SLAA732A February 2017 – April 2021 PGA460 , PGA460-Q1
4.4.2 Tuning Capacitor
When using the transformer driven mode, the equivalent circuit of the transformer introduces additional parasitics. The parasitic characteristic with the greatest performance-impact is the secondary-side leakage inductance (LSEC) of the transformer. The transducer resonates most efficiently at a single frequency. For instance, a 40-kHz transducer cannot be driven at 20, 30, or 50 kHZ; any drift from the resonant frequency yields a loss in SPL. When the series inductance is introduced to the transducer, the driving frequency, equivalent BVD model of the transducer, and effective versus expected receiving frequency will be at a mismatch. To match the secondary inductance of the transformer to the resonant frequency of the transducer, a tuning capacitor (CTUNE) is added in parallel to the transducer (see Figure 4-4).
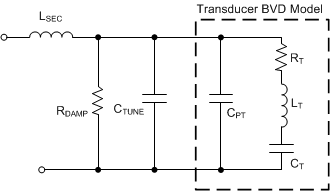 Figure 4-4 Transducer and Transformer Electrical Model With Tuning Components
Figure 4-4 Transducer and Transformer Electrical Model With Tuning ComponentsUse Equation 2 to calculate the value of CTUNE.
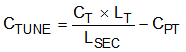
If the tuning capacitor is too large, the attenuation factors increases significantly. Typical values for tuning capacitance ranges from 100 pF to 2000 pF. When driving the transducer in half-bridge configuration and full-bridge, configuration resonance is primarily dependent on the transducer and therefore a tuning capacitor is not required.