SPRACQ1 May 2020 TMS320F28374D , TMS320F28374S , TMS320F28375D , TMS320F28375S , TMS320F28376D , TMS320F28376S , TMS320F28377D , TMS320F28377S , TMS320F28379D , TMS320F28379S , TMS320F28384D , TMS320F28384D-Q1 , TMS320F28384S , TMS320F28384S-Q1 , TMS320F28386D , TMS320F28386D-Q1 , TMS320F28386S , TMS320F28386S-Q1 , TMS320F28388D , TMS320F28388S
-
Migration Between TMS320F2837x and TMS320F2838x
- Trademarks
- 1 Feature Differences Between F2837x and F2838x
- 2 PCB Hardware Changes
- 3
Feature Differences for System Consideration
- 3.1
New Features in F2838x Device
- 3.1.1 Fast Integer Division (FINTDIV)
- 3.1.2 VCRC Unit
- 3.1.3 EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC)
- 3.1.4 Background CRC (BGCRC)
- 3.1.5 Diagnostic Features (PBIST/HWBIST)
- 3.1.6 Power Management Bus Module (PMBus)
- 3.1.7 Fast Serial Interface (FSI)
- 3.1.8 Embedded Real-time Analysis and Diagnostic (ERAD)
- 3.1.9 Dual-Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 3.1.10 Connectivity Manager (CM)
- 3.2 Features Differences/Enhancements in F2838x
- 3.3 Other Device Changes
- 3.4 Power Management
- 3.5 Power Consumption
- 3.6 GPIO
- 3.1
New Features in F2838x Device
- 4 Application Code Migration From F2837x to F2838x
- 5 References
1.1 F2837x and F2838x Feature Comparison
The functional block diagram of F2838x is shown in Figure 1, while the feature comparison of the superset part numbers for theF2837x and F2838x devices are shown in Table 1.
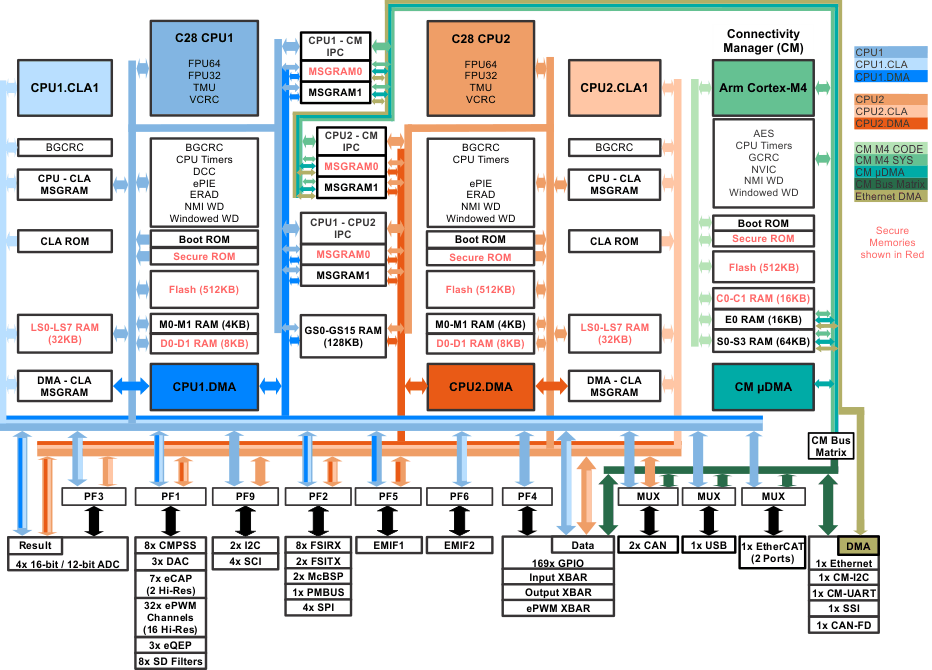 Figure 1. F2838x Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1. F2838x Functional Block Diagram Table 1. F28379D and F28388D (Superset) Device Comparison
| FEATURE (1) | F28388D | F28379D | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C28x Subsystem | |||
| C28x | Number | 2 | |
| Frequency (MHz) | 200 | ||
| Floating-Point Unit (FPU) | 32 bit and 64 bit | 32 bit | |
| VCRC | Yes | - | |
| VCU-II | - | Yes | |
| TMU | Yes – Type 0 | ||
| FINTDIV | Yes | - | |
| CLA | Number | 2 (1 per CPU) – Type 2 | 2 (1 per CPU) – Type 1 |
| Frequency (MHz) | 200 | 200 | |
| C28x Flash | 1MB (512KW)
[512KB(256KW) per CPU] |
1MB (512KW)
[512KB (256KW) per CPU] |
|
| C28x RAM | Dedicated RAM | 24KB (12KW) [12KB (6KW) per CPU] | |
| Local Shared RAM | 64KB (32KW) [32KB
(16KW) per CPU] |
48KB (24KW)
[24KB (12KW) per CPU] |
|
| Global Shared RAM | 128KB (64KW) (Shared between CPUs) | ||
| Total RAM | 216KB (108KW) | 200KB (100KW) | |
| Background Cyclic Redundancy Check (BGCRC) module | 4 (2 per CPU/CLA) | - | |
| Configurable Logic Block (CLB) | 8 tiles | 4 tiles | |
| 32-bit CPU timers | 6 (3 per CPU) | ||
| 6-Channel DMA | 2 (1 per CPU) – Type 0 | ||
| Dual-zone Code Security Module (DCSM) for on-chip flash and RAM | Yes | ||
| Embedded Real-time Analysis and Diagnostic (ERAD) | Yes | - | |
| Dual Clock Comparator (DCC) | Yes | - | |
| EMIF | EMIF1 (16-bit or 32-bit) | 1 | |
| EMIF2 (16-bit) | 1 | ||
| External interrupts | 5 | ||
| GPIO | I/O pins (shared among CPU1, CPU2, and CM) | 169 | |
| Input XBAR | Yes | ||
| Output XBAR | Yes | ||
| Message RAM | C28x CPU1, C28x CPU2, and Cortex-M4 | 24KB (4KB each direction between each of the three pairs) | 4KB [2KB per CPU] |
| C28x CPUs and CLAs | 1KB (256 bytes each direction between each CPU and CLA pair) | ||
| DMAs and CLAs | 1KB (256 bytes each direction between each DMA and CLA pair) | - | |
| Nonmaskable Interrupt Watchdog (NMIWD) timers | 2 (1 per CPU) | ||
| Watchdog (WD) timers | 2 (1 per CPU) | ||
| Connectivity Manager (CM) Subsystem | |||
| Arm®Cortex®-M4 | 125 MHz | - | |
| M4 Flash | 512KB | - | |
| M4 RAM | 96KB | - | |
| Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Accelerator | 1 | - | |
| CPU timers | 3 | - | |
| Generic Cyclic Redundancy Check (GCRC) module | 1 | - | |
| Memory Protection Unit (MPU) for Cortex-M4, µDMA, and Ethernet DMA | 3 | - | |
| CM Nonmaskable Interrupt (CMNMI) Module | 1 | - | |
| Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU) | 1 | - | |
| µDMA | 1 | - | |
| Watchdog (WD) timer | 1 | - | |
| C28x Analog Peripherals | |||
| Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) (configurable to 12-bit or 16-bit) | 4 | ||
| ADC 16-bit mode | MSPS | 1.1 | |
| Conversion Time (ns) | 915 | ||
| Input channels (single-ended mode) | 24 | - | |
| Input channels (differential mode) | 12 | ||
| ADC 12-bit mode | MSPS | 3.5 | |
| Conversion Time (ns) | 280 | ||
| Input channels (single-ended) | 24 | ||
| Temperature sensor | 1 | ||
| Comparator subsystem (CMPSS) (each CMPSS has two comparators and two internal DACs) | 8 | ||
| Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) | 3 | ||
| C28x Control Peripherals | |||
| eCAP/HRCAP | Total inputs | 7 – Type 1 | 6 – Type 0 |
| Channels with high-resolution capability | 2 | - | |
| ePWM/HRPWM | Total channels | 32 – Type 4 | |
| Channels with high-resolution capability | 16 | ||
| ePWM XBAR | Yes | ||
| eQEP modules | 3 – Type 2 | ||
| SDFM channels | 8 – Type 2 | ||
| C28x Communications Peripherals | |||
| Fast Serial Interface (FSI) RX | 8 – Type 1 | ||
| Fast Serial Interface (FSI) TX | 2 – Type 1 | - | |
| Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) | 2 – Type 0 | ||
| Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) | 2 – Type 1 | ||
| Power Management Bus (PMBus) | 1 – Type 0 | - | |
| Serial Communications Interface (SCI) | 4 – Type 0 | ||
| Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) | 4 – Type 2 | 3 – Type 2 | |
| Controller Area Network (CAN) 2.0B | 2 – Type 0 (can be assigned to CPU1, CPU2, or CM) | 2 – Type 0 (can be assigned to CPU1 or CPU2) | |
| Universal Serial Bus (USB) | 1 – Type 0 (can be assigned to CPU1 or CM) | 1 – Type 0 (only on CPU1) | |
| uPP | - | 1 | |
| Connectivity Manager (CM) Communications Peripherals | |||
| CAN with Flexible Data-Rate (CAN-FD) | 1 | - | |
| Ethernet for Control Automation Technology (EtherCAT) | 1 (can be assigned to CPU1 or CM) | - | |
| Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) | 1 | - | |
| CM Inter-Integrated Circuit (CM-I2C) | 1 | - | |
| Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) | 1 | - | |
| CM Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter (CM-UART) | 1 | - | |
| Package Options | |||
| Package Options | 337-Ball ZWT | Yes | |
| 176-Pin PTP | future | Yes | |
| 100-Pin PZP | No | Yes | |
- A type change represents a major functional feature difference in a peripheral module. Within a peripheral type, there may be minor differences between devices that do not affect the basic functionality of the module. For more information, see the C2000 Real-Time Control Peripherals Reference Guide.