SNAA393 January 2024 LMK6C , LMK6D , LMK6H , LMK6P
3.4 Spurious View Modes
Some PNAs can change how spurs are represented in phase noise plots. Power or Spurs Enabled mode can show the full power of spurs without any filtering. Normalized mode will divide down the spur power by the frequency offset, meaning higher frequency spurs will appear proportionally smaller compared to spurs that are close to the carrier frequency. Omit or Spurs Off mode will remove spurs entirely from the phase noise plot. The following images show a comparison between spurious view modes for a LMK6P 156.25MHz variant.
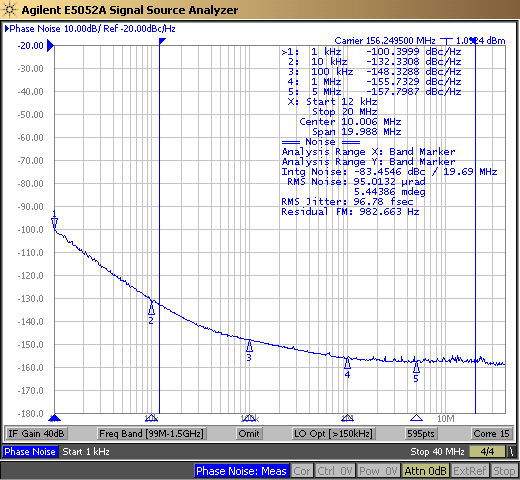 Figure 3-1 Omit Spur
View
Figure 3-1 Omit Spur
View |
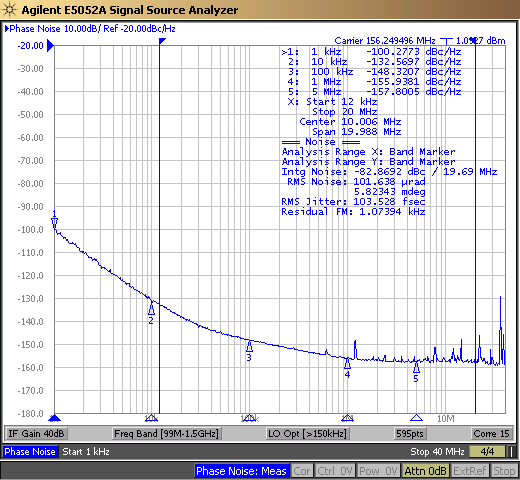 Figure 3-2 Normalized
Spur view
Figure 3-2 Normalized
Spur view |
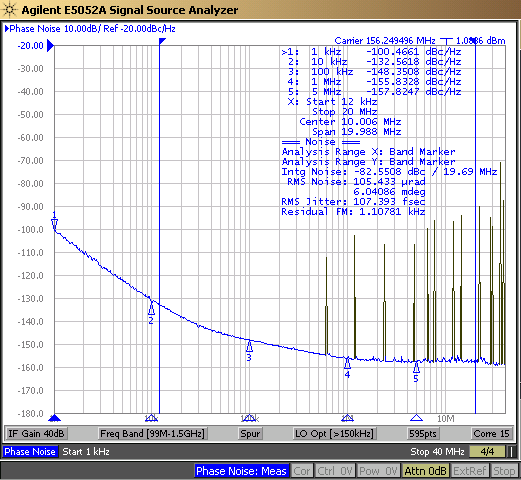 Figure 3-3 Power Spur
View
Figure 3-3 Power Spur
View |