-
Decrease Power Consumption with an LDO
Decrease Power Consumption with an LDO
Chonghyuk Kwon
A low-dropout regulator (LDO) can function as a DC linear voltage regulator at an output voltage very close to the supply voltage, which is an important factor in decreasing power dissipation across the LDO. This capability is the primary difference between a linear voltage regulator and a LDO. “Low-dropout” is self-explanatory; however, there are other characteristics where implementing LDOs can benefit design size and performance.
A significant advantage that a LDO has over a DC/DC regulator is the nonexistence of switching noise. This benefit proves critical for applications involving ripples in the output voltage that may affect the accuracy of devices such as sensors, timers, and controllers. Another key feature of a LDO is the quiescent current, IQ. Applications that do not require constant operation should have low IQ to minimize power dissipation during idle periods. Figure 1 is a block diagram of a related TI Designs reference design, LDO Regulator Post AC/DC Rectifier Ripple Cleaner Reference Design for Industrial Applications (TID-00896).
Many industrial applications require the microcontroller unit (MCU) be in sleep mode when the operation is not running to reduce battery consumption. Figure 1 is a conceptual block diagram of an isolated AC to DC rectification signal being filtered by an LDO. The blue blocks indicate the variability of applications that require this low IQ power management design in order to reduce power dissipation when the MCU is in sleep mode.
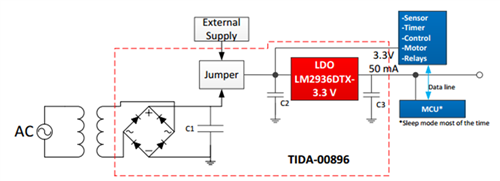 Figure 1 TIDA-00896 High-level Block
Diagram
Figure 1 TIDA-00896 High-level Block
DiagramFigure 2 shows the TI LM2936 with a 15-µA ultra-low IQ at a 100-µA load. Notice the linearity of the low IQ supported by the LM2936 as the input voltage rises. This feature distinguishes the LM2936 to be an optimal choice in battery operated systems due to the consistency of low IQ in the standby mode.
 Figure 2 IQ For
LM2936
Figure 2 IQ For
LM2936Another significant characteristic for LDOs in industrial applications is the wide input-voltage (VIN) range. The LM2936 has a wide-VIN range and 40-V maximum operating voltage limit that make it crucial for applications with acute transients at the input.
The power-supply rejection ratio (PSRR) blocks unwanted noise generated by the power supply. Figure 3 illustrates that the PSRR for the LM2936 is at a steady 60-dB from low frequencies all the way up to 10-kHz. This feature is important for noise-sensitive applications such as motion detectors, smart meters, and smoke detectors.
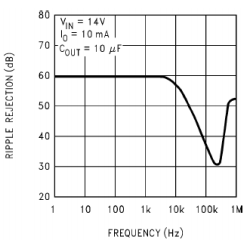 Figure 3 PSRR for LM2936
Figure 3 PSRR for LM2936Noise can be a defining factor for selecting an LDO over other devices used in applications such as medical and test and measurement devices. The two key components that drive noise-sensitive end equipment are PSRR and output-voltage noise; the LP38798 offers high PSRR and ultra-low output-voltage noise. Table 1 highlights the PSRR and output-voltage noise values for the LP38798.

|
There are many applications, especially industrial, that require standby time to minimize power consumption, using less power during times that aren’t necessary for the entire system to be in the on-state. Often, these applications can be battery powered, thus, conserving power will increase efficiency and ultimately save battery life. Therefore, when designing a system that requires optimal performance at a low power rating, implementing an LDO to power the devices that require frequent standby times can preserve power usage. For more information on this topic, read the blog post, “How LDOs contribute to power efficiency.”
Check out TI’s complete LDO portfolio.
Additional Resources:
- Download the TI Designs:
- LDO Regulator Post AC/DC Rectifier Ripple Cleaner Reference Design for Industrial Applications (TIDA-00896).
- Rail Cleaner with Adjustable Output Voltage Drop and Soft-start Capabilities Reference Design (TIDA-00533).
IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS” AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims, damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2023, Texas Instruments Incorporated