SLUUCV7 December 2023 TPS1213-Q1
3.1.4 Inrush Current Limit Test
Use the following instructions to measure the inrush current during startup in low power mode.
- Populate R3 = 10 Ω and C1 = 15 nF on the EVM.
- Connect 220 µF at the output terminals of the EVM.
- Apply 12 V at the input of the EVM at no-load.
- Enable the EN/UVLO to HIGH.
- Observe the waveform at VOUT (TP3) with an oscilloscope to measure the slew rate and risetime with a given input voltage of 12 V.
- Repeat the same test with 0.5A load at the output to see the state transition from LPM to active mode.
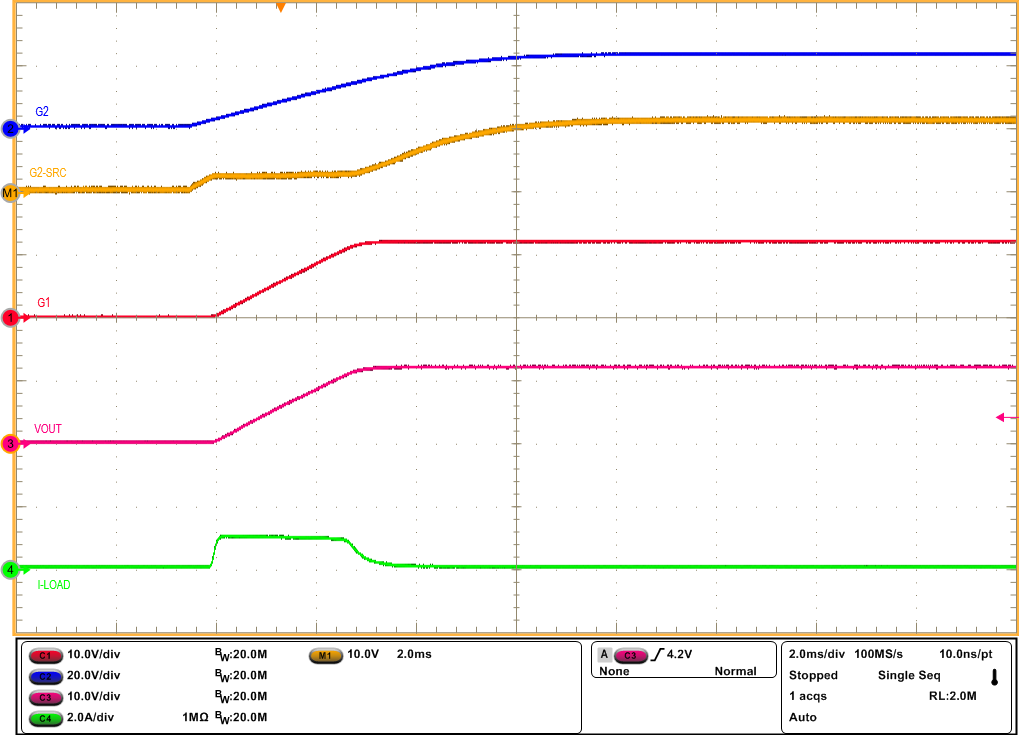 Figure 3-8 Inrush Current Profile with 220 µF at the
Output (LPMb = Low)
Figure 3-8 Inrush Current Profile with 220 µF at the
Output (LPMb = Low)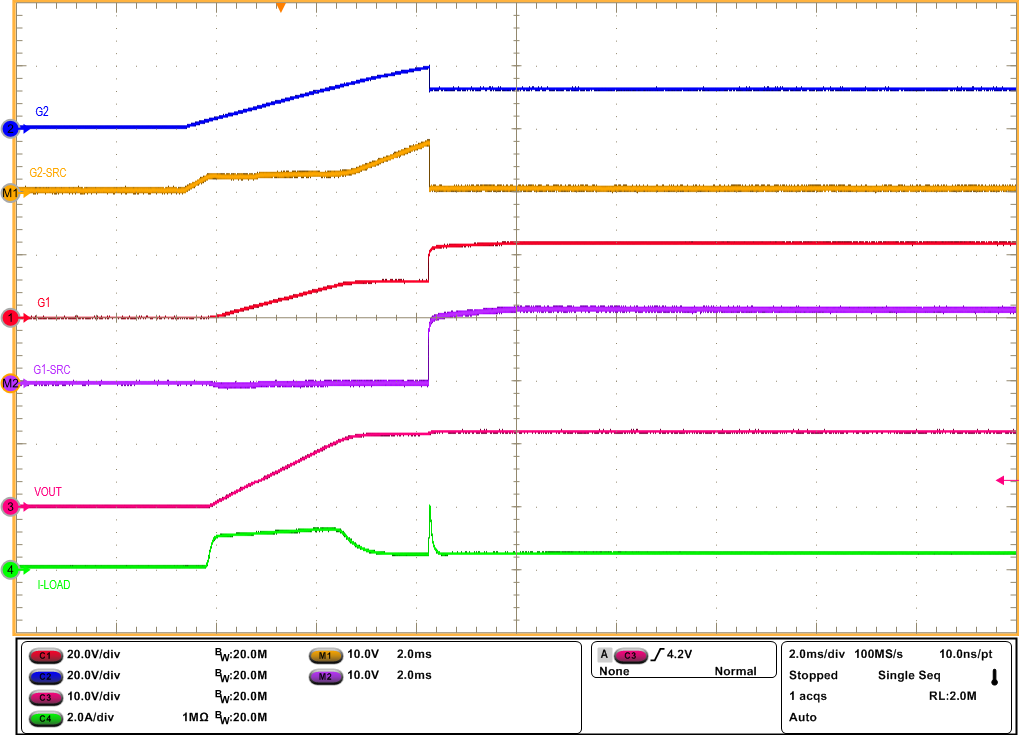 Figure 3-9 Inrush Current Profile with 220 µF at the
Output and 0.5A Load (LPMb = Low)
Figure 3-9 Inrush Current Profile with 220 µF at the
Output and 0.5A Load (LPMb = Low)