SPRUII0F May 2019 – June 2024 TMS320F28384D , TMS320F28384D-Q1 , TMS320F28384S , TMS320F28384S-Q1 , TMS320F28386D , TMS320F28386D-Q1 , TMS320F28386S , TMS320F28386S-Q1 , TMS320F28388D , TMS320F28388S
- 1
- Read This First
- 1 ► C28x SYSTEM RESOURCES
- 2 C2000™ Microcontrollers Software Support
-
3 C28x System Control and Interrupts
- 3.1 C28x System Control Introduction
- 3.2 System Control Functional Description
- 3.3
Resets
- 3.3.1 Reset Sources
- 3.3.2 External Reset (XRSn)
- 3.3.3 Simulate External Reset
- 3.3.4 Power-On Reset (POR)
- 3.3.5 Debugger Reset (SYSRS)
- 3.3.6 Simulate CPU1 Reset
- 3.3.7 Watchdog Reset (WDRS)
- 3.3.8 NMI Watchdog Reset (NMIWDRS)
- 3.3.9 Secure Code Copy Reset (SCCRESET)
- 3.3.10 ESC Reset Output
- 3.3.11 Test Reset (TRST)
- 3.4 Peripheral Interrupts
- 3.5
Exceptions and Non-Maskable
Interrupts
- 3.5.1 Configuring and Using NMIs
- 3.5.2 Emulation Considerations
- 3.5.3
NMI Sources
- 3.5.3.1 Missing Clock Detection
- 3.5.3.2 RAM Uncorrectable Error
- 3.5.3.3 Flash Uncorrectable ECC Error
- 3.5.3.4 ROM Uncorrectable Error
- 3.5.3.5 NMI Vector Fetch Mismatch
- 3.5.3.6 CPU2 Watchdog or NMI Watchdog Reset
- 3.5.3.7 CM NMI Watchdog Reset
- 3.5.3.8 EtherCAT Reset out
- 3.5.3.9 CRC Fail
- 3.5.3.10 ERAD NMI
- 3.5.4 Illegal Instruction Trap (ITRAP)
- 3.6 Safety Features
- 3.7 Clocking
- 3.8 Clock Configuration Semaphore
- 3.9 32-Bit CPU Timers 0/1/2
- 3.10 Watchdog Timers
- 3.11 Low-Power Modes
- 3.12
Memory Controller Module
- 3.12.1
Functional Description
- 3.12.1.1 Dedicated RAM (Dx RAM)
- 3.12.1.2 Local Shared RAM (LSx RAM)
- 3.12.1.3 Global Shared RAM (GSx RAM)
- 3.12.1.4 CPU Message RAM (CPU MSG RAM)
- 3.12.1.5 CLA Message RAM (CLA MSGRAM)
- 3.12.1.6 CLA-DMA MSG RAM
- 3.12.1.7 Access Arbitration
- 3.12.1.8 Access Protection
- 3.12.1.9 Memory Error Detection, Correction and Error Handling
- 3.12.1.10 Application Test Hooks for Error Detection and Correction
- 3.12.1.11 ROM Test
- 3.12.1.12 RAM Initialization
- 3.12.1
Functional Description
- 3.13 JTAG
- 3.14 System Control Register Configuration Restrictions
- 3.15
Software
- 3.15.1 SYSCTL Examples
- 3.15.2
MEMCFG Examples
- 3.15.2.1 Correctable & Uncorrectable Memory Error Handling
- 3.15.2.2 Shared RAM Management (CPU1) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.2.3 Shared RAM Management (CPU2) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.2.4 Demonstrate memconfig diagnostics and error handling. - CM
- 3.15.2.5 Shared RAM Management (CPU1) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.2.6 Shared RAM Management (CPU2) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.3 NMI Examples
- 3.15.4 TIMER Examples
- 3.15.5 WATCHDOG Examples
- 3.16
System Control Registers
- 3.16.1 SYSCTRL Base Address Table (C28)
- 3.16.2 ACCESS_PROTECTION_REGS Registers
- 3.16.3 CLK_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.16.4 CM_CONF_REGS Registers
- 3.16.5 CPU_SYS_REGS Registers
- 3.16.6 CPU_ID_REGS Registers
- 3.16.7 CPU1_PERIPH_AC_REGS Registers
- 3.16.8 CPUTIMER_REGS Registers
- 3.16.9 DEV_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.16.10 DMA_CLA_SRC_SEL_REGS Registers
- 3.16.11 MEM_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.16.12 MEMORY_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.16.13 NMI_INTRUPT_REGS Registers
- 3.16.14 PIE_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 3.16.15 ROM_PREFETCH_REGS Registers
- 3.16.16 ROM_WAIT_STATE_REGS Registers
- 3.16.17 SYNC_SOC_REGS Registers
- 3.16.18 SYS_STATUS_REGS Registers
- 3.16.19 TEST_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.16.20 UID_REGS Registers
- 3.16.21 WD_REGS Registers
- 3.16.22 XINT_REGS Registers
- 3.16.23
Register to Driverlib Function Mapping
- 3.16.23.1 ASYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.2 CPUTIMER Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.3 DCSM Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.4 MEMCFG Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.5 NMI Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.6 PIE Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.7 SYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.8 WWD Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.9 XINT Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 4 C28x Processor
-
5 ROM Code and Peripheral Booting
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 Device Boot Sequence
- 5.3 Device Boot Modes
- 5.4 Device Boot Configurations
- 5.5 Device Boot Flow Diagrams
- 5.6 Device Reset and Exception Handling
- 5.7
Boot ROM Description
- 5.7.1 CPU1 Boot ROM Configuration Registers
- 5.7.2 Booting CPU2 and CM
- 5.7.3 Entry Points
- 5.7.4 Wait Points
- 5.7.5 Memory Maps
- 5.7.6 ROM Tables
- 5.7.7 Boot Modes and Loaders
- 5.7.8 GPIO Assignments for CPU1
- 5.7.9 Secure ROM Function APIs
- 5.7.10 Clock Initializations
- 5.7.11 Boot Status information
- 5.7.12 ROM Version
- 5.8 Application Notes for Using the Bootloaders
- 5.9 Software
-
6 Dual Code Security Module (DCSM)
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 Functional Description
- 6.3 Flash and OTP Erase/Program
- 6.4 Secure Copy Code
- 6.5 SecureCRC
- 6.6 CSM Impact on Other On-Chip Resources
- 6.7
Incorporating Code Security in User Applications
- 6.7.1 Environments That Require Security Unlocking
- 6.7.2 CSM Password Match Flow
- 6.7.3 C Code Example to Unsecure C28x Zone1
- 6.7.4 C Code Example to Resecure C28x Zone1
- 6.7.5 Environments That Require ECSL Unlocking
- 6.7.6 ECSL Password Match Flow
- 6.7.7 ECSL Disable Considerations for any Zone
- 6.7.8 Device Unique ID
- 6.8 Software
- 6.9 DCSM Registers
- 7 Background CRC-32 (BGCRC)
-
8 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 CLA Interface
- 8.3 CLA, DMA, and CPU Arbitration
- 8.4 CLA Configuration and Debug
- 8.5 Pipeline
- 8.6
Software
- 8.6.1
CLA Examples
- 8.6.1.1 CLA arcsine(x) using a lookup table (cla_asin_cpu01)
- 8.6.1.2 CLA arcsine(x) using a lookup table (cla_asin_cpu01) - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.3 CLA Arcsine Example. - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.4 CLA arctangent(x) using a lookup table (cla_atan_cpu01)
- 8.6.1.5 CLA 2 Pole 2 Zero Infinite Impulse Response Filter (cla_iir2p2z_cpu01) - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.6 CLA 2-pole 2-zero IIR Filter Example for F2837xD. - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.7 CLA background nesting task
- 8.6.1.8 Controlling PWM output using CLA
- 8.6.1.9 Just-in-time ADC sampling with CLA
- 8.6.1.10 Optimal offloading of control algorithms to CLA
- 8.6.1.11 Handling shared resources across C28x and CLA
- 8.6.1
CLA Examples
- 8.7
Instruction Set
- 8.7.1 Instruction Descriptions
- 8.7.2 Addressing Modes and Encoding
- 8.7.3
Instructions
- MABSF32 MRa, MRb
- MADD32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MAND32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MASR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MBCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCLRC BGINTM
- MCMP32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MDEBUGSTOP
- MDEBUGSTOP1
- MEALLOW
- MEDIS
- MEINVF32 MRa, MRb
- MEISQRTF32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI32 MRa, MRb
- MFRACF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MLSL32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MLSR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MMACF32 MR3, MR2, MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMAXF32 MRa, MRb
- MMAXF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMINF32 MRa, MRb
- MMINF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMOV16 MARx, MRa, #16I
- MMOV16 MARx, mem16
- MMOV16 mem16, MARx
- MMOV16 mem16, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MSTF
- MMOV32 MRa, mem32 [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MSTF, mem32
- MMOVD32 MRa, mem32
- MMOVF32 MRa, #32F
- MMOVI16 MARx, #16I
- MMOVI32 MRa, #32FHex
- MMOVIZ MRa, #16FHi
- MMOVZ16 MRa, mem16
- MMOVXI MRa, #16FLoHex
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MMPYF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc||MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc ||MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MNEGF32 MRa, MRb[, CNDF]
- MNOP
- MOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MRCNDD [CNDF]
- MSETC BGINTM
- MSETFLG FLAG, VALUE
- MSTOP
- MSUB32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MSWAPF MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MTESTTF CNDF
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MXOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- 8.8 CLA Registers
-
9 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 9.1 Introduction
- 9.2 Description
- 9.3 CLB Input/Output Connection
- 9.4 CLB Tile
- 9.5 CPU Interface
- 9.6 DMA Access
- 9.7 CLB Data Export Through SPI RX Buffer
- 9.8 CLB Pipeline Mode
- 9.9
Software
- 9.9.1
CLB Examples
- 9.9.1.1 CLB Empty Project
- 9.9.1.2 CLB Combinational Logic
- 9.9.1.3 CLB GPIO Input Filter
- 9.9.1.4 CLB Auxilary PWM
- 9.9.1.5 CLB PWM Protection
- 9.9.1.6 CLB Event Window
- 9.9.1.7 CLB Signal Generator
- 9.9.1.8 CLB State Machine
- 9.9.1.9 CLB External Signal AND Gate
- 9.9.1.10 CLB Timer
- 9.9.1.11 CLB Timer Two States
- 9.9.1.12 CLB Interrupt Tag
- 9.9.1.13 CLB Output Intersect
- 9.9.1.14 CLB PUSH PULL
- 9.9.1.15 CLB Multi Tile
- 9.9.1.16 CLB Tile to Tile Delay
- 9.9.1.17 CLB based One-shot PWM
- 9.9.1.18 CLB AOC Control
- 9.9.1.19 CLB AOC Release Control
- 9.9.1.20 CLB XBARs
- 9.9.1.21 CLB AOC Control
- 9.9.1.22 CLB Serializer
- 9.9.1.23 CLB LFSR
- 9.9.1.24 CLB Lock Output Mask
- 9.9.1.25 CLB INPUT Pipeline Mode
- 9.9.1.26 CLB Clocking and PIPELINE Mode
- 9.9.1.27 CLB SPI Data Export
- 9.9.1.28 CLB SPI Data Export DMA
- 9.9.1.29 CLB Trip Zone Timestamp
- 9.9.1.30 CLB CRC
- 9.9.1
CLB Examples
- 9.10 CLB Registers
- 10Dual-Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 11Direct Memory Access (DMA)
-
12External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 12.1 Introduction
- 12.2
EMIF Module Architecture
- 12.2.1 EMIF Clock Control
- 12.2.2 EMIF Requests
- 12.2.3 EMIF Signal Descriptions
- 12.2.4 EMIF Signal Multiplexing Control
- 12.2.5
SDRAM Controller and Interface
- 12.2.5.1 SDRAM Commands
- 12.2.5.2 Interfacing to SDRAM
- 12.2.5.3 SDRAM Configuration Registers
- 12.2.5.4 SDRAM Auto-Initialization Sequence
- 12.2.5.5 SDRAM Configuration Procedure
- 12.2.5.6 EMIF Refresh Controller
- 12.2.5.7 Self-Refresh Mode
- 12.2.5.8 Power-Down Mode
- 12.2.5.9 SDRAM Read Operation
- 12.2.5.10 SDRAM Write Operations
- 12.2.5.11 Mapping from Logical Address to EMIF Pins
- 12.2.6 Asynchronous Controller and Interface
- 12.2.7 Data Bus Parking
- 12.2.8 Reset and Initialization Considerations
- 12.2.9 Interrupt Support
- 12.2.10 DMA Event Support
- 12.2.11 EMIF Signal Multiplexing
- 12.2.12 Memory Map
- 12.2.13 Priority and Arbitration
- 12.2.14 System Considerations
- 12.2.15 Power Management
- 12.2.16 Emulation Considerations
- 12.3
Example Configuration
- 12.3.1 Hardware Interface
- 12.3.2
Software Configuration
- 12.3.2.1
Configuring the SDRAM Interface
- 12.3.2.1.1 PLL Programming for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.2 SDRAM Timing Register (SDRAM_TR) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.3 SDRAM Self Refresh Exit Timing Register (SDR_EXT_TMNG) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.4 SDRAM Refresh Control Register (SDRAM_RCR) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.5 SDRAM Configuration Register (SDRAM_CR) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.2 Configuring the Flash Interface
- 12.3.2.1
Configuring the SDRAM Interface
- 12.4
Software
- 12.4.1
EMIF Examples
- 12.4.1.1 Pin setup for EMIF module accessing ASRAM.
- 12.4.1.2 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM.
- 12.4.1.3 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM through CPU1 and CPU2. - C28X_DUAL
- 12.4.1.4 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM trhough CPU1 and CPU2. - C28X_DUAL
- 12.4.1.5 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit ASRAM as code memory.
- 12.4.1.6 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit SDRAM using memcpy_fast_far().
- 12.4.1.7 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit SDRAM then puts into Self Refresh mode before entering Low Power Mode.
- 12.4.1.8 EMIF1 module accessing 32bit SDRAM using DMA.
- 12.4.1.9 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit SDRAM using alternate address mapping.
- 12.4.1.10 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM HIC FSI
- 12.4.1.11 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 8bit HIC controller.
- 12.4.1
EMIF Examples
- 12.5 EMIF Registers
-
13Flash Module
- 13.1 Introduction to Flash and OTP Memory
- 13.2 Flash Bank, OTP, and Pump
- 13.3 Flash Module Controller (FMC)
- 13.4 Flash and OTP Memory Power-Down Modes and Wakeup
- 13.5 Active Grace Period
- 13.6 Flash and OTP Memory Performance
- 13.7 Flash Read Interface
- 13.8 Flash Erase and Program
- 13.9 Error Correction Code (ECC) Protection
- 13.10 Reserved Locations Within Flash and OTP Memory
- 13.11 Migrating an Application from RAM to Flash
- 13.12 Procedure to Change the Flash Control Registers
- 13.13 Flash Pump Ownership Semaphore
- 13.14 Software
- 13.15
Flash Registers
- 13.15.1 FLASH Base Address Table (C28)
- 13.15.2 CM FLASH Base Address Table (CM)
- 13.15.3 FLASH_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 13.15.4 FLASH_ECC_REGS Registers
- 13.15.5 CM_FLASH_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 13.15.6 CM_FLASH_ECC_REGS Registers
- 13.15.7 FLASH_PUMP_SEMAPHORE_REGS Registers
- 13.15.8 FLASH Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
14Embedded Real-time Analysis and Diagnostic (ERAD)
- 14.1 Introduction
- 14.2 Enhanced Bus Comparator Unit
- 14.3 System Event Counter Unit
- 14.4 ERAD Ownership, Initialization and Reset
- 14.5 ERAD Programming Sequence
- 14.6 Cyclic Redundancy Check Unit
- 14.7 Program Counter Trace
- 14.8
Software
- 14.8.1
ERAD Examples
- 14.8.1.1 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 14.8.1.2 ERAD Profile Function
- 14.8.1.3 ERAD Profile Function
- 14.8.1.4 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 14.8.1.5 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 14.8.1.6 ERAD Profile Function
- 14.8.1.7 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 14.8.1.8 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 14.8.1.9 ERAD Stack Overflow
- 14.8.1.10 ERAD Profile Interrupts CLA
- 14.8.1.11 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 14.8.1.12 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 14.8.1.13 ERAD MEMORY ACCESS RESTRICT
- 14.8.1.14 ERAD INTERRUPT ORDER
- 14.8.1.15 ERAD AND CLB
- 14.8.1.16 ERAD PWM PROTECTION
- 14.8.1
ERAD Examples
- 14.9 ERAD Registers
-
15General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 15.1 Introduction
- 15.2 Configuration Overview
- 15.3 Digital General-Purpose I/O Control
- 15.4 Input Qualification
- 15.5 USB Signals
- 15.6 SPI Signals
- 15.7 GPIO and Peripheral Muxing
- 15.8 Internal Pullup Configuration Requirements
- 15.9 Software
- 15.10
GPIO Registers
- 15.10.1 GPIO Base Address Table (C28)
- 15.10.2 CM GPIO Base Address Table (CM)
- 15.10.3 GPIO_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 15.10.4 GPIO_DATA_REGS Registers
- 15.10.5 GPIO_DATA_READ_REGS Registers
- 15.10.6 CM_GPIO_DATA_REGS Registers
- 15.10.7 CM_GPIO_DATA_READ_REGS Registers
- 15.10.8 GPIO Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
16Interprocessor Communication (IPC)
- 16.1 Introduction
- 16.2 Message RAMs
- 16.3 IPC Flags and Interrupts
- 16.4 IPC Command Registers
- 16.5 Free-Running Counter
- 16.6 IPC Communication Protocol
- 16.7
Software
- 16.7.1
IPC Examples
- 16.7.1.1 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.2 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.3 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.4 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.5 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.6 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.7 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.8 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.9 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.10 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.11 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.12 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1
IPC Examples
- 16.8
IPC Registers
- 16.8.1 IPC Base Address Table (C28)
- 16.8.2 CM IPC Base Address Table (CM)
- 16.8.3 CPU1TOCPU2_IPC_REGS_CPU1VIEW Registers
- 16.8.4 CPU1TOCPU2_IPC_REGS_CPU2VIEW Registers
- 16.8.5 CPU1TOCM_IPC_REGS_CPU1VIEW Registers
- 16.8.6 CPU1TOCM_IPC_REGS_CMVIEW Registers
- 16.8.7 CPU2TOCM_IPC_REGS_CPU2VIEW Registers
- 16.8.8 CPU2TOCM_IPC_REGS_CMVIEW Registers
- 16.8.9 IPC Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
17Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 17.1 Input X-BAR and CLB Input X-BAR
- 17.2 ePWM, CLB, and GPIO Output X-BAR
- 17.3 XBAR Registers
- 18► ANALOG PERIPHERALS
- 19Analog Subsystem
-
20Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 20.1 Introduction
- 20.2 ADC Configurability
- 20.3 SOC Principle of Operation
- 20.4 SOC Configuration Examples
- 20.5 ADC Conversion Priority
- 20.6 Burst Mode
- 20.7 EOC and Interrupt Operation
- 20.8 Post-Processing Blocks
- 20.9 Opens/Shorts Detection Circuit (OSDETECT)
- 20.10 Power-Up Sequence
- 20.11 ADC Calibration
- 20.12 ADC Timings
- 20.13 Additional Information
- 20.14
Software
- 20.14.1
ADC Examples
- 20.14.1.1 ADC Software Triggering
- 20.14.1.2 ADC ePWM Triggering
- 20.14.1.3 ADC Temperature Sensor Conversion
- 20.14.1.4 ADC Synchronous SOC Software Force (adc_soc_software_sync)
- 20.14.1.5 ADC Continuous Triggering (adc_soc_continuous)
- 20.14.1.6 ADC Continuous Conversions Read by DMA (adc_soc_continuous_dma)
- 20.14.1.7 ADC PPB Offset (adc_ppb_offset)
- 20.14.1.8 ADC PPB Limits (adc_ppb_limits)
- 20.14.1.9 ADC PPB Delay Capture (adc_ppb_delay)
- 20.14.1.10 ADC ePWM Triggering Multiple SOC
- 20.14.1.11 ADC Burst Mode
- 20.14.1.12 ADC Burst Mode Oversampling
- 20.14.1.13 ADC SOC Oversampling
- 20.14.1.14 ADC PPB PWM trip (adc_ppb_pwm_trip)
- 20.14.1.15 ADC High Priority SOC (adc_high_priority_soc)
- 20.14.1.16 ADC Interleaved Averaging in Software
- 20.14.1.17 ADC Open Shorts Detection (adc_open_shorts_detection)
- 20.14.1
ADC Examples
- 20.15 ADC Registers
- 21Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 22Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 23► CONTROL PERIPHERALS
-
24Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 24.1 Introduction
- 24.2 Description
- 24.3 Configuring Device Pins for the eCAP
- 24.4 Capture and APWM Operating Mode
- 24.5
Capture Mode Description
- 24.5.1 Event Prescaler
- 24.5.2 Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 24.5.3 Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 24.5.4 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 24.5.5 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 24.5.6 eCAP Synchronization
- 24.5.7 Interrupt Control
- 24.5.8 DMA Interrupt
- 24.5.9 Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 24.5.10 APWM Mode Operation
- 24.6
Application of the eCAP Module
- 24.6.1 Example 1 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 24.6.2 Example 2 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 24.6.3 Example 3 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 24.6.4 Example 4 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 24.7 Application of the APWM Mode
- 24.8 Software
- 24.9 eCAP Registers
- 25High Resolution Capture (HRCAP)
-
26Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 26.1 Introduction
- 26.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 26.3 ePWM Modules Overview
- 26.4
Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 26.4.1 Purpose of the Time-Base Submodule
- 26.4.2 Controlling and Monitoring the Time-Base Submodule
- 26.4.3 Calculating PWM Period and Frequency
- 26.4.4 Phase Locking the Time-Base Clocks of Multiple ePWM Modules
- 26.4.5 Simultaneous Writes to TBPRD and CMPx Registers Between ePWM Modules
- 26.4.6 Time-Base Counter Modes and Timing Waveforms
- 26.4.7 Global Load
- 26.5 Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 26.6 Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 26.7 Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 26.8 PWM Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 26.9 Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 26.10 Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 26.11 Digital Compare (DC) Submodule
- 26.12 ePWM Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 26.13
Applications to Power Topologies
- 26.13.1 Overview of Multiple Modules
- 26.13.2 Key Configuration Capabilities
- 26.13.3 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Independent Frequencies
- 26.13.4 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Same Frequencies
- 26.13.5 Controlling Multiple Half H-Bridge (HHB) Converters
- 26.13.6 Controlling Dual 3-Phase Inverters for Motors (ACI and PMSM)
- 26.13.7 Practical Applications Using Phase Control Between PWM Modules
- 26.13.8 Controlling a 3-Phase Interleaved DC/DC Converter
- 26.13.9 Controlling Zero Voltage Switched Full Bridge (ZVSFB) Converter
- 26.13.10 Controlling a Peak Current Mode Controlled Buck Module
- 26.13.11 Controlling H-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter
- 26.14 Register Lock Protection
- 26.15
High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 26.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 26.15.1.1 Controlling the HRPWM Capabilities
- 26.15.1.2 HRPWM Source Clock
- 26.15.1.3 Configuring the HRPWM
- 26.15.1.4 Configuring High-Resolution in Deadband Rising-Edge and Falling-Edge Delay
- 26.15.1.5 Principle of Operation
- 26.15.1.6 Deadband High-Resolution Operation
- 26.15.1.7 Scale Factor Optimizing Software (SFO)
- 26.15.1.8 HRPWM Examples Using Optimized Assembly Code
- 26.15.2 SFO Library Software - SFO_TI_Build_V8.lib
- 26.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 26.16
Software
- 26.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 26.16.1.1 ePWM Trip Zone
- 26.16.1.2 ePWM Up Down Count Action Qualifier
- 26.16.1.3 ePWM Synchronization
- 26.16.1.4 ePWM Digital Compare
- 26.16.1.5 ePWM Digital Compare Event Filter Blanking Window
- 26.16.1.6 ePWM Valley Switching
- 26.16.1.7 ePWM Digital Compare Edge Filter
- 26.16.1.8 ePWM Deadband
- 26.16.1.9 ePWM DMA
- 26.16.1.10 ePWM Chopper
- 26.16.1.11 EPWM Configure Signal
- 26.16.1.12 Realization of Monoshot mode
- 26.16.1.13 EPWM Action Qualifier (epwm_up_aq)
- 26.16.2 HRPWM Examples
- 26.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 26.17 ePWM Registers
-
27Enhanced Quadrature
Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 27.1 Introduction
- 27.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 27.3 Description
- 27.4 Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 27.5 Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 27.6 eQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 27.7 eQEP Watchdog
- 27.8 eQEP Unit Timer Base
- 27.9 QMA Module
- 27.10 eQEP Interrupt Structure
- 27.11
Software
- 27.11.1
EQEP Examples
- 27.11.1.1 Frequency Measurement Using eQEP
- 27.11.1.2 Position and Speed Measurement Using eQEP
- 27.11.1.3 ePWM frequency Measurement Using eQEP via xbar connection
- 27.11.1.4 Frequency Measurement Using eQEP via unit timeout interrupt
- 27.11.1.5 Motor speed and direction measurement using eQEP via unit timeout interrupt
- 27.11.1
EQEP Examples
- 27.12 eQEP Registers
-
28Sigma Delta Filter Module
(SDFM)
- 28.1 Introduction
- 28.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 28.3 Input Qualification
- 28.4 Input Control Unit
- 28.5 SDFM Clock Control
- 28.6 Sinc Filter
- 28.7 Data (Primary) Filter Unit
- 28.8 Comparator (Secondary) Filter Unit
- 28.9 Theoretical SDFM Filter Output
- 28.10 Interrupt Unit
- 28.11 Software
- 28.12 SDFM Registers
- 29► COMMUNICATION PERIPHERALS
-
30Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 30.1 Introduction
- 30.2 Functional Description
- 30.3 Operating Modes
- 30.4 Multiple Clock Source
- 30.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 30.6 DMA Functionality
- 30.7 Parity Check Mechanism
- 30.8 Debug Mode
- 30.9 Module Initialization
- 30.10 Configuration of Message Objects
- 30.11
Message Handling
- 30.11.1 Message Handler Overview
- 30.11.2 Receive/Transmit Priority
- 30.11.3 Transmission of Messages in Event Driven CAN Communication
- 30.11.4 Updating a Transmit Object
- 30.11.5 Changing a Transmit Object
- 30.11.6 Acceptance Filtering of Received Messages
- 30.11.7 Reception of Data Frames
- 30.11.8 Reception of Remote Frames
- 30.11.9 Reading Received Messages
- 30.11.10 Requesting New Data for a Receive Object
- 30.11.11 Storing Received Messages in FIFO Buffers
- 30.11.12 Reading from a FIFO Buffer
- 30.12 CAN Bit Timing
- 30.13 Message Interface Register Sets
- 30.14 Message RAM
- 30.15
Software
- 30.15.1
CAN Examples
- 30.15.1.1 NMI handling - C28X_DUAL
- 30.15.1.2 CAN External Loopback
- 30.15.1.3 Watchdog Reset - C28X_DUAL
- 30.15.1.4 CAN Loopback - CM
- 30.15.1.5 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts
- 30.15.1.6 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts - C28X_DUAL
- 30.15.1.7 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts - CM
- 30.15.1.8 CAN-A to CAN-B External Transmit
- 30.15.1.9 CAN-A to CAN-B External Transmit - CM
- 30.15.1.10 CAN External Loopback with DMA
- 30.15.1.11 CAN Transmit and Receive Configurations - CM
- 30.15.1.12 CAN Transmit and Receive Configurations
- 30.15.1.13 CAN Error Generation Example
- 30.15.1.14 CAN Remote Request Loopback
- 30.15.1.15 CAN example that illustrates the usage of Mask registers
- 30.15.1
CAN Examples
- 30.16 CAN Registers
-
31EtherCAT®
Slave Controller
(ESC)
- 31.1
Introduction
- 31.1.1 ECAT Related Collateral
- 31.1.2 ESC Features
- 31.1.3 ESC Subsystem Integrated Features
- 31.1.4 F2838x ESC versus Beckhoff ET1100
- 31.1.5 EtherCAT IP Block Diagram
- 31.1.6
ESC Functional Blocks
- 31.1.6.1 Interface to EtherCAT Master
- 31.1.6.2 Process Data Interface
- 31.1.6.3 General-Purpose Inputs and Outputs
- 31.1.6.4 EtherCAT Processing Unit (EPU)
- 31.1.6.5 Fieldbus Memory Management Unit (FMMU)
- 31.1.6.6 Sync Manager
- 31.1.6.7 Monitoring
- 31.1.6.8 Reset Controller
- 31.1.6.9 PHY Management
- 31.1.6.10 Distributed Clock (DC)
- 31.1.6.11 EEPROM
- 31.1.6.12 Status / LEDs
- 31.1.7 EtherCAT Physical Layer
- 31.1.8 EtherCAT Protocol
- 31.1.9 EtherCAT State Machine (ESM)
- 31.1.10 More Information on EtherCAT
- 31.1.11 Beckhoff® Automation EtherCAT IP Errata
- 31.2
ESC and ESCSS Description
- 31.2.1 ESC RAM Parity and Memory Address Maps
- 31.2.2 Local Host Communication
- 31.2.3 Debug Emulation Mode Operation
- 31.2.4 ESC SubSystem
- 31.2.5 Interrupts and Interrupt Mapping
- 31.2.6 Power, Clocks, and Resets
- 31.2.7 LED Controls
- 31.2.8 Slave Node Configuration and EEPROM
- 31.2.9 General-Purpose Inputs and Outputs
- 31.2.10 Distributed Clocks – Sync and Latch
- 31.3 Software Initialization Sequence and Allocating Ownership
- 31.4 ESC Configuration Constants
- 31.5 EtherCAT IP Registers
- 31.1
Introduction
-
32Fast Serial Interface
(FSI)
- 32.1 Introduction
- 32.2 System-level Integration
- 32.3
FSI Functional Description
- 32.3.1 Introduction to Operation
- 32.3.2 FSI Transmitter Module
- 32.3.3
FSI Receiver Module
- 32.3.3.1 Initialization
- 32.3.3.2 FSI_RX Clocking
- 32.3.3.3 Receiving Frames
- 32.3.3.4 Ping Frame Watchdog
- 32.3.3.5 Frame Watchdog
- 32.3.3.6 Delay Line Control
- 32.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 32.3.3.8 CRC Submodule
- 32.3.3.9 Using the Zero Bits of the Receiver Tag Registers
- 32.3.3.10 Conditions in Which the Receiver Must Undergo a Soft Reset
- 32.3.3.11 FSI_RX Reset
- 32.3.4 Frame Format
- 32.3.5 Flush Sequence
- 32.3.6 Internal Loopback
- 32.3.7 CRC Generation
- 32.3.8 ECC Module
- 32.3.9 Tag Matching
- 32.3.10 TDM Configurations
- 32.3.11 FSI-SPI Compatibility Mode
- 32.4 FSI Programing Guide
- 32.5
Software
- 32.5.1
FSI Examples
- 32.5.1.1 FSI Multi-Rx Tag-Match - C28X_DUAL
- 32.5.1.2 FSI Loopback:CPU Control
- 32.5.1.3 FSI Multi-Rx Tag-Match - C28X_DUAL
- 32.5.1.4 FSI Loopback CLA control
- 32.5.1.5 FSI DMA frame transfers:DMA Control
- 32.5.1.6 FSI data transfer by external trigger
- 32.5.1.7 FSI data transfers upon CPU Timer event
- 32.5.1.8 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex6_spi_main_tx)
- 32.5.1.9 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex7_spi_remote_rx)
- 32.5.1.10 FSI P2Point Connection:Rx Side
- 32.5.1.11 FSI P2Point Connection:Tx Side
- 32.5.1.12 FSI star connection topology example. FSI communication using CPU control
- 32.5.1.13 FSI daisy chain topology, lead device example
- 32.5.1.14 FSI daisy chain topology, node device example
- 32.5.1
FSI Examples
- 32.6 FSI Registers
-
33Inter-Integrated Circuit Module (I2C)
- 33.1 Introduction
- 33.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 33.3
I2C Module Operational Details
- 33.3.1 Input and Output Voltage Levels
- 33.3.2 Selecting Pullup Resistors
- 33.3.3 Data Validity
- 33.3.4 Operating Modes
- 33.3.5 I2C Module START and STOP Conditions
- 33.3.6 Non-repeat Mode versus Repeat Mode
- 33.3.7 Serial Data Formats
- 33.3.8 Clock Synchronization
- 33.3.9 Arbitration
- 33.3.10 Digital Loopback Mode
- 33.3.11 NACK Bit Generation
- 33.4 Interrupt Requests Generated by the I2C Module
- 33.5 Resetting or Disabling the I2C Module
- 33.6
Software
- 33.6.1
I2C Examples
- 33.6.1.1 C28x-I2C Library source file for FIFO interrupts
- 33.6.1.2 C28x-I2C Library source file for FIFO using polling
- 33.6.1.3 C28x-I2C Library source file for FIFO interrupts
- 33.6.1.4 I2C Loopback with Slave Receive Interrupt - CM
- 33.6.1.5 I2C Digital Loopback with FIFO Interrupts
- 33.6.1.6 I2C EEPROM
- 33.6.1.7 I2C Digital External Loopback with FIFO Interrupts
- 33.6.1.8 I2C EEPROM
- 33.6.1.9 I2C controller target communication using FIFO interrupts
- 33.6.1.10 I2C EEPROM
- 33.6.1
I2C Examples
- 33.7 I2C Registers
-
34Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 34.1 Introduction
- 34.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 34.3
McBSP Operation
- 34.3.1 Data Transfer Process of McBSPs
- 34.3.2 Companding (Compressing and Expanding) Data
- 34.3.3 Clocking and Framing Data
- 34.3.4 Frame Phases
- 34.3.5 McBSP Reception
- 34.3.6 McBSP Transmission
- 34.3.7 Interrupts and DMA Events Generated by a McBSP
- 34.4 McBSP Sample Rate Generator
- 34.5 McBSP Exception/Error Conditions
- 34.6
Multichannel Selection Modes
- 34.6.1 Channels, Blocks, and Partitions
- 34.6.2 Multichannel Selection
- 34.6.3 Configuring a Frame for Multichannel Selection
- 34.6.4 Using Two Partitions
- 34.6.5 Using Eight Partitions
- 34.6.6 Receive Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.6.7 Transmit Multichannel Selection Modes
- 34.6.8 Using Interrupts Between Block Transfers
- 34.7 SPI Operation Using the Clock Stop Mode
- 34.8
Receiver Configuration
- 34.8.1 Programming the McBSP Registers for the Desired Receiver Operation
- 34.8.2 Resetting and Enabling the Receiver
- 34.8.3 Set the Receiver Pins to Operate as McBSP Pins
- 34.8.4 Digital Loopback Mode
- 34.8.5 Clock Stop Mode
- 34.8.6 Receive Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.8.7 Receive Frame Phases
- 34.8.8 Receive Word Lengths
- 34.8.9 Receive Frame Length
- 34.8.10 Receive Frame-Synchronization Ignore Function
- 34.8.11 Receive Companding Mode
- 34.8.12 Receive Data Delay
- 34.8.13 Receive Sign-Extension and Justification Mode
- 34.8.14 Receive Interrupt Mode
- 34.8.15 Receive Frame-Synchronization Mode
- 34.8.16 Receive Frame-Synchronization Polarity
- 34.8.17 Receive Clock Mode
- 34.8.18 Receive Clock Polarity
- 34.8.19 SRG Clock Divide-Down Value
- 34.8.20 SRG Clock Synchronization Mode
- 34.8.21 SRG Clock Mode (Choose an Input Clock)
- 34.8.22 SRG Input Clock Polarity
- 34.9
Transmitter Configuration
- 34.9.1 Programming the McBSP Registers for the Desired Transmitter Operation
- 34.9.2 Resetting and Enabling the Transmitter
- 34.9.3 Set the Transmitter Pins to Operate as McBSP Pins
- 34.9.4 Digital Loopback Mode
- 34.9.5 Clock Stop Mode
- 34.9.6 Transmit Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.9.7 XCERs Used in the Transmit Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.9.8 Transmit Frame Phases
- 34.9.9 Transmit Word Lengths
- 34.9.10 Transmit Frame Length
- 34.9.11 Enable/Disable the Transmit Frame-Synchronization Ignore Function
- 34.9.12 Transmit Companding Mode
- 34.9.13 Transmit Data Delay
- 34.9.14 Transmit DXENA Mode
- 34.9.15 Transmit Interrupt Mode
- 34.9.16 Transmit Frame-Synchronization Mode
- 34.9.17 Transmit Frame-Synchronization Polarity
- 34.9.18 SRG Frame-Synchronization Period and Pulse Width
- 34.9.19 Transmit Clock Mode
- 34.9.20 Transmit Clock Polarity
- 34.10
Emulation and Reset Considerations
- 34.10.1 McBSP Emulation Mode
- 34.10.2 Resetting and Initializing McBSPs
- 34.11 Data Packing Examples
- 34.12 Interrupt Generation
- 34.13 McBSP Modes
- 34.14 Special Case: External Device is the Transmit Frame Master
- 34.15
Software
- 34.15.1
MCBSP Examples
- 34.15.1.1 Pin Setup for McBSP module
- 34.15.1.2 McBSP loopback example
- 34.15.1.3 McBSP loopback with DMA example.
- 34.15.1.4 McBSP loopback with interrupts example
- 34.15.1.5 McBSP loopback with interrupts example
- 34.15.1.6 McBSP loopback example using SPI mode
- 34.15.1.7 McBSP external loopback example
- 34.15.1.8 McBSP external loopback example using SPI mode
- 34.15.1.9 McBSP TDM-8 Test
- 34.15.1
MCBSP Examples
- 34.16 McBSP Registers
-
35Power Management Bus Module (PMBus)
- 35.1 Introduction
- 35.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 35.3
Slave Mode
Operation
- 35.3.1 Configuration
- 35.3.2
Message Handling
- 35.3.2.1 Quick Command
- 35.3.2.2 Send Byte
- 35.3.2.3 Receive Byte
- 35.3.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 35.3.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 35.3.2.6 Process Call
- 35.3.2.7 Block Write
- 35.3.2.8 Block Read
- 35.3.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 35.3.2.10 Alert Response
- 35.3.2.11 Extended Command
- 35.3.2.12 Group Command
- 35.4
Master Mode
Operation
- 35.4.1 Configuration
- 35.4.2
Message Handling
- 35.4.2.1 Quick Command
- 35.4.2.2 Send Byte
- 35.4.2.3 Receive Byte
- 35.4.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 35.4.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 35.4.2.6 Process Call
- 35.4.2.7 Block Write
- 35.4.2.8 Block Read
- 35.4.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 35.4.2.10 Alert Response
- 35.4.2.11 Extended Command
- 35.4.2.12 Group Command
- 35.5 PMBus Registers
-
36Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 36.1 Introduction
- 36.2 Architecture
- 36.3 SCI Module Signal Summary
- 36.4 Configuring Device Pins
- 36.5 Multiprocessor and Asynchronous Communication Modes
- 36.6 SCI Programmable Data Format
- 36.7 SCI Multiprocessor Communication
- 36.8 Idle-Line Multiprocessor Mode
- 36.9 Address-Bit Multiprocessor Mode
- 36.10 SCI Communication Format
- 36.11 SCI Port Interrupts
- 36.12 SCI Baud Rate Calculations
- 36.13 SCI Enhanced Features
- 36.14 Software
- 36.15 SCI Registers
-
37Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 37.1 Introduction
- 37.2 System-Level Integration
- 37.3 SPI Operation
- 37.4 Programming Procedure
- 37.5 Software
- 37.6 SPI Registers
-
38Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller
- 38.1 Introduction
- 38.2 Functional Description
- 38.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 38.4 USB Global Interrupts
- 38.5
Software
- 38.5.1
USB Examples
- 38.5.1.1 Wrapper for interrupt functions and USB support pins. - CM
- 38.5.1.2 USB CDC serial example
- 38.5.1.3 USB Composite Serial Device (usb_dev_cserial) - CM
- 38.5.1.4 USB HID Mouse Device
- 38.5.1.5 USB HID Mouse Device - CM
- 38.5.1.6 Data structures defining the USB mouse device. - CM
- 38.5.1.7 USB Device Keyboard
- 38.5.1.8 USB HID Keyboard Device (usb_dev_keyboard) - CM
- 38.5.1.9 Data structures defining the USB keyboard device. - CM
- 38.5.1.10 Data structures defining this bulk USB device. - CM
- 38.5.1.11 USB Generic Bulk Device (usb_dev_bulk) - CM
- 38.5.1.12 USB Generic Bulk Device
- 38.5.1.13 USB HID Mouse Host
- 38.5.1.14 USB HID Mouse Host (usb_host_mouse) - CM
- 38.5.1.15 USB HID Keyboard Host (usb_host_keyboard) - CM
- 38.5.1.16 USB HID Keyboard Host
- 38.5.1.17 USB Mass Storage Class Host
- 38.5.1.18 USB Mass Storage Class Host (usb_host_msc) - CM
- 38.5.1.19 USB Dual Detect
- 38.5.1.20 Data structures defining this bulk USB device. - CM
- 38.5.1.21 USB Throughput Bulk Device Example (usb_ex9_throughput_dev_bulk) - CM
- 38.5.1.22 USB HUB Host example - CM
- 38.5.1.23 USB Throughput Bulk Device Example (usb_ex9_throughput_dev_bulk)
- 38.5.1.24 USB HUB Host example
- 38.5.1
USB Examples
- 38.6 USB Registers
- 39► CONNECTIVITY MANAGER (CM)
- 40Connectivity Manager Subsystem
-
41Connectivity
Manager System Control and Interrupts
- 41.1 Introduction
- 41.2 Reset
- 41.3 CM Clocking
- 41.4 SysTick
- 41.5 Watchdog Timer
- 41.6 Exceptions and NMI
- 41.7 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC)
- 41.8 32-Bit CM CPU Timers 0/1/2
- 41.9 Memory Controller Module
- 41.10 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- 41.11 Debug and Trace
- 41.12
CM-SysCtrl Registers
- 41.12.1 CM System Control Base Addresses
- 41.12.2 CM_MEMCFG_REGS Registers
- 41.12.3 CM_MEMORYDIAGERROR_REGS Registers
- 41.12.4 CM_MEMORYERROR_REGS Registers
- 41.12.5 CMSYSCTL_REGS Registers
- 41.12.6 CM_CPUTIMER_REGS Registers
- 41.12.7 MPU_REGS Registers
- 41.12.8 CM_NMI_INTRUPT_REGS Registers
- 41.12.9 NVIC Registers
- 41.12.10 SCB Registers
- 41.12.11 CSFR Registers
- 41.12.12 SYSTICK Registers
- 41.12.13 MPU Registers
- 41.12.14 CM_WD_REGS Registers
- 42Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Accelerator
-
43Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 43.1 Introduction
- 43.2 System Level Integration
- 43.3
Features
- 43.3.1 Multiple Channels and Queues Support
- 43.3.2
IEEE 1588 Timestamp Support
- 43.3.2.1
Feature Description
- 43.3.2.1.1 Clock Types
- 43.3.2.1.2 Maximum PTP Clock Frequency
- 43.3.2.1.3 Minimum PTP Clock Frequency
- 43.3.2.1.4 PTP Processing and Control
- 43.3.2.1.5 PTP Packets Over IPv4
- 43.3.2.1.6 PTP Frames Over IPv6
- 43.3.2.1.7 PTP Packets Over Ethernet
- 43.3.2.1.8 Transmit Path Functions
- 43.3.2.1.9 Receive Path Functions
- 43.3.2.2 IEEE 1588 System Time Source
- 43.3.2.3 IEEE 1588 Higher Word Register
- 43.3.2.4 IEEE 1588 Auxillary Snapshot
- 43.3.2.5 Flexible Pulse-Per-Second Output
- 43.3.2.1
Feature Description
- 43.3.3 Packet Filtering
- 43.3.4 VLAN Support
- 43.3.5
TCP/IP Offloading Features
- 43.3.5.1 Transmit Checksum Offload Engine
- 43.3.5.2 Receive Checksum Offload Engine
- 43.3.5.3 TCP/IP Segmentation Offload (TSO) Engine
- 43.3.5.4 Segmentation Versus Fragmentation
- 43.3.5.5 Using the IPv4 ARP Offload Engine
- 43.3.5.6 Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) Support
- 43.3.5.7 Automated Entry/Exit of LPI Mode in Transmit Path
- 43.3.5.8 Receive Path Functions
- 43.3.6 Loopback Mode
- 43.3.7 Reverse Media Independent Interface (RevMII)
- 43.4
Descriptors
- 43.4.1 Descriptor Structure
- 43.4.2 Transmit Descriptor
- 43.4.3 Receive Descriptor
- 43.5
Programming
- 43.5.1 Initializing DMA
- 43.5.2 Initializing MTL Registers
- 43.5.3 Initializing MAC
- 43.5.4 Performing Normal Receive and Transmit Operation
- 43.5.5 Stopping and Starting Transmission
- 43.5.6
Programming Guidelines for Multi-Channel Multi-Queuing
- 43.5.6.1 Transmit
- 43.5.6.2 Receive
- 43.5.6.3 Programming Guidelines for Recovering from DMA Channel Failure
- 43.5.6.4 Programming Guidelines for IEEE 1588 Timestamping
- 43.5.6.5 Programming Guidelines for Energy Efficient Ethernet
- 43.5.6.6 Programming Guidelines for Flexible Pulse-Per-Second Output
- 43.5.6.7 Programming Guidelines for TSO
- 43.6
Software
- 43.6.1
ETHERNET Examples
- 43.6.1.1 Ethernet + IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 43.6.1.2 Ethernet + IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 43.6.1.3 Ethernet MAC Internal Loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.4 Ethernet Basic Transmit and Receive PHY Loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.5 Ethernet Threshold mode with level PHY loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.6 Ethernet PTP Basic Master - CM
- 43.6.1.7 Ethernet PTP Basic Slave - CM
- 43.6.1.8 Ethernet PTP Offload Master - CM
- 43.6.1.9 Ethernet PTP Offload Slave - CM
- 43.6.1.10 Ethernet MAC CRC and Checksum Offload - CM
- 43.6.1.11 Ethernet Transmit Segmentation Offload - CM
- 43.6.1.12 Ethernet MAC Internal Loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.13 Ethernet RevMII Example MII side - CM
- 43.6.1.14 Ethernet RevMII Example RevMII side - CM
- 43.6.1.15 Ethernet Low Latency Interrupt - CM
- 43.6.1
ETHERNET Examples
- 43.7 Ethernet Registers
- 44Generic Cyclic Redundancy Check (GCRC)
-
45Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 45.1 MCAN Introduction
- 45.2 MCAN Environment
- 45.3 CAN Network Basics
- 45.4 MCAN Integration
- 45.5
MCAN Functional Description
- 45.5.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 45.5.2 Interrupt Requests
- 45.5.3 Operating Modes
- 45.5.4 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 45.5.5 Restricted Operation Mode
- 45.5.6 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 45.5.7 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 45.5.8 Clock Stop Mode
- 45.5.9 Test Modes
- 45.5.10 Timestamp Generation
- 45.5.11 Timeout Counter
- 45.5.12 Safety
- 45.5.13 Rx Handling
- 45.5.14 Tx Handling
- 45.5.15 FIFO Acknowledge Handling
- 45.5.16 Message RAM
- 45.6
Software
- 45.6.1
MCAN Examples
- 45.6.1.1 MCAN Internal Loopback with Interrupt - CM
- 45.6.1.2 MCAN Internal Loopback with Interrupt
- 45.6.1.3 MCAN External Loopback with Interrupt - CM
- 45.6.1.4 MCAN Loopback with Interrupts Example Using SYSCONFIG Tool
- 45.6.1.5 MCAN receive using Rx Buffer
- 45.6.1.6 MCAN External Reception (with mask filter) into RX-FIFO1
- 45.6.1.7 MCAN Classic frames transmission using Tx Buffer
- 45.6.1.8 MCAN External Reception (with RANGE filter) into RX-FIFO1
- 45.6.1.9 MCAN External Transmit using Tx Buffer
- 45.6.1.10 MCAN receive using Rx Buffer
- 45.6.1.11 MCAN Internal Loopback with Interrupt
- 45.6.1.12 MCAN External Transmit using Tx Buffer
- 45.6.1
MCAN Examples
- 45.7 MCAN Registers
-
46Connectivity Manager
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Module
- 46.1 Introduction
- 46.2
Functional Description
- 46.2.1
I2C Bus Functional Overview
- 46.2.1.1 START and STOP Conditions
- 46.2.1.2 Data Format With 7-Bit Address
- 46.2.1.3 Data Validity
- 46.2.1.4 Acknowledge
- 46.2.1.5 Repeated START
- 46.2.1.6 Clock Low Time-out (CLTO)
- 46.2.1.7 Dual Address
- 46.2.1.8 Arbitration
- 46.2.1.9 Glitch Suppression in Multi-Master Configuration
- 46.2.1.10 SMBus Operation
- 46.2.2 Available Speed Modes
- 46.2.3 Interrupts
- 46.2.4 Loopback Operation
- 46.2.5 FIFO and µDMA Operation
- 46.2.6 Command Sequence Flow Charts
- 46.2.1
I2C Bus Functional Overview
- 46.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 46.4 CM I2C Registers
-
47Synchronous Serial Interface
(SSI)
- 47.1 Introduction
- 47.2
Functional Description
- 47.2.1 Bit Rate Generation
- 47.2.2 FIFO Operation
- 47.2.3 SSInFSS Function
- 47.2.4 Interrupts
- 47.2.5 Frame Formats
- 47.2.6 DMA Operation
- 47.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 47.4 Software
- 47.5 SSI Registers
- 48Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
-
49Micro Direct Memory Access (µDMA)
- 49.1 Introduction
- 49.2 Functional Description
- 49.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 49.4 Software
- 49.5 µDMA Registers
- 50Revision History
32.3.10 TDM Configurations
The FSI module in this device supports multi-slave TDM configurations, whereas a single master device can control multiple slave devices. To use the FSI module in the multi-slave TDM configuration described, the slave device must utilize tag matching and the CLB module.
This multi-slave TDM configuration is supported in the FSI module through time-division multiplexing. When TDM is enabled, each slave device must also have tag matching enabled. Figure 32-10 shows a scheme where a single master device is communicating with multiple slave devices. All FSI receive modules in the slave devices are directly connected to the master device transmit module. The transmit modules of the slave devices are chained serially such that each transmit module is connected to the next slave device and the last slave device output connects to the master device receive module. Each slave device decides, based on the received frame's tag, whether to transmit the data or to enter bypass mode where the previous slave device transmit module directly connects to the next slave device. This is done by using the FSI transmit module TDM_IN.
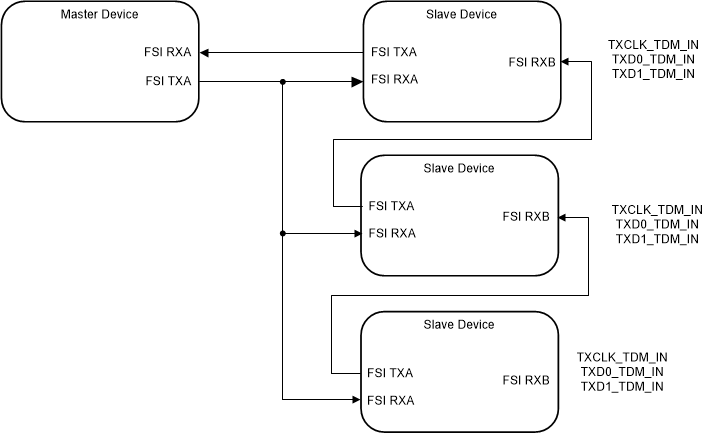 Figure 32-10 FSI Multi-Slave TDM
Configuration
Figure 32-10 FSI Multi-Slave TDM
ConfigurationWhen an FSI transmitter module is used in TDM mode, TXCLK_TDM_IN, TXD0_TDM_IN and TXD1_TDM_IN pins are used if the transmitter is required to enter bypass mode. Figure 32-11 shows how the FSI module operates when in multi-slave TDM mode.
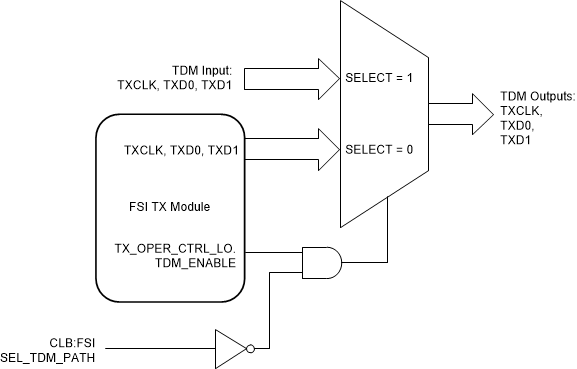 Figure 32-11 FSI Transmitter Multi-Slave TDM
Multiplexing
Figure 32-11 FSI Transmitter Multi-Slave TDM
MultiplexingThe SEL_TDM_PATH signal is sourced from the CLB module. The CLB module also generates the transmit trigger for the FSI transmitter. The CLB module must be configured to decide when to generate the FSI transmit trigger based on the status of the data, ping, and frame tag match generated by the FSI receiver module. The FSITX module must be configured to transmit on an external trigger and the corresponding CLB trigger input must be selected. In a broadcast scenario (FSI tag match notifies all slave devices that a match has occurred), the CLB module inside each slave device generates a trigger and SEL_TDM_PATH signal. The main key here is that the trigger and the SEL_TDM_PATH signal must be generated at a different time interval in a non-overlapping manner. Figure 32-12 shows an example of FSI transmit triggers and the multi-slave TDM SEL_TDM_PATH signals generated by the RX_TRIGx signal or the CLB module of the slave devices in a broadcast scenario.
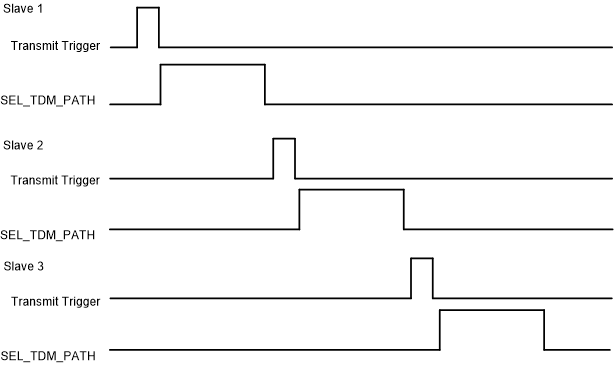 Figure 32-12 Generated Signals for FSI Multi-Slave TDM
Configuration
Figure 32-12 Generated Signals for FSI Multi-Slave TDM
Configuration
The TXCLK_TDM_IN, TXD0_TDM_IN, and TXD1_TDM_IN for the FSI transmit modules available in this device are shown in Table 32-10.
| FSI Transmit Module | TXCLK_TDM_IN | TXD0_TDM_IN | TXD1_TDM_IN |
|---|---|---|---|
| FSITXA | FSIRXB RXCLK | FSIRXB RXD0 | FSIRXB RXD1 |
| FSITXB | FSIRXA RXCLK | FSIRXA RXD0 | FSIRXA RXD1 |
The FSI transmit modules are configured to use the external triggers generated by the CLB to initiate the transmission. Through appropriate configurations, the logic is designed to work assuming that only one TDM trigger is generated until the transmission is completed. In the case where there is another trigger before the current transmission is competed, an error is flagged in the TX_EVT_ERR_STATUS register. Figure 32-13 shows the connections between CLB, FSITX, and FSIRX modules.
 Figure 32-13 FSI and CLB Multi-Slave TDM
Connections
Figure 32-13 FSI and CLB Multi-Slave TDM
Connections
In Figure 32-10, the master device is connected to three slave devices. The master device uses FSITXA to transmit frames to the three slave devices. Each slave device receives every frame, using the FSIRXA. The slave devices are chained together using the FSITXA output and FSIRXB inputs (configured as FSITXA TDM input). When a slave device receives a frame using the FSIRXA, the device checks the tag of the frame to see if the tag matches the specified reference value in the tag compare register. When a match does occur, the CLB module configures the FSITXA of the slave device to select the local FSITXA outputs as the source for the output pins. However, if a match does not occur, the FSITXA of the slave device is configured to enter bypass mode. There, the device selects the FSITXA TDM inputs (which is FSIRXB) to be passed on to the output pins.
In this case, when a frame is transmitted by the master device and the frame tag is matched only in one of the slave devices, all other devices with non-matching tags enter the bypass mode to allow the master device to receive frames from the chosen slave device.