SLVU446B March 2011 – July 2021 TPS56221
8.3 Control Loop Gain and Phase Measurement Procedure
- Follow Section 8.1 to set VIN and LOAD to desired operating condition.
- Connect isolation transformer to test points TP7 and TP10 as shown in Figure 8-2.
- Connect input signal amplitude measurement probe (Channel A) to TP7 as shown in Figure 8-2.
- Connect output signal amplitude measurement probe (Channel B) to TP10 as shown in Figure 8-2.
- Connect ground lead of Channel A and Channel B to TP8 and TP9 as shown in Figure 8-2, respectively.
- Inject 10 mV or less signal through the isolation transformer.
- Sweep the frequency from 500 Hz to 500 kHz with 10-Hz or lower post filter.
- Control loop gain can be measured by
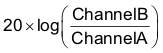 .
. - Control loop phase can be measured by the phase difference between Channel A and Channel B.
- Follow Section Section 8.1 to power down.
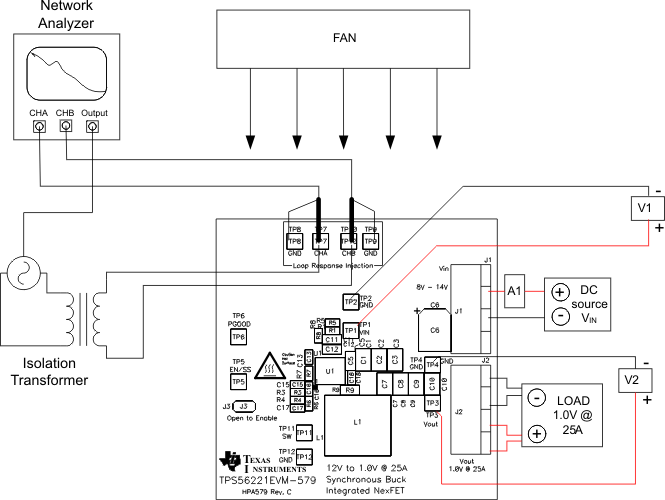 Figure 8-2 Control Loop Measurement Setup
Figure 8-2 Control Loop Measurement Setup