SLAAEM1 June 2024 MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1105
3.5.2 Control Method
In this solution, a dual-loop control strategy was adopted for speed and current as shown in Figure 3-7.
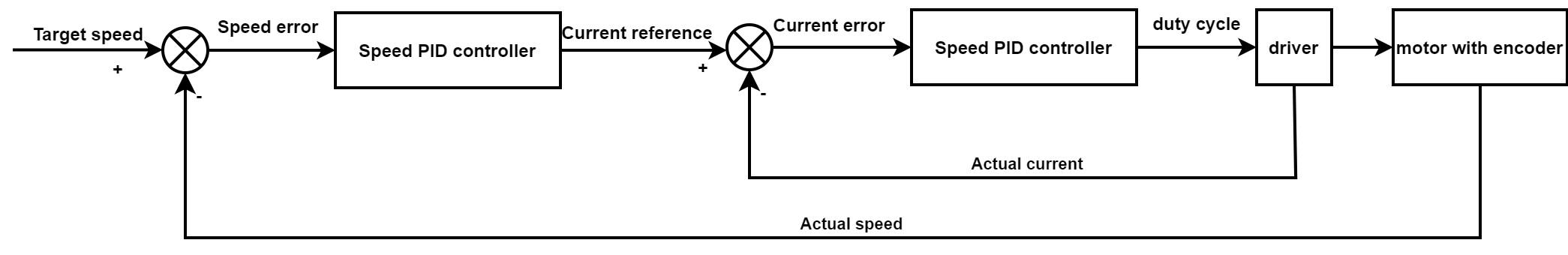 Figure 3-7 Control Block Diagram
Figure 3-7 Control Block DiagramIn the speed control loop, a target speed is settled and the actual speed is measured. The difference between the target speed and the actual speed is then used to generate an error signal. This error signal is processed by a control algorithm to produce a control command, which adjusts the motor's input voltage or PWM signal to regulate the motor speed.
In the current control loop, the motor current is monitored and adjusted to ensure that sufficient torque is provided under any load condition. The current control loop can also provide overload and short-circuit protection for the motor.
By employing this speed outer loop and current inner loop control method, high-precision and high-performance control of brushed DC motors can be achieved. Consequently, this approach is widely used in applications requiring precise and reliable control, such as industrial automation, robotics, and various motion control applications.