SLVAF40 July 2021 TPS2661
2 Discrete Solution With PTC
Figure 2-1 shows a typical discrete solution based on a positive temperature coefficient device (PTC) used to protect the current input of an analog input module.
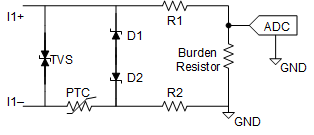
Figure 2-1 Discrete Solution With PTC
The downsides of a typical solution are:
- System size due to the BOM in terms of size and count of the components (see Figure 2-1)
- Constraint of high-power dissipation of the burden resistor in overcurrent condition reduces the choice of selection
- Temperature dependency of the front end (mainly from PTC)
- Higher voltage drop at the analog input limits the length of the current loop
- Lack of status (overcurrent versus normal operation)