SLAA936A September 2020 – March 2021 TAS2563
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2Quick Tuning Procedure
- 2.1 Initialize Tuning
- 2.2 Flatten Protection
- 2.3 Frequency Response Matching
- 2.4 Microphone Setup
- 2.5 Record Reference Device Response
- 2.6 Set Input Gain
- 2.7 Equalizer
- 2.8 Dynamic Range Compression (DRC)
- 2.9 Smart Amp Protection
- 2.10 Speaker Protection Verification
- 2.11 System Signal Chain
- 2.12 Tuning Elements
- 2.13 PDM MIC
- 3Related Documentation
- 4Revision History
2.12.1 Input Gain
Located in the upper-right corner of the Audio Processing page, the input gain is a simple digital gain on the input signal. The ideal setting can vary widely between speakers and is usually subject to user preference. For mobile phone and tablet speakers, the input gain is typically set between +2 dB to +12 dB. Setting the input gain too high can result in a loud but very compressed or distorted sound at the output when the input signal is large. Choosing an overly aggressive setting with this gain to achieve a high SPL output is common, but this has negative consequences on sound quality. Toggling the  symbol also allows the user to quickly mute or unmute the input signal.
symbol also allows the user to quickly mute or unmute the input signal.
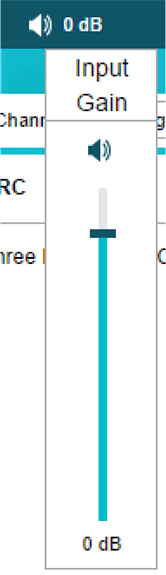 Figure 2-14 Input Gain Control
Figure 2-14 Input Gain Control