SLVS847A November 2008 – December 2016 TPS54917
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.2 Slow Start or Enable (SS/ENA)
- 8.3.3 VBIAS Regulator (VBIAS)
- 8.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.5 Oscillator and PWM Ramp
- 8.3.6 Error Amplifier
- 8.3.7 PWM Control
- 8.3.8 Dead-Time Control and MOSFET Drivers
- 8.3.9 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.11 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Figure 20 shows a generalized PCB layout guide for the TPS54917. The VIN pins must be connected together on the printed-circuit board (PCB) and bypassed with a low-ESR ceramic bypass capacitors. Take care to minimize the loop area formed by the bypass capacitor connections, the VIN pins, and the TPS54917 ground pins. The minimum recommended bypass capacitance is 10-µF ceramic with a X5R or X7R dielectric and the optimum placement is closest to the VIN pins and the PGND pins.
The TPS54917 has two internal grounds (analog and power). The analog ground ties to all of the noise-sensitive signals, while the power ground ties to the noisier power signals. Noise injected between the two grounds can degrade the performance of the TPS54917, particularly at higher output currents. Ground noise on an analog ground plane can also cause problems with some of the control and bias signals. For these reasons, separate analog and power ground traces are recommended. There must be an area of ground on the top layer directly under the IC, with an exposed area for connection to the PowerPAD. Use vias to connect this ground area to any internal ground planes. Use additional vias at the ground side of the input and output filter capacitors as well. The AGND and PGND pins must be tied to the PCB ground by connecting them to the ground area under the device as shown. Use a separate wide traces for the analog ground signal path. This analog ground must be used for the voltage setpoint divider, timing resistor RT, slow-start capacitor, and bias capacitor grounds. Connect this trace the top-side ground area near AGND (Pin 1).
The PH pins must be tied together and routed to the output inductor. Because the PH connection is the switching node, the inductor must be placed very close to the PH pins and the area of the PCB conductor minimized to prevent excessive capacitive coupling.
Connect the boot capacitor between the phase node and the BOOT pin as shown. Keep the boot capacitor close to the IC and minimize the conductor trace lengths.
Connect the output filter capacitor(s) as shown between the VOUT trace and PGND. It is important to keep the loop formed by the PH pins, Lout, Cout and PGND as small as practical.
Place the compensation components from the VOUT trace to the VSENSE and COMP pins. Do not place these components too close to the PH trace. Due to the size of the IC package and the device pinout, the components has to be routed somewhat close, but maintain as much separation as possible while still keeping the layout compact.
Connect the bias capacitor from the VBIAS pin to analog ground using the isolated analog ground trace. If a slow-start capacitor or RT resistor is used, or if the SYNC pin is used to select 350-kHz operating frequency, connect them to this trace as well.
11.1.1 Estimated Circuit Area
The estimated printed-circuit board area for the components used in the design of Figure 10 is 0.55 in2. This area does not include test points or connectors.
11.2 Layout Example
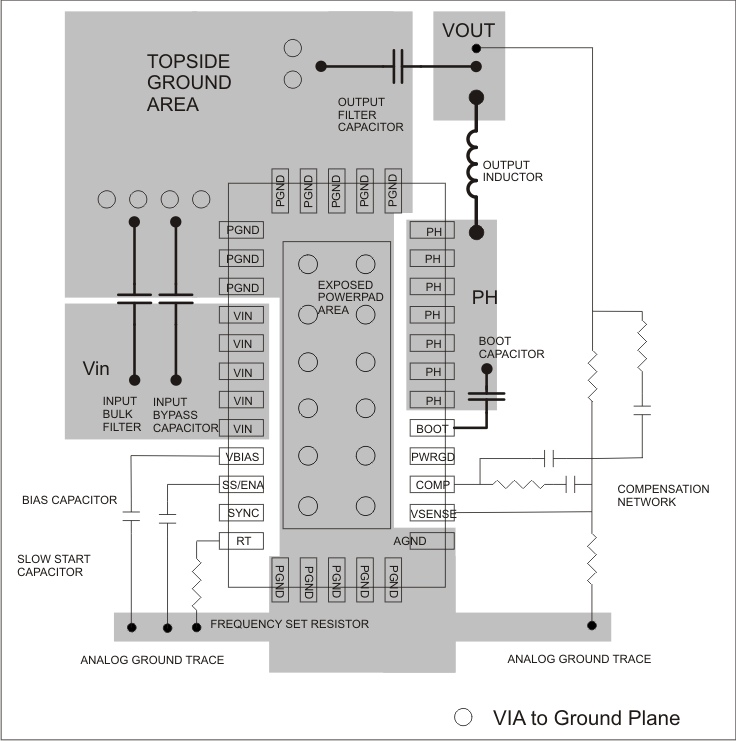 Figure 20. TPS54917 PCB Layout
Figure 20. TPS54917 PCB Layout
11.3 Thermal Considerations
The RUV package has been chosen to enable a thermal management scheme, allowing a grund plane to extend beyond both ends of the package.
For operation at full rated load current, the analog ground plane must provide an adequate heat dissipating area. A 3-inch by 3-inch plane of 1-ounce copper is recommended, though not mandatory, depending on ambient temperature and airflow. Most applications have larger areas of internal ground plane available, and the PowerPAD must be connected to the largest area available. Additional areas on the top or bottom layers also help dissipate heat, and any area available must be used when 6 A or greater operation is desired. Connection from the exposed area of the PowerPAD to the analog ground plane layer must be made using 0.013-inch diameter vias to avoid solder wicking through the vias.
12 vias must be in the PowerPAD area placed under the device package. Additional vias beyond the twelve recommended may be added in the ground area outside the package footprint to enhance thermal performance. The size of the vias outside of the package, not in the exposed thermal pad area, can be increased to 0.018.