SLLA454A April 2019 – August 2024 TUSB211A , TUSB212 , TUSB213 , TUSB214 , TUSB215 , TUSB216 , TUSB217A
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 USB 2.0 Signal Integrity Challenges
- 3 Choosing to Use a USB 2.0 Redriver
- 4 Redrivers in Automotive
- 5 Redrivers in Enterprise
- 6 Redrivers in Medical
- 7 Re-drivers in Personal Electronics
- 8 Re-drivers in other applications
- 9 Facilitating Easy Use of TUSB211A Using the TUSB211PICO-EVM
- 10Summary
- 11References
- 12Revision History
4 Redrivers in Automotive
Many automotive applications require long cable reach for smart phone data communication and charging between head unit or media hub ports. USB2.0 does not guarantee compliance beyond 1.5m cable length, in such applications we need to add re-drivers to preserve the signal integrity.
The applications where USB2.0 re-drivers can be used in automotive are:
- Firmware update using USB2.0
- Connecting to external music to the infotainment unit
AUTOMOTIVE USB CHARGE: (A to C point)
- The signal transmission of D+ and D- from the SOC is connected to a mobile phone through a USB interface. This can enable applications like car-play on the mobile phone.
DIGITAL COCKPIT PROCESSING UNIT: (A to B point)
- USB2.0 re-driver needed as the USB rear seat plug (charger) is about 1.5m distance from head-unit so they needed re-driver to make sure signal integrity and pass compliance, else eye-diagram test can fail.
Systems sending USB2 data must pass a near-end USB 2.0 compliance eye diagram at the connector located at the far end of the cable, that is The Remote Port.
System fails USB 2.0 compliance when in channel is loss is high, for example, during high temperatures or when using long cables. USB2.0 does not guarantee compliance beyond 1.5m, hence re-driver is needed. User’s personal device cannot communicate with vehicle head unit.
The TUSB21x-Q1 can be implemented to enable support of up to a five-meter cable to pass USB 2.0 near-endeye testing, CarPlay, and Android auto compliance.
Different Automotive Applications of USB2.0 shows a typical car where we see the various points where signal transmission occurs. From A to C for automotive USB charge, and from A to B for a digital cockpit processing unit. The long distance between the various points warrants the use of a USB2.0 re-driver.
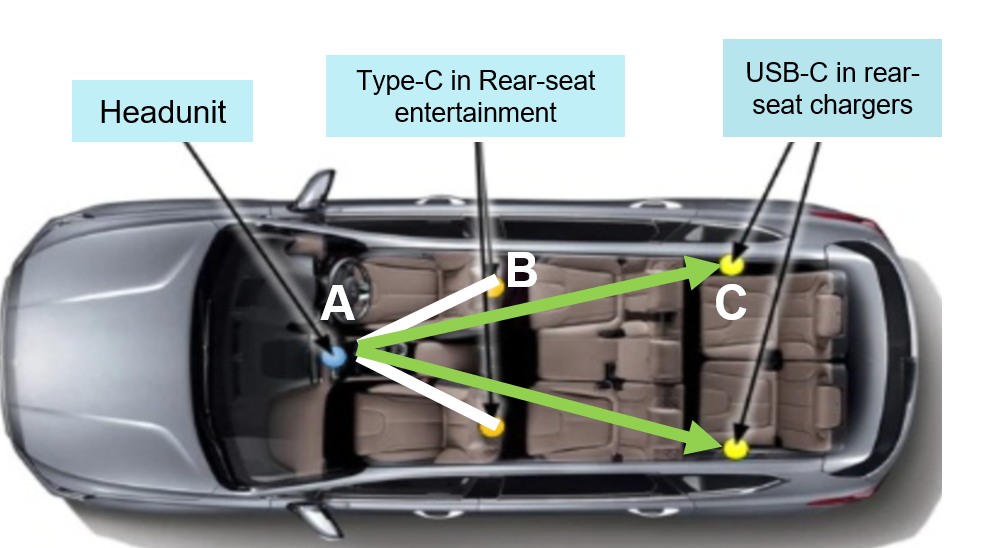 Figure 4-1 Different
Automotive Applications of USB2.0
Figure 4-1 Different
Automotive Applications of USB2.0Figure 4-2 shows a passing near-end eye diagram using the TUSB217 with a 5m cable. The TUSB217 is also capable of passing the near-end eye diagram across various different cable lengths up to 5m with a single configuration (with typical 28AWG USB cables).
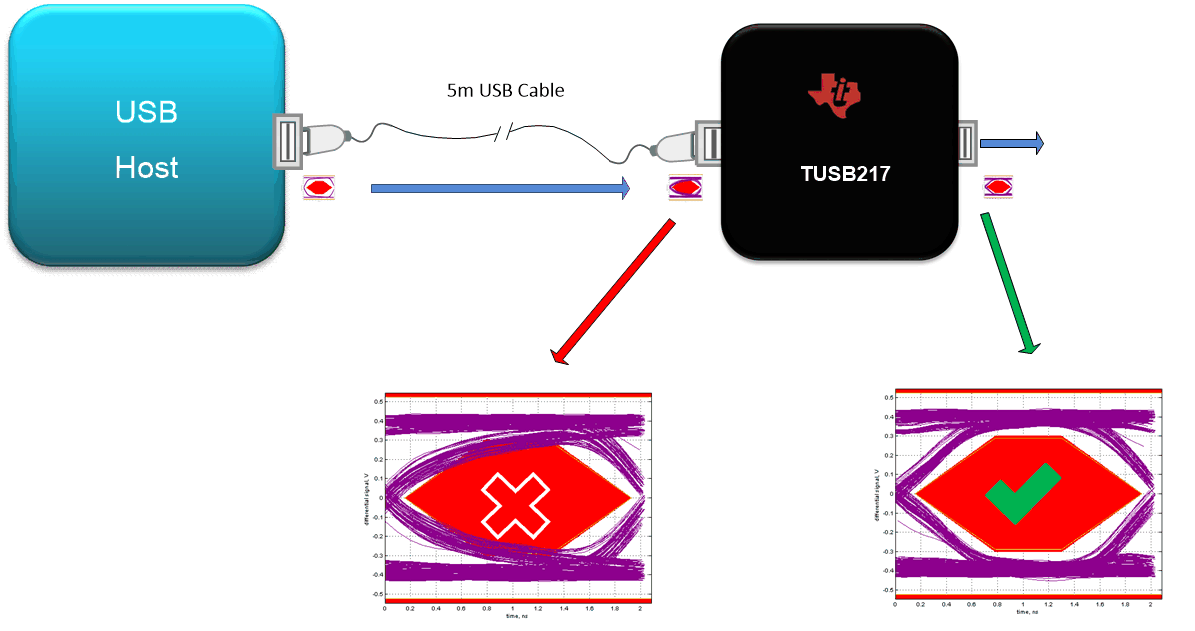 Figure 4-2 TUSB217 Signal Recovery
Figure 4-2 TUSB217 Signal Recovery