SLUUCJ2C july 2021 – august 2023 UCC14240-Q1 , UCC14241-Q1 , UCC15240-Q1 , UCC15241-Q1
5.9.1 Output UVLO
Figure 5-21 shows the effect of mismatched bias loading at startup where the load on VEE-COM is greater than the load on VDD-COM. A fixed resistive load of 340-Ω (73 mW) is applied to VEE-COM while VDD-COM is left unloaded. VDD-VEE is regulating at 20-V, as expected but VDD-COM is measuring 17.8 V (target value is 15 V) and VEE-COM is measuring 2.2 V (target value is 5 V). Since VDD-COM is not directly monitored by feedback, over-voltage protection (OVP) is not triggered even though the measured voltage is 18% above the target value. Also, since VEE-COM is overloaded, the regulated voltage is only reaching 2.2 V which is 56% below the targeted set value of 5-V, therefore, VEE-COM UVLO is triggered. RLIM is internally switched to VDD (20 V) and is attempting to overcome the imbalance by sourcing current into the capacitor midpoint, COM, connection. FBVDD and FBVEE must both be between 90%-110% of their target set value before 16-ms, which is thw maximum allowable soft-start time as defined by the internal watch-dog-timer. The 16-ms, watch-dog-timer UVLO fault protection is enabled to protect the UCC14240-Q1 from output short-circuit or soft overload conditions. Once the UVLO fault is triggered, RLIM is internally switched to VEE, helping to discharge the outputs. When activated, as illustrated in Figure 5-21, the outputs are latched off into a protected sate. EN or VIN must be recycled to clear the UVLO fault and attempt to restart the module.
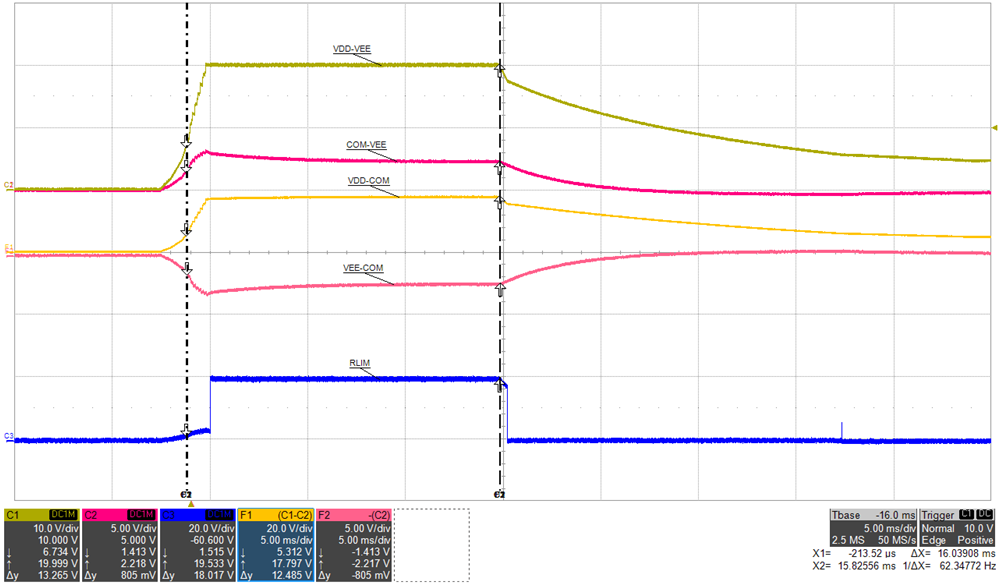
| top: VDD-VEE, 10 V/div, | mid3: VEE-COM, 5 V/div, |
| mid1: COM-VEE, 5 V/div, | bot: RLIM, 20 V/div, |
| mid2: VDD-COM, 20 V/div, | time = 5 ms/div |