SLVUB26D May 2017 – February 2022 TPSM846C23
2 Getting Started
Figure 2-1 highlights the user interface items associated with the EVM. The polarized input power terminal block (TB1) is used for connection to the host input supply. TB2 and TB3 allow four terminals for VOUT and TB4 and TB5 allow four terminals for PGND for connection to the load. These terminal blocks can accept up to 12 AWG wire.
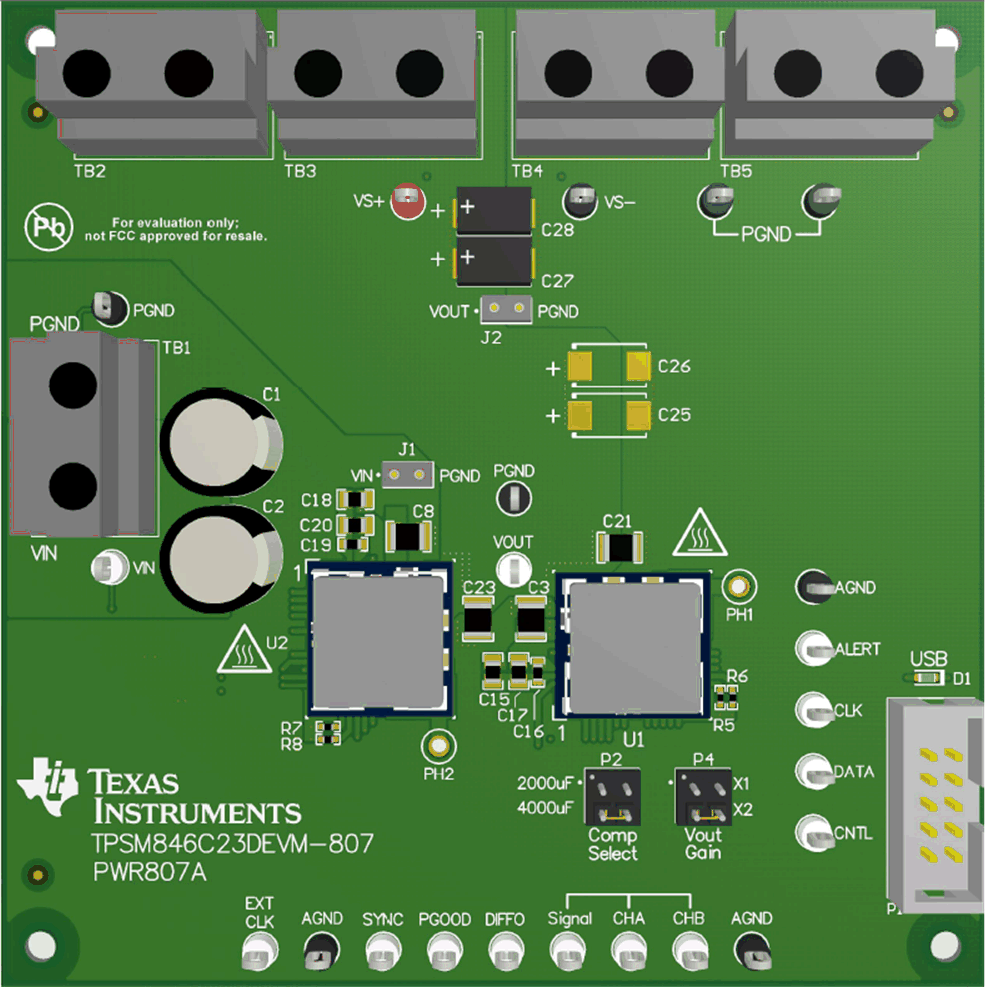 Figure 2-1 EVM User Interface
Figure 2-1 EVM User InterfaceThe VIN Monitor (VIN and PGND) and VOUT Monitor (VS+ and VS–) test points located near the input terminal block and the output terminal blocks are intended to be used as voltage monitoring points where voltmeters can be connected to measure the input and output voltages. Do not use these VIN and VOUT monitoring test points as the input supply or output load connection points. The PCB traces connecting to these test points are not designed to support high currents.
The VIN Scope (J1) and VOUT Scope (J2) test points can be used to monitor VIN and VOUT waveforms with an oscilloscope. These test points are intended for use with un-hooded scope probes outfitted with a low-inductance ground lead (ground spring) mounted to the scope probe barrel. The two sockets of each test point are on 0.1-inch centers. The scope probe tip should be inserted into the socket labeled VIN or VOUT, and the scope probe ground lead should be inserted into the hole of the socket labeled PGND.
The test points located directly below the device are made available to test the features of the device. Any external connections made to these test points should be referenced to one of the AGND test points located along the bottom of the EVM. Refer to Section 3 for more information on the individual control test points.
The PMBus connector (P1) is provided to connect the USB-to-GPIO interface pod to the EVM. The USB-to-GPIO interface pod connects the EVM to a computer USB port which allows the TI “Fusion” Graphical User Interface (GUI) to communicate and control the EVM. To download the latest software visit, http://www.ti.com/tool/fusion_digital_power_designer.
The ALERT, DATA, CLK, and CNTL test points are used to monitor and control the module through PMBus. Reference the TPS546C23 PG1.0 Supported PMBus Commands document for details on the supported PMBus commands.
The Vout Gain jumper (P4) is used to set the output voltage. Select X1 for an output voltage between 0.35 V–1.65 V and select X2 for output voltages between 0.70 V–2 V. The default loading is the X1 position.
The Comp Select jumper (P2) sets the proper frequency compensation for the total amount of output capacitance present on the VOUT bus. The EVM is shipped with approximately 2000 µF of output capacitance loaded on the board. Locations are provided on the board to add another 2000 µF of output capacitance (C28–C31). The default jumper load is the 2000-µF position.
When two TPSM846C23 devices are paralleled, the SYNC pins of the loop controller and the loop follower must be supplied with a 50% duty cycle external clock signal at the desired switching frequency. A 500-kHz clock is present on the EVM, which supplies the required 50% duty cycle signal. The loop controller device (U1) locks to the rising edge of the clock and the loop follower device (U2) locks to the falling edge of the clock.
Resistors R5, R6, R7, and R8 set the PMBus address for the modules. The controller module PMBus address is 54 decimal (36 hex) and the follower address is 52 decimal (34 hex).