-
Test Report for Cascading Analog Multiplexers
Test Report for Cascading Analog Multiplexers
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1 Introduction
Analog multiplexers are used in electronic systems to control a specific transmission path for an analog signal. These devices are used in a wide variety of applications, such as USB3, PCIe and HDMI system.
There can possible be a situation where the desired number of input channels are not available in multiplexers of a particular system. Cascading refers to a process where large multiplexers can be designed and implemented using smaller multiplexers. For instance, 8:1 Multiplexers can be designed using three 4:1 Multiplexers and similarly it can be designed using seven 2:1 multiplexer as shown in the below Figure 1-1.
 Figure 1-1 Casacding of Multiplexers
Figure 1-1 Casacding of Multiplexers2 Major Parameters of Multiplexers
2.1 Ron resistance
One of the major parameters of analog multiplexers is On resistance. On-resistance (RON) is the resistance of the multiplexers path between the drain and source terminal when the multiplexer is closed. Ideally, RON needs to be kept as low as possible in order to keep the signal loss and propagation delays to be small. The On resistance value of the multiplexer translates into multiple performance characteristics of a signal multiplexer. For example, RON impacts the multiplexer’s power consumption, propagation delay, and the bandwidth of the signals that can pass through the multiplexer without distortion. In most cases, lower RON values are preferred in order to achieve optimal design.
2.2 Bandwidth
An analog multiplexer also has many ac specifications, such as bandwidth and insertion loss. Bandwidth is an important parameter to characterize the performance of many electrical systems. The term bandwidth refers to the pass band width of a filter, and in the case of a low-pass filter, the bandwidth is equal to the –3 dB frequency and indicates the upper limit of the frequency of signals passing through the multiplexers. Understanding the bandwidth capability of a signal multiplexer helps to determine if a multiplexer meets the performance requirements of the target application. A good rule of thumb is BW should be greater than or equal to 1.5 or 2 times Nyquist frequency.
2.3 Insertion Loss and Return Loss
Other important AC parameters are insertion loss and return loss. At high frequency, signal loss produces signal attenuation and distortion; the signal will be attenuated by conductor resistance and leakage in the material. The design of high-speed circuits therefore requires a knowledge of not only BW and Ron resistor, but also the dielectric constant and loss parameter.
Insertion loss and return loss are widely used terms in the field of microwave technologies. They play an important role in designing and development of high-speed devices such as filters, multiplexers. Insertion loss and return loss are what is used in cascading multiplexer’s analysis.
So what are Insertion loss and return loss? Technically, when some system or circuit is inserted between a source and a load, some of the signal power from the source is dissipated through the circuit components due to their resistive nature that results in losses. Therefore, not all the transmitted signal power is transferred to the load. The losses between the incident power and the transmitted power is called insertion Loss. Likewise, the difference between the incident power and the reflected power is called return loss.
 Figure 2-1 Two Ports Network.
Figure 2-1 Two Ports Network. Insertion loss and return loss are linked with the scattering perimeters when the source and the load of the system is matched to the same reference impedance (say 50 Ohms). S parameters are the modern way of analyzing N-port networks. It is very helpful in optimizing the circuit to its best. It is capable of determining even smaller return loss and insertion loss in the form of s-parameters namely S11, S22, S12, S21:
-
S12 = forward transmission coefficient
-
S21 = reverse transmission coefficient
-
S11 = input reflection coefficient
-
S22 = output reflection coefficient
3 Cascading Multiplexers Testing
3.1 Simulation with S-parameters Model for Cascading Multiplexers
Now let’s look at an example of simulation with S-parameters model for two cascading TMUXHS4212 multiplexers. S-parameters are easily imported and used for circuit simulations in EDA tools like ADS. S-parameters are the shared language between simulation and measurement. Figure 3-1 ADS Simulation of Cascading
Multiplexers.
Figure 3-1 ADS Simulation of Cascading
Multiplexers.  Figure 3-2 Insertion Loss of
TMUXHS4212.
Figure 3-2 Insertion Loss of
TMUXHS4212. Figure 3-3 is the eye diagram of the 10-Gbps input signal, Figure 3-4 is the output eye diagram from the first multiplexer, Figure 3-5 is the output eye diagram from second multiplexer. From Figure 3-5, we can see waveform is degraded after two cascading multiplexers.
 Figure 3-3 Input Signal Eye Diargam
at 10Gbps.
Figure 3-3 Input Signal Eye Diargam
at 10Gbps.  Figure 3-4 Eye Diagram after 1st
Multiplexer.
Figure 3-4 Eye Diagram after 1st
Multiplexer.  Figure 3-5 Eye Diagram after 2nd
Multiplexer.
Figure 3-5 Eye Diagram after 2nd
Multiplexer. 3.2 Testing Results with Scope
Last, let’s look at the real scope measurement and see how they correlate with the simulation result. Figure 3-6 is the waveform of the 10Gbps input signal, Figure 3-7 is the output waveform from the first multiplexer, Figure 3-8 is the output waveform form the second multiplexer. From Figure 3-7 and Figure 3-8, real measurement is correlated well with simulation result.
 Figure 3-6 Input Waveform of 10Gbps Signal.
Figure 3-6 Input Waveform of 10Gbps Signal.  Figure 3-7 Output Waveform after 1st Multiplexer.
Figure 3-7 Output Waveform after 1st Multiplexer. 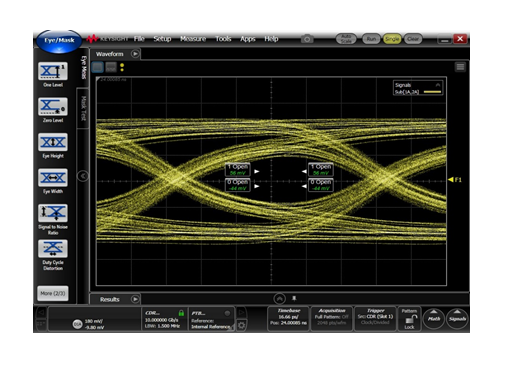 Figure 3-8 Output Waveform after 2nd Multiplexer.
Figure 3-8 Output Waveform after 2nd Multiplexer.