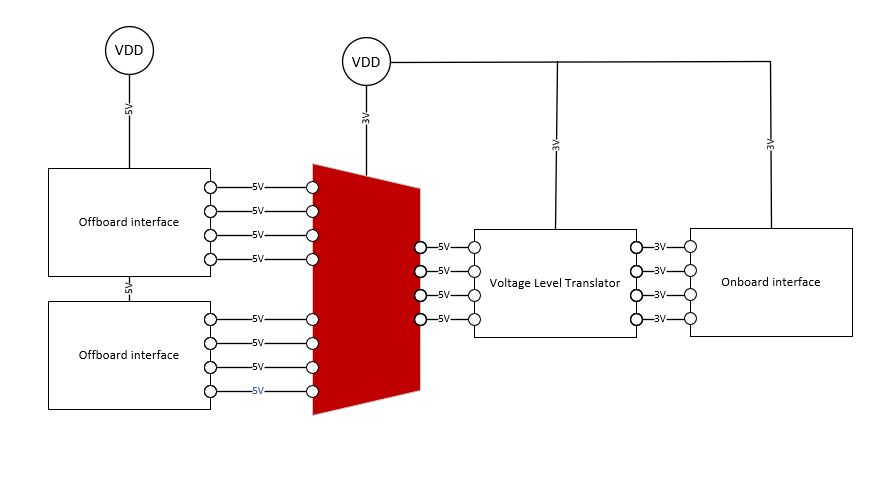 Figure 2-2 TMUX1574 a 2:1 4-Channel Multiplexer Powered by a 3V Supply, Passing Four 5V Input Signals to a Voltage Translator Then to the Onboard Interface.
Figure 2-2 TMUX1574 a 2:1 4-Channel Multiplexer Powered by a 3V Supply, Passing Four 5V Input Signals to a Voltage Translator Then to the Onboard Interface.Multiplexers with the capability of Beyond the Supply with positive signal operation also have powered-off-protection. The protection makes sure the device maintains high impedance performance while the device is not powered, while also preventing the device from back powering. Which prevents a device from providing power to downstream components in the system.