SNVA966 July 2020 – MONTH LP8864-Q1 , LP8864S-Q1 , LP8866-Q1 , LP8866S-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1Fault Handling Routine
- 2Different Fault and Diagnostic Handling Method Recommendation
- 3Summary
-
A Fault-Related
Functions
-
A.1 Protection and Fault Detections
- A.1.1 Supply Faults
-
A.1.2 Boost Faults
- A.1.2.1 Boost Overvoltage Faults (BSTOVPL, BSTOVPH)
- A.1.2.2 Boost Overcurrent Faults (BSTOCP)
- A.1.2.3 LEDSET Resistor Missing Faults (LEDSET)
- A.1.2.4 MODE Resistor Missing Faults (MODESEL)
- A.1.2.5 FSET Resistor Missing Faults (FSET)
- A.1.2.6 ISET Resistor Out of Range Faults (ISET)
- A.1.2.7 Thermal Shutdown Faults (TSD)
- A.1.3 LED Faults
- A.1.4 Overview of the Fault and Protection Schemes
- A.2 Programming Examples
-
A.1 Protection and Fault Detections
A.1.2.6 ISET Resistor Out of Range Faults (ISET)
If the ISET pin resistor is shorted to GND during normal operation, the maximum current for each LED channel can be calculated in the following equation:
Equation 4. 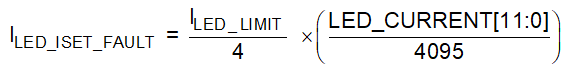
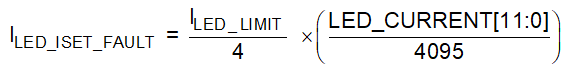
LED_CURRENT[11:0] register will be written to 1/4 of latest programmed data through I2C. The default value of LED_CURRENT[11:0] register is 0xFFF if it is not programmed after device enabling. If ISET pin voltage returns back to above 1.1 V, the LED_CURRENT[11:0] register data is written to latest programmed data through I2C. The ISET_STATUS fault bit will be set in the BOOST_FAULT_STATUS register and the INT pin is triggered.